0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views4 pagesDocument Chem
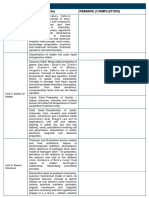
The document outlines important laws, rules, and definitions in chemistry, covering topics such as basic concepts, atomic structure, periodicity, chemical bonding, states of matter, thermodynamics, equilibrium, redox reactions, and organic chemistry. Key laws include the Law of Conservation of Mass, Dalton's Atomic Theory, and Boyle's Law, among others. It also discusses various types of hydrocarbons and their properties.
Uploaded by
shantanu0106Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views4 pagesDocument Chem
The document outlines important laws, rules, and definitions in chemistry, covering topics such as basic concepts, atomic structure, periodicity, chemical bonding, states of matter, thermodynamics, equilibrium, redox reactions, and organic chemistry. Key laws include the Law of Conservation of Mass, Dalton's Atomic Theory, and Boyle's Law, among others. It also discusses various types of hydrocarbons and their properties.
Uploaded by
shantanu0106Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd