0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views3 pagesDegree of Polymerization
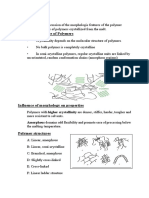
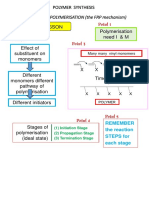
The degree of polymerization (DP) indicates the number of monomer units in a polymer, influencing its mechanical strength, thermal stability, and solubility. Higher DP results in stronger materials and affects properties like elasticity and melting point, while different polymerization methods (addition and condensation) yield varying DP levels. Factors such as monomer reactivity, temperature, and reaction time also impact DP, which is crucial for various industrial applications.
Uploaded by
mahezwizard321Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views3 pagesDegree of Polymerization
The degree of polymerization (DP) indicates the number of monomer units in a polymer, influencing its mechanical strength, thermal stability, and solubility. Higher DP results in stronger materials and affects properties like elasticity and melting point, while different polymerization methods (addition and condensation) yield varying DP levels. Factors such as monomer reactivity, temperature, and reaction time also impact DP, which is crucial for various industrial applications.
Uploaded by
mahezwizard321Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd