0% found this document useful (0 votes)
350 views3 pagesSalamander Classification & Dichotomous Key
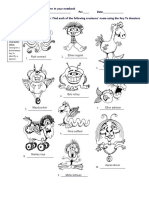
The document provides a guide on salamander classification using a dichotomous key, which helps users identify various salamander species through a series of statements with two options. It includes a simple example of a dichotomous key and a detailed key for identifying different salamander species based on physical characteristics. Users are instructed to examine pictures of salamanders and write their identifications based on the key.
Uploaded by
isha singhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
350 views3 pagesSalamander Classification & Dichotomous Key
The document provides a guide on salamander classification using a dichotomous key, which helps users identify various salamander species through a series of statements with two options. It includes a simple example of a dichotomous key and a detailed key for identifying different salamander species based on physical characteristics. Users are instructed to examine pictures of salamanders and write their identifications based on the key.
Uploaded by
isha singhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd