Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syllabus
Uploaded by
Anudeep ChimakurthiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Syllabus
Uploaded by
Anudeep ChimakurthiCopyright:
Available Formats
EE 8001 Engineering Economics & Accountancy IV Year B.Tech. (EEE) Semester II Lectures + Tutorial Marks (Int. + Ext.
) : : 4+0 Periods/week 30 + 70 Credits : 3 External Exam : 3 hrs
ENGINEERING ECONOMICS: Unit -I Introduction to engineering economics- Fundamental concepts- Time value of money Cash Flow and Time Diagrams Choosing between alternative investment proposals Methods of Economic analysis (pay back, ARR, NPV, IRR and B/C ratio). The effect of borrowing on investment Equity Vs Debt Financing concept of Leverage Income tax leverage. UnitII Depreciation and methods of calculating depreciation (straight line, sum of the years digit method, Declining balance method ,Annuity method, Sinking fund method) National income accounting Methods of estimation Various concepts of national income-Significance of national income Estimation and its limitations. Unit-III Inflation-Definition Process and Theories of inflation and Measure of control. New economic policy 1991(Industrial policy, Fiscal policy), impact on industry. ACCOUNTANCY Unit-IV Accounting Principles, procedure Double entry system Journal, Ledger, Trial Balance Cashbook preparation of Trading and Profit Loss account Balance sheet. Cost Accounting-Introduction Classification of costs- Methods of costing- Techniques of costing cost sheet and preparation of cost sheet Breakeven Analysis Meaning and its application, Limitation. BOOKS RECOMMENDED: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Henry Malcom steinar Engineering Economics Principles, Mc Graw Hill Publishers Dewett K.K Modern Economic Theory, Sultan Chand and Company A.N.Agarwal Indian Economy Willy Eastern Limited, New Delhi Jain and Narang Accounting Part -I, Kalyani Publishers Arrora, M.N. Cost Accounting, Vikas Publication.
EE 8002
POWER SYSTEM OPERATION & CONTROL IV Year B.Tech. (EEE) Semester II
Lectures + Tutorial Marks (Int. + Ext.)
: :
4+1 Periods/week 30 + 70
Credits : 4 External Exam : 3 hrs
UnitI Economic operation of power systems: Economic dispatch in thermal power station: Heat rate curves, cost curves, incremental fuel and production costs, economic distribution of load between units without consideration to line losses; transmission line losses as a function of plant generation, calculation of loss coefficients, optimum generation allocation between thermal plants; capability diagram of a synchronous generator. UnitII Quality of power: Importance of keeping voltage and frequency constant in a power system The two main control loops- (P- ) and (Q V ) loops: Load frequency control (LFC) single area case, the P- loop: Schematic of load frequency and AVR of a synchronous generator, mathematical modelling of generator, loads, prime mover and speed governor for LFC & corresponding block diagram representation, LFC block diagram of an isolated power system , steady state analysis, dynamic response. The automatic generation control (AGC) scheme AGC in a single area system, block diagram representation of AGC for an isolated power system UnitIII Reactive power and voltage control: Reactive power control in synchronous generators:The role of excitation systemexciter, generator and sensor models , simplified AVR block diagram, steady state response for a step change in terminal voltage. Reactive power compensation of loads : Shunt compensating devices Transmission line compensation : Series compensation, shunt compensation, static VAR compensators thyristor controlled reactors (TCR) , thyristor switched capacitors (TSC) , combined TCR and TSC , schematic of all three types ; STATCOM and FACTS devices Voltage control of distribution systems: Tap changing, booster transformers, synchronous phase modifiers, induction regulators and static capacitors. UnitIV Power System Control centers : Aim of control centres, Funtions of Control centres Planning, Monitoring & Data acquisition and System control. Setup, locations, central & civil facilities. Facilities in control room. Communication-PLCC. Emergency control Distribution Automation: Flow diagram for man machine power system interface. Schematic diagram of Remote Terminal Unit. Block diagram of smart and intelligent transmitter, SCADA system Text Books: 1) Power system analysis by H.Saadat , McGraw Hill 2) Modern power system analysis by D.P.Kothari & I.J.Nagrath McGraw Hill 3) Power System Analysis operation and control by Abhijit Chakrabarti & Sunita Halder, PHI Reference Books: 1) Economic operation of interconnected systems by L.K.Kirchmeyer 2) Power System Analysis by T.K.Nagsarkar M.S.Sukhija, OXFORD university press, 2007 3) Generation Distribution and utilization of Electrical Energy by CL Wadhwa, New Age Int. Pub , Revised 2/E 4) Electrical Energy Systems by John Weedy, Willey Eastern
EE 8003 Elective Course-III IV Year B.Tech. (EEE) Semester II Lectures + Tutorial Marks (Int. + Ext.) : : 4+1 Periods/week 30 + 70 Credits : 4 External Exam : 3 hrs
EE 8003/1
COMPUTER AIDED POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS
UnitI Incidence & Network Matrices: Element-node incidence matrix, reduced incidence matrix or bus incidence matrix, basic loop incidence matrix, augmented loop incidence matrix, basic cut-set incidence matrix, augmented cut-set incidence matrix, branch path incidence matrix, concept of primitive network, primitive impedance and admittance matrices with and without mutual coupling, network performance equations, formation of network matrices using singular & nonsingular transformation UnitII Algorithm for formation of network matrices: Formation of bus admittance and bus impedance matrices and respective algorithms, modifications of bus impedance and admittance matrices for changes in the networks with and without mutual coupling, representation of three phase network elements for balanced and unbalanced systems, Short circuit studies: Short circuit calculations for symmetrical and unsymmetrical faults using bus impedance matrix. UnitIII Load Flow Studies: Introduction, non-linear equations, solution techniques using Gauss iterative, Gauss Seidal , Newton Raphson (rectangular and polar) methods, Fast decoupled Load flow using bus admittance matrix, acceleration of convergence, development of flow charts for load flow problems, comparison of different load flow methods. UnitIV Transient Stability Studies: Introduction - types of stability swing equation, representing synchronous machine by constant voltage behind transient reactance (d- axis) Representation of loads, and network by steady state equations; Solution techniques- Modified Eulers method, Runge-Kutta method alternating solution approach for transient stability solving algebraic equations and differential equations alternately; Flow chart for digital simulation of transient stability problem. Representation of Exciter and governor control systems Text Books: 1. Computer methods in Power System Analysis by Stagg, G.W. & El-Abiad 2. Computer Techniques in Power System Analysis by M.A. Pai , TMH Reference Books 1. Modern power system analysis by Nagrath & Kothari 2. Advanced Power System Analysis and Dynamics by L.P.Singh 3. Computer Techniques and Models in Power Systems by K.Uma Rao, I.K.Int. Pub.
eLECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS IV Year B.Tech. (EEE) Semester II Lectures + Tutorial Marks (Int. + Ext.) : : 4+0 Periods/week 30 + 70 Credits : 4 External Exam : 3 hrs
UnitI Distribution systems planning and automation: Planning and forecast techniques, Present and future role of computers in distribution system planning automation, Methods of improvement, Load characteristics, Definitions, load growth, tariffs, Diversified demand method UnitII Distribution transformers: Types, Regulation and Efficiency, Use of monograms for obtaining efficiency, distribution factors, KW-KVA-Method of determining regulation Deign of sub transmission lines and distribution substations: Introduction, sub-transmission systems, distribution substation, Sub-station bus schemes, description and comparison of switching schemes, sub-station location and rating, Application of network flow techniques in rural distribution networks to determine optimum location of sub-station UnitIII Design considerations on primary systems: Introduction, types of feeders, voltage levels, Radial type feeders, feeders with uniformly distributed load and non-uniformly distributed loads Design considerations of secondary systems: Introduction, secondary voltage levels, Secondary banking, existing systems improvement Distribution system Protection: Basic definitions, over current protection devices-fuses, automatic circuit reclosures, automatic line sectionalizers, objectives of distribution system protection, co-ordination of protective devices- Fuse to Fuse co-ordination, Fuse to circuit breaker co-ordination, Reclosure to circuit breaker co-ordination Unit-IV Voltage drop and power loss calculations: Three phase primary lines, non 3 phase primary lines, 4 wire multi grounded primary lines, copper loss, Distribution feeder costs, loss reduction and voltage improvement in rural distribution networks. Applications of Capacitors to distribution systems: Effect of series and shunt capacitors, Power factor correction, economic justification for capacitors, a computerized method to determine the economic power factor, Procedure to determine the best and optimum capacitor location Distribution System Voltage Regulation: Basic definitions, Quality of service, voltage control, line drop compensation Text Book: Electric Power Distribution system Engg. by Turan Gonen, MGH Reference Book: Electric Power Distribution by A.S.Pabla, TMH, 4th Ed., 1997
You might also like
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- CBGS 8 Sem050318033746 PDFDocument9 pagesCBGS 8 Sem050318033746 PDFshashank barsainyaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 5th SemDocument21 pagesSyllabus 5th SemAmit SahuNo ratings yet
- Jntuk Eee 4-2 Sem Syllabus Book (R10)Document23 pagesJntuk Eee 4-2 Sem Syllabus Book (R10)Venkat KickNo ratings yet
- M.tech 2ND Sem SyllabusDocument6 pagesM.tech 2ND Sem SyllabusraghuNo ratings yet
- Cmps QBFFDocument80 pagesCmps QBFFFeliscio Ascione FelicioNo ratings yet
- TE Part I Electrical Engg. 2014Document37 pagesTE Part I Electrical Engg. 2014sordfish143No ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Engg. B.Tech. Semester-Vii: Course Code Course Title L T P CreditsDocument26 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engg. B.Tech. Semester-Vii: Course Code Course Title L T P CreditsAbhishek Kumar ChambelNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of Jntu IV - I Psoc 08 Batch R 07Document2 pagesSyllabus of Jntu IV - I Psoc 08 Batch R 07Krishna Prasad100% (1)
- 8THDocument11 pages8THPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- EA6210 Protection and Switchgear Lab GuideDocument5 pagesEA6210 Protection and Switchgear Lab GuideAvi PokiNo ratings yet
- Curriculum For MTech in Power Systems ProgrammeDocument20 pagesCurriculum For MTech in Power Systems ProgrammeheerapotterNo ratings yet
- EEE 4-1 SyllubusDocument10 pagesEEE 4-1 SyllubusSai ChanduNo ratings yet
- Mtech 2sem SyllabusDocument8 pagesMtech 2sem Syllabusrajavgr243No ratings yet
- M.E. Power Systems Engineering Curriculum and SyllabusDocument38 pagesM.E. Power Systems Engineering Curriculum and SyllabusSundar Rajan ANo ratings yet
- Pre PHD ANU-SyllabusDocument8 pagesPre PHD ANU-SyllabuskishorebabNo ratings yet
- Syllabus VI-EEDocument6 pagesSyllabus VI-EERam DinNo ratings yet
- CBGS 7 Sem 20-21290521110137Document18 pagesCBGS 7 Sem 20-21290521110137kushagra vashishthaNo ratings yet
- Jntua B.tech 4-1 Eee r15 SyllabusDocument26 pagesJntua B.tech 4-1 Eee r15 Syllabusaravind0% (1)
- EE4051 Computer Modelling of Electrical Power SystemsDocument2 pagesEE4051 Computer Modelling of Electrical Power SystemsBharath PulavarthiNo ratings yet
- JNTUA College of Engineering Course on Economic Operation of Power SystemsDocument31 pagesJNTUA College of Engineering Course on Economic Operation of Power SystemsChakala BhargavNo ratings yet
- Power System 1: CO1 CO2 CO3 CO4 CO5 CO6Document2 pagesPower System 1: CO1 CO2 CO3 CO4 CO5 CO6Anonymous HyOfbJ6No ratings yet
- Mtech PS SyllabusDocument25 pagesMtech PS SyllabusJithendra NathNo ratings yet
- ImportantDocument6 pagesImportantKamalika DuttaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus B ElectricalDocument6 pagesSyllabus B ElectricalnetprosenjitNo ratings yet
- Amie Syllabus Sec B ElectricalDocument19 pagesAmie Syllabus Sec B ElectricalvenkatNo ratings yet
- Electri Sem 8Document4 pagesElectri Sem 8Ajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- B.Tech III Semester Syllabi for ECEN Numerics, Circuits and EconomicsDocument9 pagesB.Tech III Semester Syllabi for ECEN Numerics, Circuits and EconomicsYukti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ee2401 Power System Operation and ControlDocument2 pagesEe2401 Power System Operation and Controlsshivakumar98No ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Anantapur B. Tech III-II Sem. (EEE) 15A02603-Power System AnalysisDocument2 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University Anantapur B. Tech III-II Sem. (EEE) 15A02603-Power System AnalysisAmaranatha Reddy GNo ratings yet
- 4 Psoc As Aurora CollegeDocument56 pages4 Psoc As Aurora CollegeKvv BapirajuNo ratings yet
- EE May 04 2011Document40 pagesEE May 04 2011ChandanUpadhyayNo ratings yet
- EPSDocument28 pagesEPSChakala BhargavNo ratings yet
- BE VII Sem Electrical Engg JEC JabalpurDocument13 pagesBE VII Sem Electrical Engg JEC JabalpursvmgrgNo ratings yet
- EE2401 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL Syllabus Regulation 2008Document2 pagesEE2401 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL Syllabus Regulation 2008Muruga RajNo ratings yet
- EE1101Document2 pagesEE1101balajiNo ratings yet
- Cmps QB PDFDocument80 pagesCmps QB PDFDse YtNo ratings yet
- Eee-Vii-computer Techniques in Power System Analysis (10ee71) - Notes123098Document144 pagesEee-Vii-computer Techniques in Power System Analysis (10ee71) - Notes123098Angsuman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mtech Power Systems ControlDocument25 pagesMtech Power Systems ControlJosé SánchezNo ratings yet
- MTech EE Power Common Syllabus 10.04.14!2!2Document22 pagesMTech EE Power Common Syllabus 10.04.14!2!2alfred_googleNo ratings yet
- 6THDocument19 pages6THPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Vasa College Recruitment Guide for Electrical EngineeringDocument5 pagesVasa College Recruitment Guide for Electrical EngineeringjaberyemeniNo ratings yet
- PowSysEnggDocument38 pagesPowSysEnggvinodlifeNo ratings yet
- JNTUH M.TECH PEDS 2013 SyllabusDocument24 pagesJNTUH M.TECH PEDS 2013 SyllabusSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- Power ElectronicsDocument24 pagesPower ElectronicsSunilkumarNo ratings yet
- B.E. 301 - Engineering Mathematics Ii Unit I: EC-302 Computer System OrganizationDocument5 pagesB.E. 301 - Engineering Mathematics Ii Unit I: EC-302 Computer System OrganizationRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Modern Control Theory and Power ElectronicsDocument34 pagesModern Control Theory and Power ElectronicsHarshal VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Scheme: Paper-1 General Studies & Mental AbilityDocument2 pagesScheme: Paper-1 General Studies & Mental AbilityRajashekar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Sastra Universiy: B.Tech (Eee) ProgrammeDocument13 pagesSastra Universiy: B.Tech (Eee) ProgrammeSriram VenkatachariNo ratings yet
- B. Tech Electrical Engineering 5th Sem CurriculumDocument19 pagesB. Tech Electrical Engineering 5th Sem CurriculumBijayKumarDasNo ratings yet
- Electrical Control Engineering Design and CostingDocument6 pagesElectrical Control Engineering Design and CostingminjutNo ratings yet
- PsocDocument1 pagePsocGayan ShashiNo ratings yet
- CC C CCC C C C C - C - !" #$%!&' !! - : Paper-2 (Concerned Subject) Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesCC C CCC C C C C - C - !" #$%!&' !! - : Paper-2 (Concerned Subject) Electrical EngineeringRamadugula Rama Subrahmanya VenkateswararaoNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem SyllabusDocument7 pages6th Sem SyllabusNitin MauryaNo ratings yet
- Ex 8 Sem SyllabusDocument6 pagesEx 8 Sem SyllabusMayank KatariaNo ratings yet
- MT Sy PeedDocument7 pagesMT Sy Peedrajat tiwariNo ratings yet
- Converter-Based Dynamics and Control of Modern Power SystemsFrom EverandConverter-Based Dynamics and Control of Modern Power SystemsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power System Frequency Control: Modeling and AdvancesFrom EverandPower System Frequency Control: Modeling and AdvancesDillip Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
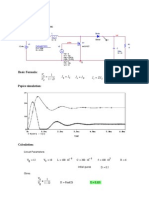
- Boost Converter (Calculation Curcuit Parameters)Document5 pagesBoost Converter (Calculation Curcuit Parameters)Peeyush TripathiNo ratings yet
- 1 Report - 7 Exam Secrets in 30 MinutesDocument12 pages1 Report - 7 Exam Secrets in 30 MinutesAnudeep ChimakurthiNo ratings yet
- 89 FT1630 Through Hole WirelessDocument1 page89 FT1630 Through Hole WirelessPrakash ChandraNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Resistors & Circuits: Ohm's LawDocument8 pagesResistors & Circuits: Ohm's LawH Aries OñaNo ratings yet
- LECT18: Rectangular Horn AntennasDocument28 pagesLECT18: Rectangular Horn AntennasRobert GrubeNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors Notes PDFDocument20 pagesSemiconductors Notes PDFVishalNo ratings yet
- Zone Sensor LT460 - Installation ManualDocument16 pagesZone Sensor LT460 - Installation ManualLuis Alberto Huamán MalcaNo ratings yet
- C37 1-1987 PDFDocument52 pagesC37 1-1987 PDFAlejandro Noe NavarroNo ratings yet
- Power Systems ClipperDocument8 pagesPower Systems ClipperBilly SeasonsNo ratings yet
- NightVisionTechnology Seminar ReportDocument10 pagesNightVisionTechnology Seminar ReportAfrah RamsheedNo ratings yet
- Industrial ElectronicsDocument324 pagesIndustrial Electronicsshambhu32100% (1)
- NEMA Standard Motor CurvesDocument1 pageNEMA Standard Motor CurvesbradrogerNo ratings yet
- Moeller Sasy 60iDocument50 pagesMoeller Sasy 60iOscar TorresNo ratings yet
- De-Embedding Transmission Line Measurements For Accurate Modeling of IC DesignsDocument7 pagesDe-Embedding Transmission Line Measurements For Accurate Modeling of IC DesignsXin LINo ratings yet
- Limiting Circuits Experiment GuideDocument31 pagesLimiting Circuits Experiment Guideعبدالرحمن النويصرNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electromagnetic Wave PropagationDocument26 pagesFundamentals of Electromagnetic Wave PropagationUMEESSNo ratings yet
- Internship Report TemplateDocument9 pagesInternship Report TemplateSarwer Hussain FaisalNo ratings yet
- Design of A High Speed 6 Bit Successive Approximate Register Analog To Digital Converter SAR ADC Using 45nm CMOS TechnologyDocument10 pagesDesign of A High Speed 6 Bit Successive Approximate Register Analog To Digital Converter SAR ADC Using 45nm CMOS TechnologyTENS DeviceNo ratings yet
- LM392Document6 pagesLM392Brzata PticaNo ratings yet
- CIGRE Brochure348Document114 pagesCIGRE Brochure348christiansasso100% (5)
- Solar Floating at EGAT 'S ProjectDocument41 pagesSolar Floating at EGAT 'S ProjectChong Jiazhen50% (2)
- Institute of Aeronautical EngineeringDocument4 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical EngineeringACE PROFILESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ConsumerizationDocument29 pagesChapter 5 ConsumerizationDanieal HakimNo ratings yet
- Unit No.7 AURETB002 1Document17 pagesUnit No.7 AURETB002 1faisal nazirNo ratings yet
- INNOVA5568 SchematicsDocument10 pagesINNOVA5568 Schematicscork_ie100% (1)
- Ericsson Minilink TN R4Document15 pagesEricsson Minilink TN R4Ebenezer AnnanNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Ohmic HeatingDocument171 pagesThesis On Ohmic HeatingDr-Paras PorwalNo ratings yet
- Panasonic - SC-HTB770GN PDFDocument164 pagesPanasonic - SC-HTB770GN PDFboroda2410100% (1)
- Mshengeli Issa H.150 323481421Document20 pagesMshengeli Issa H.150 323481421roger damianNo ratings yet
- Metamaterial Graphene Photodetector With 500 GHZ BWDocument7 pagesMetamaterial Graphene Photodetector With 500 GHZ BWarashmokhtariNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric Educational Solutions 2018-115-117Document3 pagesSchneider Electric Educational Solutions 2018-115-117Amanda GamayaniNo ratings yet
- Tine: Trdsforner Naaibun: Hourard Kva, LvaDocument12 pagesTine: Trdsforner Naaibun: Hourard Kva, LvaRekha NairNo ratings yet
- GTP For 250kva Star-2Document6 pagesGTP For 250kva Star-2Geetha BNo ratings yet