0% found this document useful (0 votes)
103 views2 pagesRay Optics Notes JK
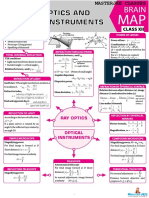
The document provides detailed notes on Ray Optics, covering key concepts such as reflection, refraction, spherical mirrors, and lenses. It includes laws, formulas, and applications, emphasizing the importance of sign conventions and diagram visualization. Additionally, it discusses optical instruments and the dispersion of light.
Uploaded by
Khan ShahenazCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
103 views2 pagesRay Optics Notes JK
The document provides detailed notes on Ray Optics, covering key concepts such as reflection, refraction, spherical mirrors, and lenses. It includes laws, formulas, and applications, emphasizing the importance of sign conventions and diagram visualization. Additionally, it discusses optical instruments and the dispersion of light.
Uploaded by
Khan ShahenazCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd