0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesWith 5 Seperate PDF
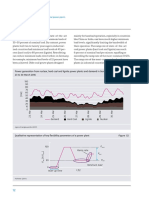
This research outlines significant advancements in renewable energy technologies, focusing on solar, wind, geothermal, hydropower, and bioenergy. It highlights breakthroughs in efficiency, cost reductions, and the implications for global energy transition and climate change mitigation. The document emphasizes the increasing competitiveness of renewable energy sources compared to fossil fuels and the importance of integrating these technologies into modern energy systems.
Uploaded by
phyominthant2217Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesWith 5 Seperate PDF
This research outlines significant advancements in renewable energy technologies, focusing on solar, wind, geothermal, hydropower, and bioenergy. It highlights breakthroughs in efficiency, cost reductions, and the implications for global energy transition and climate change mitigation. The document emphasizes the increasing competitiveness of renewable energy sources compared to fossil fuels and the importance of integrating these technologies into modern energy systems.
Uploaded by
phyominthant2217Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd