0% found this document useful (0 votes)
139 views5 pagesStatistical Formulas and Concepts Guide
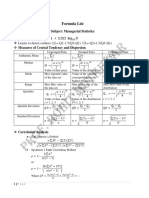
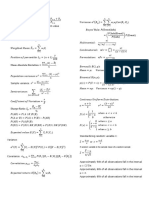
This document provides formulas and concepts for descriptive statistics, probability theory, random variables, hypothesis testing, and regression. It includes formulas for mean, variance, covariance, correlation, binomial and normal distributions, confidence intervals, test statistics, analysis of variance, and linear regression. Key concepts covered are means, variances, probabilities, independence, distributions, hypothesis testing, and fitting lines to data.
Uploaded by
Ian HowardCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
139 views5 pagesStatistical Formulas and Concepts Guide
This document provides formulas and concepts for descriptive statistics, probability theory, random variables, hypothesis testing, and regression. It includes formulas for mean, variance, covariance, correlation, binomial and normal distributions, confidence intervals, test statistics, analysis of variance, and linear regression. Key concepts covered are means, variances, probabilities, independence, distributions, hypothesis testing, and fitting lines to data.
Uploaded by
Ian HowardCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd