0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views11 pagesMicroprocessor Class 10
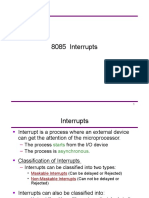
The document discusses interrupts in microprocessors, explaining their role in allowing external devices to signal the processor and suspend normal execution for servicing. It categorizes interrupts into maskable and non-maskable types, as well as hardware and software interrupts, detailing specific examples and their vector addresses. Additionally, it outlines the priority levels of various interrupts and their masking capabilities.
Uploaded by
sureshpv36Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views11 pagesMicroprocessor Class 10
The document discusses interrupts in microprocessors, explaining their role in allowing external devices to signal the processor and suspend normal execution for servicing. It categorizes interrupts into maskable and non-maskable types, as well as hardware and software interrupts, detailing specific examples and their vector addresses. Additionally, it outlines the priority levels of various interrupts and their masking capabilities.
Uploaded by
sureshpv36Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd