Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Appendix
Uploaded by
Katey Silverio UmaliOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Appendix
Uploaded by
Katey Silverio UmaliCopyright:
Available Formats
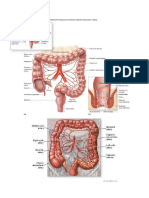
APPENDIX The appendix is a tubular, blind-ended, vestigial structure which is attached to the caecum.
Anatomically the location of the appendix corresponds to the right iliac fossa which is at the lower right quadrant of our abdomen.
Functions of the appendix are: it contains lymphoid follicles which secrete immunoglobulin it contains serotonins which are neuroendocrine hormones it has a bacteriological function where it helps to control the normal gut bacteria Surgical functions - where the appendix is used as an 'urinary conduit' in bladder reconstruction in bladder surgery & it can also be used as an 'appendicostomy' which can be used for antegrade colonic enema (wash-out of faeces) in patients with constipation.
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: The appendix lies in close proximity to the caecum (the beginning of our large intestines). Approximately 75% of the appendix lies behind the caecum (retrocaecal), 20% in the pelvis and the remaining 5% either pre- or post-ileal (infront or behind the small bowel). Appendix attached to the caecum
Acute appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix. It is the commonest acute surgical condition in the abdomen. It typically presents with an initial pain around the umbilical region which later migrates and localises in the right iliac fossa.
Sign and Symptoms as follows: low grade fever, loss of appetite and nausea. tenderness of the abdomen localised at the right iliac fossa Note: which is typically described as at McBurney's point (2/3 along the line drawn between the umbilicus and the anterior superior iliac spine). Severe cases of appendicitis severe abdominal pain, high spiking temperature & dehydration. This usually happens when there is a delay in diagnosis and the appendix perforates leading to purulent or faeculent peritonitis (contamination of the abdominal cavity with pus or faeces). Treatment: Appendicectomy (surgical excision of the appendix) This procedure was traditionally done as an open surgery but most surgeons are doing laparoscopic (minimally invasive) appendicectomies now. The complications of appendicetomy includes: -wound infection (<5% risk) -intra-abdominal abscess -faecal fistula (leakage of faeces from the resected appendix stump) Chronic appendicitis - this usually occurs in patients who were treated with antibiotics or antiinflammatories for a bout of lower abdominal pain. They develop a chronic grumbling right iliac fossa pain which is very vague. It is usully a diagnosis of exclusion.
You might also like
- Appendicitis & Appendectomy: Jenny Juniora AjocDocument31 pagesAppendicitis & Appendectomy: Jenny Juniora AjocJenny AjocNo ratings yet
- 2 Semester 1 Major Patho AnatoDocument49 pages2 Semester 1 Major Patho AnatoManushi HenadeeraNo ratings yet
- Appendicectomy Step by Step PDFDocument9 pagesAppendicectomy Step by Step PDFOlugbenga A Adetunji100% (1)
- Appendicitis Def - It Is An Inflammation of The AppendixDocument9 pagesAppendicitis Def - It Is An Inflammation of The AppendixSanthu SuNo ratings yet
- AppendectomyDocument35 pagesAppendectomyleighjagNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument17 pagesAppendicitisAhmed Halaby100% (1)
- AppendectomyDocument5 pagesAppendectomyCris EstoniloNo ratings yet
- Small & Large Intestines - LectureDocument70 pagesSmall & Large Intestines - Lecturehussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- AppendectomyDocument5 pagesAppendectomyRoseben SomidoNo ratings yet
- Peritonitis. Classifications. Open Abdomen and Staged Abdominal Repair.Document7 pagesPeritonitis. Classifications. Open Abdomen and Staged Abdominal Repair.Ibraheem SairiNo ratings yet
- Sabitson - Appendiks EngDocument17 pagesSabitson - Appendiks Engzeek powerNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis & AppendectomyDocument28 pagesAppendicitis & Appendectomyhakunamatata_15100% (5)
- Appendic It eDocument58 pagesAppendic It eZayneb ZeroualNo ratings yet
- Colon, Rectum and AnusDocument30 pagesColon, Rectum and AnusKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis: Made By: Madhurpreet KaurDocument46 pagesAppendicitis: Made By: Madhurpreet KaurRAJAT DUGGALNo ratings yet
- Exploratory Laparotomy Biopsy, and Principles of Abdominal Closure.Document5 pagesExploratory Laparotomy Biopsy, and Principles of Abdominal Closure.dewa anomNo ratings yet
- APPENDICITISDocument37 pagesAPPENDICITISjohn paul richard mindanaoNo ratings yet
- Gynecological LaparosDocument32 pagesGynecological LaparosYosef Dwi Cahyadi Salan100% (1)
- Jejunal and Ileal AtresiasDocument37 pagesJejunal and Ileal AtresiasABDUL RAHIM UMAR FAROUKNo ratings yet
- 70 Neonatal Anaesthesia 2 Anaesthesia For Neonates With Abdominal Wall DefectsDocument10 pages70 Neonatal Anaesthesia 2 Anaesthesia For Neonates With Abdominal Wall DefectsParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- By: Kinjal Banerjee SU-6Document40 pagesBy: Kinjal Banerjee SU-6Dr Ari SembiringNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy ReadingDocument3 pagesAppendectomy Readingjenn212No ratings yet
- Appendicitis NotesDocument15 pagesAppendicitis NotesHero MondaresNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis: San Roque Extension, Roxas City, Capiz 5800Document10 pagesAppendicitis: San Roque Extension, Roxas City, Capiz 5800GUEZIL JOY DELFINNo ratings yet
- Hirschprung DiseaseDocument61 pagesHirschprung DiseaseAdditi Satyal100% (1)
- Acute AppendicitisDocument5 pagesAcute AppendicitisPrasetya Ismail PermadiNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Surgical EmergenciesDocument17 pagesNeonatal Surgical EmergenciesfaisaldanyaniNo ratings yet
- EsophagusDocument168 pagesEsophagusnancy voraNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument7 pagesAppendicitisTim LuoNo ratings yet
- 2 2017 03 26!08 03 00 PMDocument10 pages2 2017 03 26!08 03 00 PManakayamNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy: Colegio de San Juan de Letran - CalambaDocument14 pagesAppendectomy: Colegio de San Juan de Letran - CalambaJiedNo ratings yet
- AppendectomyDocument15 pagesAppendectomyAia JavierNo ratings yet
- Medscape Abdominal HerniasDocument47 pagesMedscape Abdominal HerniasSary OktiviaNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument23 pagesAppendicitisGina LositoNo ratings yet
- Hospital of AffiliationDocument4 pagesHospital of Affiliationdanni LNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Rectum and Anal CanalDocument68 pagesDiseases of Rectum and Anal CanalKoridor Falua Sakti Halawa 21000063No ratings yet
- AppendectomyDocument7 pagesAppendectomyLeis FatwaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The IntestinesDocument64 pagesDisorders of The IntestinesCharmaine Torio PastorNo ratings yet
- Git 301 Final 2021 Section TwoDocument8 pagesGit 301 Final 2021 Section TwoBright LunetaNo ratings yet
- The 3rd Edition: Prevention & Management: Complications of Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia RepairDocument5 pagesThe 3rd Edition: Prevention & Management: Complications of Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia RepairVishnu KumarNo ratings yet
- Intussusception 161007042729 PDFDocument44 pagesIntussusception 161007042729 PDFDina MarselinaNo ratings yet
- Git تجميعاتDocument146 pagesGit تجميعاتMenna SalemNo ratings yet
- Absite Master PileDocument23 pagesAbsite Master PileJames JosephNo ratings yet
- Acute AppendicytisDocument17 pagesAcute AppendicytisMethew Brian0% (1)
- Traditional Open AppendectomyDocument14 pagesTraditional Open AppendectomyBayu NoviandaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Atresia, Volvulus, Meckel's Diverticulum: BowelDocument45 pagesAnatomy Atresia, Volvulus, Meckel's Diverticulum: BowelkedokterankeluargaNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy For Achalasia: Robert N. Cacchione, M.D., Dan N. Tran, M.D., Diane H. Rhoden, M.DDocument5 pagesLaparoscopic Heller Myotomy For Achalasia: Robert N. Cacchione, M.D., Dan N. Tran, M.D., Diane H. Rhoden, M.Dgabriel martinezNo ratings yet
- 46 Diverticula of The Oesophagus. Classification. Diagnosis. Treatment.Document4 pages46 Diverticula of The Oesophagus. Classification. Diagnosis. Treatment.ManusheeNo ratings yet
- Colostomy & Colostomy CareDocument56 pagesColostomy & Colostomy Careapi-3722454100% (31)
- Appendiktomi Translate BookDocument19 pagesAppendiktomi Translate Bookalyntya melatiNo ratings yet
- © 2021 Lippincott Advisor - Treatments - HysterectomyDocument5 pages© 2021 Lippincott Advisor - Treatments - HysterectomyJoyJoy Tabada CalunsagNo ratings yet
- Whipple's OperationDocument35 pagesWhipple's OperationSunaina AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis: Michael Alan Cole Robert David HuangDocument10 pagesAcute Appendicitis: Michael Alan Cole Robert David HuangandreaNo ratings yet
- Gastroschisis Dan Omphalocele LNKPPTDocument41 pagesGastroschisis Dan Omphalocele LNKPPTAswad AffandiNo ratings yet
- Gastroschisis Dan Omphalocele LNKPPTDocument41 pagesGastroschisis Dan Omphalocele LNKPPTAswad Affandi100% (1)
- Laparoscopic AppendectomyDocument24 pagesLaparoscopic AppendectomyMosher MundaNo ratings yet
- Colitis: A Practical Approach to Colon and Ileum Biopsy InterpretationFrom EverandColitis: A Practical Approach to Colon and Ileum Biopsy InterpretationAnne Jouret-MourinNo ratings yet