0% found this document useful (0 votes)
304 views3 pagesDetailed Notes On Negation
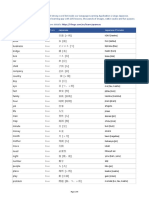
Negation in English grammar involves making statements negative using words like 'no', 'not', and 'never'. Key types of negative markers include negative adverbs, determiners, and pronouns, each serving different grammatical functions. Important rules include avoiding double negatives, using auxiliary verbs with 'not', and correctly applying 'no' versus 'not' in sentences.
Uploaded by
haramin1110Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
304 views3 pagesDetailed Notes On Negation
Negation in English grammar involves making statements negative using words like 'no', 'not', and 'never'. Key types of negative markers include negative adverbs, determiners, and pronouns, each serving different grammatical functions. Important rules include avoiding double negatives, using auxiliary verbs with 'not', and correctly applying 'no' versus 'not' in sentences.
Uploaded by
haramin1110Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd