0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views2 pagesAct 1 M6
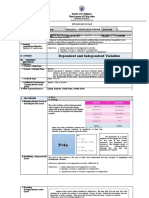
The document explains the difference between univariate and bivariate data, providing examples of bivariate data such as hours of study and exam scores. It identifies independent and dependent variables in various scenarios, including the effects of water on plant height and stress management training on sick days. Additionally, it presents a sampling distribution of sample means from monthly incomes of workers, calculating the mean and standard error of the sample means.
Uploaded by
54k2k4qx6pCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views2 pagesAct 1 M6
The document explains the difference between univariate and bivariate data, providing examples of bivariate data such as hours of study and exam scores. It identifies independent and dependent variables in various scenarios, including the effects of water on plant height and stress management training on sick days. Additionally, it presents a sampling distribution of sample means from monthly incomes of workers, calculating the mean and standard error of the sample means.
Uploaded by
54k2k4qx6pCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd