0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesSurgery To Aman
The document discusses the importance of sterilization in veterinary surgery, detailing methods to eliminate microbial life from surgical instruments and operation sites to prevent infections and ensure successful outcomes. It outlines various surgical instruments, wound types, and methods for disinfection and pre-operative care, emphasizing the need for proper aseptic techniques and patient monitoring. Additionally, it covers post-operative care, including pain management, wound care, and the management of complications such as surgical site infections and fractures.
Uploaded by
ub119828Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesSurgery To Aman
The document discusses the importance of sterilization in veterinary surgery, detailing methods to eliminate microbial life from surgical instruments and operation sites to prevent infections and ensure successful outcomes. It outlines various surgical instruments, wound types, and methods for disinfection and pre-operative care, emphasizing the need for proper aseptic techniques and patient monitoring. Additionally, it covers post-operative care, including pain management, wound care, and the management of complications such as surgical site infections and fractures.
Uploaded by
ub119828Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
Sterilization refers to the process of eliminating or
destroying all forms of microbial life including
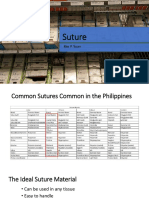
bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores, from an object, Name of surgical instruments:- -Wound: Any injury that breaks the skin or other
surface, or environment. The goal of sterilization is to Scalpel: Used for making incisions in body tissues. Wounds can range from minor cuts and
make the area or item completely free from viable tissues Forceps: Grasping and holding tissues or scratches to deep punctures or lacerations, and they
microorganisms that could potentially cause objects during surgery. Scissors: Cutting tissues, require varying degrees of treatment depending on
infection, contamination, or disease. sutures, or other materials during surgery. their severity. -Burns and Scalds: Burns are
Sterilization of surgical instruments is very Needle Holder: Holding and manipulating surgical injuries caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, or
important:- 1.Infection Prevention: Guards needles for suturing. Retractor: Used to hold back radiation, leading to tissue damage. Scalds specifically
against introducing harmful microorganisms into tissues or organs to provide better access to the refer to burns caused by hot liquids or steam. Burns
animals during medical procedures. 2.Animal Health: surgical area. Surgical Probe: Used for exploring are classified by degree (1st, 2nd, 3rd) based on their
Reduces the risk of post-surgical infections and wounds or body cavities during surgery. severity and depth. -Tumors: Abnormal growths of
complications in animals. 3.Regulatory Compliance: Surgical Suction Device: Removing blood, fluids, or cells that can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant
Ensures adherence to standards and guidelines for debris from the surgical site. Hemostat: Clamping (cancerous). Tumors can develop in any part of the
animal care and welfare. 4.Disease Transmission blood vessels to control bleeding during surgery. body and can cause a range of symptoms depending
Prevention: Minimizes the potential for, cross-species Speculum: Used to hold open or expand a body on their location and size. -Inflammation: The
infection and disease spread. 5.Surgical Success: orifice during examination or surgery.
body's natural response to injury, infection, or
Contributes to accurate veterinary procedures and Towel clips: Grasping and holding dressings or other
irritation, characterized by redness, swelling, heat,
positive treatment outcomes. . Ethical Responsibility: materials during wound care.
and pain. Inflammation is a protective mechanism
Upholds the ethical obligation to provide safe and Suture material refers to the threads or materials that helps the body to heal and fight off harmful
effective The methods of sterilization or used by surgeons to stitch together wounds or substances. -Cyst: A closed sac or pouch-like
reducing contamination at operation sites:- surgical incisions. These materials are designed to
structure that contains fluid, air, or other substances.
Sterilizing operation sites in animals is crucial to hold tissues together until they heal and can be
Cysts can develop anywhere in the body and may or
prevent infections and ensure successful surgical absorbed by the body or removed later, depending
may not cause symptoms. They can be benign or
outcomes. Following are the methods of sterilization on the type of suture. Types of suture materials:-
1. Natural Sutures: Silk: Made from natural silk fibers, malignant. -Suppurative and Abscess:
1.Preoperative Preparations: Thoroughly clean and
silk sutures are smooth and easy to handle. They are Suppurative refers to the formation of pus, which is a
disinfect the surgical site using antiseptic solutions to
commonly used in delicate tissue and ophthalmic thick fluid composed of dead white blood cells,
reduce the microbial load 2. Clip and Shave: Hair
surgery. Catgut: Derived from the submucosal fibrous bacteria, and tissue debris. An abscess is a localized
around the surgical site is clipped and shaved to
tissue of sheep intestines, catgut sutures are collection of pus within a tissue or organ, often
minimize contamination and provide better access
absorbable and used for soft tissue approximation. caused by a bacterial infection. -Necrosis: The
2.Antiseptic Solutions: Apply antiseptic solutions,
They come in both plain and chromic varieties.2. death of cells or tissues due to injury, infection, or
such as iodine or chlorhexidine, to disinfect the skin
Synthetic Sutures: Nylon (Polyamide): Nylon sutures disease. Necrosis can be localized or widespread and
and reduce the risk of infection. 3.Sterile Draping:
are strong, flexible, and have excellent knot security. can lead to the breakdown of affected tissues if not
Use sterile drapes to create a barrier around the
surgical site, maintaining a sterile field during the They are commonly used in general surgery, treated promptly. -Ulcers: Open sores or lesions
procedure. 4.Isolation: Restrict access to the surgical cardiovascular surgery, and plastic surgery. that develop on the skin or mucous membranes,
site to prevent contamination from non-sterile Polypropylene: Polypropylene sutures are non- often as a result of poor circulation, infection, or
individuals or equipment 5. Appropriate Attire: absorbable and have high tensile strength. They are prolonged pressure. Ulcers can be painful and may
Surgical team members wear sterile gowns, gloves, suitable for use in areas where long-term wound require medical intervention to heal properly.
masks, and apron. support is needed, such as in orthopedic and hernia -Sinuses and Fistula: Sinuses are air-filled spaces
repair surgeries. Polyglactin (Vicryl): Polyglactin in the skull that are connected to the nasal cavity.
Write the methods of disinfection of the sutures are absorbable and composed of a copolymer They can become inflamed or infected, leading to
operation area? Disinfection of the operation of glycolide and lactide. They are widely used in sinusitis. A fistula is an abnormal connection or
area in animals involves reducing the number of general surgery, obstetrics, and gynecology. passageway that forms between two organs or
microorganisms present to minimize the risk of Absorbable: Catgut, Polyglactin (Vicryl), between an organ and the skin, often as a result of
infection. Here are the methods commonly used for Polydioxanone(PDS) Non-absorbable: Nylon injury, infection, or surgery.
disinfection of operation area. (Polyamide), Polypropylene, Stainless Steel,
1.Preparation: Clear the area of debris, equipment,
and non-essential items before starting the
Anesthesia is a medical practice used to prevent
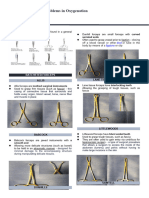
Suture patterns:- There are several different patients from feeling pain or discomfort during
disinfection process. 2.Cleaning: Thoroughly clean suture patterns that can be used in surgical surgery or other medical procedures. There are three
surfaces using water, detergent, or enzymatic procedures, each with its own specific indications and main types of anesthesia: 1.General anesthesia:
cleaners to remove visible dirt and organic matter. advantages. Here are some commonly used suture This type induces a reversible loss of consciousness.
3.Antiseptic Solution: Apply an antiseptic solution, patterns. 1.Simple Interrupted: This is the most Patients are completely unconscious and unaware of
such as iodine or chlorhexidine, to disinfect the area. basic suture pattern. - It involves individual stitches their surroundings. Examples include the use of
Follow manufacturer guidelines for proper dilution placed sequentially, with each stitch tried separately inhaled gases like sevoflurane or intravenous drugs
and application. 5.Scrubbing: Gently scrub the area - Simple interrupted sutures are versatile and can be like propofol. 2.Regional anesthesia: This blocks pain
with an antiseptic scrub brush or sponge to ensure used for a wide range of tissues types and wound in a specific part of the body while the patient
thorough coverage. 6.Contact Time: Allow the location. 2.Continuous (Running): In this pattern, a remains conscious. Examples include epidural
antiseptic solution to remain in contact with the continuous suture line is created by placing anesthesia commonly used in childbirth or spinal
surface for the recommended duration to effectively consecutive stitches without tying, individual knots anesthesia for lower abdominal or lower limb
kill microorganisms. 7.Rinsing: If necessary, rinse the - Continuous sutures are efficient and save time, surgeries. 3.Local anesthesia: This numbs a small
area with sterile water to remove residual antiseptic particularly for lung incisions on linear wounds. area of the body to prevent pain during minor
solution. 8.Drying: Ensure the area is completely dry - However, if one of stitch fails, the entire suture line procedures. Examples include lidocaine injections for
before proceeding with the surgical procedure. may be compromised. 3.Vertical Mattress: The dental work or skin surgeries.
Pre-Surgical Asepsis: Hand Hygiene: Thorough vertical mattress pattern involves placing stitches in a
hand washing and/or disinfection by surgical staff vertical orientation with each stitch incorporating
tissue both shove and below the wound edge. Pre operative care of animals:-
before entering the operating room. 1.Medical Evaluation: Assessing the patient's health
Sterile Attire: Surgical staff wear sterile gowns, - This pattern provides excellent wound edge eversion
and is areas where cosmesis is important or where and history for potential risks during surgery.
gloves, masks, and hats to prevent contamination. 2.Medication Management: Adjusting medications to
Sterile Field: The operating room is prepared with there is tension on the wound
4.Horizontal Mattress: The horizontal mattress minimize surgical risks. 3.Anesthesia Consultation:
sterile drapes, instruments, and equipment to create
pattern is similar to the vertical mattress but with Meeting with an anesthesiologist to discuss
a sterile environment for surgery. Skin Preparation:
Patient's skin at the surgical site is cleaned and stitches placed in a horizontal orientation.- It provides anesthesia options and prepare for the process.
prepped with antiseptic solutions to reduce microbial good wound edge eversion and distributes tension 4.Fasting Instructions: Providing clear guidelines to
load. Proper Instrument Handling: Sterile across the wound. - The horizontal mattress pattern prevent complications during anesthesia.
instruments are handled with care and only by is often used in areas prone to wound dehiscence or 5.Counseling and Education: Informing patients
trained personnel to avoid contamination. Traffic in closure of deep layers. 6.Subcuticular: The about the procedure, risks, benefits, and recovery
Control: Limiting the number of people entering and subcuticular pattern involves placing sutures in a expectations. 6.Consent Forms: Obtaining informed
exiting the operating room to reduce the risk of continuous, buried manure just below the skin
consent from the patient or their legal representative.
contamination. Post-Surgical Asepsis: surface. - It provides excellent cosmetic results as
7.Preparing the Surgical Site: Cleaning and prepping
Wound Care: Proper care and dressing of the surgical the sutures are not visible on the skin surface. to reduce infection risk. 8.Psychological Support:
wound to prevent infection. Environmental Cleaning: 7.Purse-String: The purse-string pattern involves Addressing patient concerns and providing emotional
Thorough cleaning and disinfection of the operating placing a circular suture around an opening, cinching support as needed.
room and equipment to eliminate any potential it together, and tying it to close the opening.
pathogens. Proper Disposal: Safe disposal of all used - It is commonly used in procedures such as bowel or
materials and equipment to prevent the spread of gastric closures, wound closures around tubes or
infection. Hand Hygiene: Surgical staff should drains, and closure of umbilical hernias.
perform hand hygiene again after removing gloves
and leaving the operating room to prevent cross-
contamination. Patient Monitoring: Monitoring the - *Trauma:* Refers to physical or psychological injury
patient for signs of infection or complications post- or shock caused by an external force or event. It can
surgery to ensure timely intervention if needed. be acute, like a sudden accident, or chronic, resulting
from ongoing stress or abuse.
Post operative care of patients:-
1.Monitoring vital signs: Regularly checking
heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, and
breathing to detect any issues.
2.Pain management: Administering Rescue: Rescue involves the prompt and effective
response to a situation where an animal's life is in
medications to alleviate post-operative pain immediate danger due to trauma, injury, illness, or Procedure for management of wound in animal:-
and ensure patient comfort. 3.Wound care: other critical factors. It includes actions taken to 1.Assessment: Check the wound's size, depth, and
Cleaning and dressing surgical incisions to safely extricate, move, or transport the animal to a cleanliness. 2.Restraint: Securely restrain the animal
prevent infection and promote healing. safer location or to a veterinary facility. Rescue efforts to prevent further injury. 3.Cleaning: Gently clean
4.Fluids and nutrition: Providing adequate are done to prevent further harm, to provide physical the wound with mild antiseptic or saline solution.
hydration and nutrition to support recovery support, or to manage dangerous situations to ensure 4.Irrigation: Flush the wound with sterile solution if
and prevent complications. 5.Mobilization the animal's well-being. Different ways necessary. 5.Debridement: Remove dead tissue
to rescue animals:- Emergency Contact: around the wound carefully. 6.Hemostasis: Apply
and activity: Encouraging gradual movement Call local animal control or rescue services pressure to stop bleeding if needed. 7.Dressing:
and activity to prevent blood clots and muscle immediately. Safe Approach: Carefully handle the Cover the wound with a sterile dressing and secure it.
weakness. 6.Respiratory care: Monitoring animal with appropriate precautions. Transport 8.Medication: Administer prescribed medications,
breathing and providing interventions to Safely: Move the animal to a secure location away such as antibiotics or pain relievers. 9.Monitoring:
prevent respiratory complications such as from danger. Medical Care: Seek prompt veterinary Check the wound regularly for signs of infection or
pneumonia. 7.Medication management: attention for injured animals. Rehabilitation: Transfer poor healing. 10.Follow-Up: Seek veterinary follow-
to a specialized facility for proper care and up for further evaluation and treatment if necessary.
Administering prescribed medications, rehabilitation. Prevention: Educate others to prevent
including antibiotics and blood thinners, to future incidents and promote responsible behavior.
prevent infections and blood clots. Procedure for management of fracture:-
Assessment: Evaluate the location and severity of the
Administering first aid to animals requires careful fracture, noting any signs of pain or deformity.
Surgical site infections (SSIs) are infections consideration and often specialized techniques. Here Restraint: Safely restrain the animal to prevent
that occur at the site of a surgery. They can are some methods: Assessment: Evaluate the further injury and keep them calm. Immobilization:
range from mild skin infections to more situation and assess the animal's condition, checking Immobilize the fracture using splints or padding to
for responsiveness, breathing, and signs of injury. prevent movement and alleviate pain. Support:
serious infections that involve deeper tissues Stabilization: Safely restrain or immobilize the animal
or organs. The prevention control measures Provide support to the injured limb using slings or
to prevent further injury or harm to themselves and bandages to minimize weight-bearing.
for surgical site infections (SSIs):- 1.Antibiotic others. Wound Care: Clean and dress wounds using Transportation: Carefully transport the animal to a
Prophylaxis: Administer antibiotics before surgery. antiseptic solutions and bandages to prevent veterinary clinic for further evaluation and treatment.
2.Proper Surgical Technique: Maintain sterility and infection. Bleeding Control: Apply pressure to stop Professional Care: Seek prompt veterinary assistance
adhere to aseptic technique. 3.Skin Preparation: bleeding, and use bandages or dressings to control for proper diagnosis and treatment, which may
Cleanse the skin with antiseptic solutions pre- hemorrhage. Resuscitation: Perform CPR include x-rays, pain management, and possible
operatively. 4.Optimize Patient Health: Manage (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) if the animal is not surgical intervention.
underlying conditions like diabetes and obesity. breathing and lacks a heartbeat. Heatstroke
Treatment: Cool the animal down gradually using
5.Wound Care: Keep the surgical site clean, dry, and Procedure for management of bites:-
cool water or wet towels, and seek veterinary
monitor for signs of infection. 6.Environmental assistance. Poisoning Response: Contact a Assess the Situation: Ensure safety for both you and
Controls: Maintain a clean operating room veterinarian immediately if you suspect poisoning, the animal. Control Bleeding: Apply gentle pressure
environment with proper ventilation. and follow their instructions for first aid measures. to any bleeding wounds using a clean cloth or
7.Post-operative Monitoring: Regularly monitor Fracture Management: Immobilize fractures using bandage. Clean the Wound: Wash the wound with
patients for signs of infection, enabling early splints or bandages to prevent further injury and pain. mild soap and water to reduce the risk of infection.
detection and treatment. Transportation: Transport injured animals carefully to Use a gentle stream of water to flush out any debris.
a veterinary clinic or animal hospital for further Apply Antiseptic: Use antiseptic solution or wipes to
further clean the wound and reduce the risk of
Nutritional management in animals:- evaluation and treatment. Professional Assistance:
infection. Cover the Wound: Apply a clean dressing or
1.Species-Specific Nutrition: Tailor diets to Seek guidance from a veterinarian or animal rescue
organization for specific first aid procedures and bandage to protect the wound from further
match the natural dietary preferences and treatment protocols. contamination. Change the dressing regularly.
digestive abilities of different animal species. Monitor for Signs of Infection: Watch for signs such
2.Nutrient Requirements: Determine and as redness, swelling, warmth, or discharge from the
First aid to animal suffering from fracture wound. Seek veterinary care if these symptoms occur.
provide essential nutrients based on factors and wound Approach Gently: Approach the Seek Veterinary Attention: Animal bites can lead to
like age, weight, and activity level. animal calmly and quietly to avoid causing additional infection and may require antibiotics or other medical
4.Feeding Practices: Establish feeding stress or fear. Assessment: Evaluate the severity of treatment. Contact a veterinarian for further
schedules and portion sizes to maintain the injuries without causing further harm. Note any evaluation and care.
signs of pain, distress, or shock. Restraint: If
optimal nutrition without overfeeding or necessary, gently restrain the animal to prevent them
underfeeding. 5.Special Dietary from further injuring themselves or others. Use a
Procedure for management of poisoning:-
Remove the Source: If possible, remove the animal
Considerations: Address any specific dietary towel or blanket to create a makeshift sling or
from the area where the poisoning occurred to
needs or health conditions with adjustments restraint if they have a limb injury. Comforting: Speak
prevent further exposure. Contact a Professional:
to the diet. 6.Water Provision: Ensure to the animal in a soothing voice and provide gentle
Immediately call a veterinarian or animal poison
reassurance through petting or stroking if they are
animals have access to clean, fresh water at receptive to it. Avoid sudden movements or loud
control hotline for guidance. Provide information
all times. 7.Supplementation: Consider about the suspected toxin and the animal's
noises that could startle them. Pain Management: If
symptoms. Keep the Animal Calm: Keep the animal
additional nutrients if deficiencies are the animal appears to be in pain, avoid touching the
calm and comfortable, and prevent them from
identified or recommended by a veterinarian. injured area directly. Instead, apply a cold compress
further exposure to the toxin. Monitor Vital Signs:
or ice pack wrapped in a towel to reduce pain and
Keep an eye on the animal's breathing, heart rate,
swelling. Do not apply ice directly to the skin.
and temperature. Note any changes and report them
Wound Care: If there is an open wound, carefully
to the veterinarian. Transport Safely: If instructed by
clean the area with mild soap and water or a saline
the veterinarian, transport the animal to a veterinary
First Aid: Primary objective of first aid:- is to solution. Apply a clean bandage or dressing to cover
clinic or emergency facility for further evaluation and
preserve life - It provide immediate care to sick or the wound and protect it from further contamination.
treatment. Use a secure carrier or restraint to prevent
Fracture Management: If you suspect a fracture,
injured animals. First aid is defined as immediate avoid manipulating the injured limb. Immobilize the
injury during transportation. Follow Veterinary
medical assistance given to injured animal. It include Advice: Follow any instructions or treatment
fracture using splints or padding to prevent further
cardiopulmonary resuscitation af (CPR) complete recommendations provided by the veterinarian.
movement and pain. Transportation: Once the
treatment of minor condition. Importance of first Administer any prescribed medications as directed.
animal is stabilized, carefully transport them to a
Aid:- To preserve life of an animal -To reduce pain veterinary clinic or animal hospital for further
and suffering -To prevent deteriorating -To promote evaluation and treatment. Use a secure carrier or Ultrasonography= A procedure that uses high
improvised stretcher to minimize movement during energy sound wave to look at tissue and organs inside
Recovery -To prevent minor injury becoming a transportation. Professional Care: Seek prompt body. Sound waves make echoes that form pictures
major one -To manage emergency situation of veterinary assistance to properly diagnose and treat of the tissue and organs on a computer screen.
wound. -It is Recognized all over the world the injuries. Veterinarians can provide pain Principle of Ultrasonography:- Ultrasound is
-Untrained person First aid can participate in medication, antibiotics, and other necessary defined as high frequency sound wave greater than
-It can prevent infection. treatments to aid in the animal's recovery. audible sounds (more than 20,000Hz). 🞂 For
diagnostic purposes: frequencies of 1-10 MHz are
used. 🞂 Ultrasound imaging based on pulse-echo
principle ie., when sound wave travels in a pulse and
is reflected back, it becomes an echo.
Properties of Ultrasound:- Can not propagated Cold Therapy Indication: Acute and hyper-acute
through vacuumed area and transmission through gas injury, effective first 24 hrs of injury Technique:-Ice
is poor. -Higher frequency penetrates less far but water immersion -Ice pack application -Blowing cold
provides better resolution. -Transducer is composed water Mechanism: Cold therapy decrease local
of one or more piezo-electric crystals, upon circulation results in constriction of blood vessels,
stimulation of these crystals, shape is changed and reduce blood flow helps to reduce odema,
sound waves of particular frequency is generated. hemorrhage and inhibit of inflammatory mediators
• Therapeutic effects of cold occurs at tissue
temperature between 15-19*C • Cold application
generally combined with compression bandage.
Scanning procedure of (USG):- 1.Preparation of
the patient: by clipping, shaving and cleaning the hair
and skin. 2. Position of the patient: should be placed
on dorsal, lateral recumbency or in standing position Ultrasound Therapy:- Application:- Useful in
depending on the organ scanned. stiffness of muscle • Improve range of motion of the
3. Image interpretation: echo patterns are generally joints • Improve circulation to scar tissue. • Decrease
described in contrast to adjacent tissues or organs. pain and muscle spasm Technique: The area to be
A.Hyperechoic/echogenic: echo pattern appearance treated should be clipped. Ultrasound gel is applied
over the screen is brighter eg., bone or air. and sound head is placed over the skin. After setting
B.Hypoechoic: echo pattern appearance over screen required Frequency and time, sound head must keep
is grey or dark and given by interfaces of moderate on moving slowly over the target area.
reflection such as soft tissues. C. Anechoic/echo-free:
absence of echo, image will be black in screen.
Advantages of Ultrasonography:- Better Heat Therapy:- Indication:-After acute
inflammation has subsided -Muscle spasm
delineation of soft tissue. -Absolutely safe. -Not very
-Increase joint and tendon mobility
expensive. Indications:-Used for detecting
abnormality of organs or tissues. Examples:–heart Technique:-Superficial heat applied using hot packs,
-kidney -Adrenal glands etc. /-For detection of Hydrotherapy, Moist air Deep heat applied using
developmental stages and abnormalities of fetus. Radiant heat
X-rays= are a form of electromagnetic radiation Hot Water Application:-
characterized by high energy and short wavelengths, Indication:- Sub acute and chronic inflammation
often used for medical imaging, security screening, -Septic lesion Technique:- Hot water Mechanism
-Analgesia by softening tissue -Hyperemia results
and industrial applications. phagocytosis
factors affecting X-rays:- including: Energy of the
Electrons: The energy at which electrons are
accelerated impacts the energy and penetration
ability of the resulting X-rays. Target Material: The
material used as the target for electron collision
influences the characteristics of the produced X-rays,
including their energy spectrum. Voltage and Current
Settings: Adjusting the voltage and current settings of
the X-ray machine alters the intensity and quality of
the X-ray beam. Filtration: Filters can be used to
selectively remove low-energy X-rays, affecting the
quality and hardness of the X-ray beam. Exposure
Time: The duration for which X-rays are emitted
affects the overall exposure received by the subject
and the resulting image quality.
The biological effects of radiation are:-
1.Tissue Damage: Ionizing radiation can damage cells
by ionizing atoms and molecules within them.
2.Acute Effects: High doses over a short period can
cause radiation sickness. 3.Chronic Effects: Lower
doses over time may increase cancer risk.
4.Genetic Effects: Radiation can induce mutations in
reproductive cells, affecting future generations.
5.Therapeutic Use: Controlled doses are used in
radiation therapy for cancer treatment.
The working principle of X-rays involves:
1.Electron Acceleration: Electrons are accelerated to
high speeds using an electric field within a vacuum
tube. 2.Target Material: The accelerated electrons
collide with a target material, usually tungsten.
3.Deceleration: When electrons strike the target,
they suddenly decelerate, emitting energy in the form
of X-rays. 4.X-ray Emission: The emitted X-rays pass
through an object, and a detector captures the
remaining X-rays to create an image.
5.Image Formation: The captured X-rays are
processed by a computer to generate an image
# Physical therapy or Physiotherapy deals with
showing the internal structure of the object or body.
⦁ Rehabilitation means restoration of the functional
treatment of diseases by physical methods.
⦁ Physiotherapy and rehabilitation accelerate normal
utility of affected part. tissue healing by galvanizing
physiological processes so that the functional
normalcy of an affected part is restored faster.
Aims of physiotherapy:-Correcting deformities
-Preventing deforming tendencies -Developing
- Making the joint movement up to normal
paralyzed muscles -Faster healing -Restoring the
functional ability
Principles of physiotherapy:- 1. Decrease pain &
facilitate healing of inflamed & injured neurological &
musculoskeletal tissues 2. Maintain normal range of
motion in affected joints 3. Prevent soft tissue
contracture & fibrosis in weak or paralyzed limbs
4. Prevent further atrophy of affected musculature
5. Improve strength & function of weak or paralyzed
limbs 6. Maximize post-surgical recovery & function
of the patient.
You might also like
- Module 2. Surgical Instruments and Suture PatternNo ratings yetModule 2. Surgical Instruments and Suture Pattern73 pages
- Chapter 22 Assisting With Minor Office SurgeryNo ratings yetChapter 22 Assisting With Minor Office Surgery6 pages
- Topnotch Surgery For Moonlighters Part 1 of 2100% (1)Topnotch Surgery For Moonlighters Part 1 of 283 pages
- Basic Suturing Principles (DM Bedah Kelompok D by Dr. Wahyu Prabowo S.PB)100% (1)Basic Suturing Principles (DM Bedah Kelompok D by Dr. Wahyu Prabowo S.PB)98 pages
- Surgical Wound Classification and HealingNo ratings yetSurgical Wound Classification and Healing57 pages
- Types of Anesthesia and Sutures ExplainedNo ratings yetTypes of Anesthesia and Sutures Explained19 pages
- Surgical Infections: Prevention & TreatmentNo ratings yetSurgical Infections: Prevention & Treatment20 pages
- Basics of Instrument and Tissue HandlingNo ratings yetBasics of Instrument and Tissue Handling55 pages
- Wound Management Part One: Topical Treatments: CPD ArticleNo ratings yetWound Management Part One: Topical Treatments: CPD Article6 pages
- Surgical Infections: Causes and PreventionNo ratings yetSurgical Infections: Causes and Prevention19 pages
- Clinic Requisition - Consumable Items Sheet-1No ratings yetClinic Requisition - Consumable Items Sheet-136 pages
- History of Thread Lifting: Souphiyeh SamizadehNo ratings yetHistory of Thread Lifting: Souphiyeh Samizadeh8 pages
- Dokumen - Pub The Fundamentals of Surgical Instruments A Practical Guide To Their Recognition Use and Care 1nbsped 9781910079584 9781910079553No ratings yetDokumen - Pub The Fundamentals of Surgical Instruments A Practical Guide To Their Recognition Use and Care 1nbsped 9781910079584 9781910079553279 pages
- Bernina 2012 Embroidery Basics Sewing Machine Instruction ManualNo ratings yetBernina 2012 Embroidery Basics Sewing Machine Instruction Manual45 pages
- Bernina 330/350PE/380 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualNo ratings yetBernina 330/350PE/380 Sewing Machine Instruction Manual52 pages
- Efficacy of Barbed Sutures in Oral SurgeryNo ratings yetEfficacy of Barbed Sutures in Oral Surgery9 pages
- Wound Management Principles and TechniquesNo ratings yetWound Management Principles and Techniques36 pages
- Coated VICRYL Suture Overview and SpecsNo ratings yetCoated VICRYL Suture Overview and Specs16 pages
- Introduction to Hand Embroidery TechniquesNo ratings yetIntroduction to Hand Embroidery Techniques25 pages