0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views1 pageNursing Guidance on Common Medications
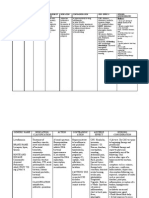
The document provides nursing guidance on managing side effects of medications such as ibuprofen and lorazepam, emphasizing the importance of taking ibuprofen with food to alleviate gastrointestinal distress. It also discusses the implications of nefazodone hydrochloride use in clients with a history of depression and highlights the critical signs of hypertensive crisis associated with phenelzine sulfate. The document underscores the nurse's role in patient education and monitoring for adverse effects without altering prescribed dosages.
Uploaded by
GeorgeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views1 pageNursing Guidance on Common Medications
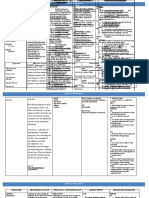
The document provides nursing guidance on managing side effects of medications such as ibuprofen and lorazepam, emphasizing the importance of taking ibuprofen with food to alleviate gastrointestinal distress. It also discusses the implications of nefazodone hydrochloride use in clients with a history of depression and highlights the critical signs of hypertensive crisis associated with phenelzine sulfate. The document underscores the nurse's role in patient education and monitoring for adverse effects without altering prescribed dosages.
Uploaded by
GeorgeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd