0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views3 pagesPresent Continuous Tense
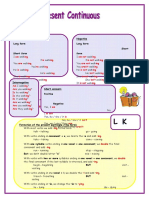
The document explains the Present Continuous tense, which is used for actions happening now, around this time, or temporarily. It includes structures for positive, negative, and interrogative forms, along with examples and classwork exercises for practice. The positive form uses 'am/is/are + verb + -ing', while the negative form adds 'not', and questions start with 'Am/Is/Are'.
Uploaded by
rzdw9z8swvCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views3 pagesPresent Continuous Tense
The document explains the Present Continuous tense, which is used for actions happening now, around this time, or temporarily. It includes structures for positive, negative, and interrogative forms, along with examples and classwork exercises for practice. The positive form uses 'am/is/are + verb + -ing', while the negative form adds 'not', and questions start with 'Am/Is/Are'.
Uploaded by
rzdw9z8swvCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd