0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views2 pagesY 10 Math
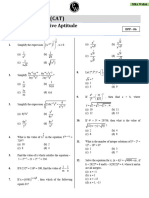
The document provides a series of exponential equations and their solutions, demonstrating various methods for solving for the variable x. It includes multiple examples with step-by-step calculations for different types of exponential equations. The solutions cover both basic and more complex equations, illustrating the application of exponent rules.
Uploaded by
rishitharaju.1207Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views2 pagesY 10 Math
The document provides a series of exponential equations and their solutions, demonstrating various methods for solving for the variable x. It includes multiple examples with step-by-step calculations for different types of exponential equations. The solutions cover both basic and more complex equations, illustrating the application of exponent rules.
Uploaded by
rishitharaju.1207Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd