0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views2 pagesFreundlich Isotherm: e F e N
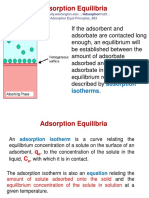
The document outlines various adsorption isotherms including Freundlich, Langmuir, BET, Temkin, Dubinin-Radushkevich, and Halsey & Harkin-Jura. Each isotherm is characterized by its unique equation and features, such as the type of adsorption (monolayer vs multilayer) and the nature of the surface (homogeneous vs heterogeneous). These models help in understanding the adsorption processes in different contexts, particularly in physical and chemical adsorption scenarios.
Uploaded by
vishakhachem2Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views2 pagesFreundlich Isotherm: e F e N
The document outlines various adsorption isotherms including Freundlich, Langmuir, BET, Temkin, Dubinin-Radushkevich, and Halsey & Harkin-Jura. Each isotherm is characterized by its unique equation and features, such as the type of adsorption (monolayer vs multilayer) and the nature of the surface (homogeneous vs heterogeneous). These models help in understanding the adsorption processes in different contexts, particularly in physical and chemical adsorption scenarios.
Uploaded by
vishakhachem2Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd