0% found this document useful (0 votes)
345 views3 pagesIBDP Biology - Questions
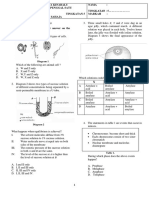
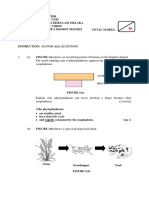
The document describes an experiment using dialysis bags to observe the effects of solute concentration changes on cells, specifically noting that the mass of the bag remains unchanged in isotonic conditions but decreases in hypertonic conditions after the addition of albumin. It also discusses the role of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in cells, explaining that while a cell can function temporarily without the ER, it cannot synthesize new ER, as organelles typically derive from pre-existing ones. The document concludes with an explanation of organelle synthesis and the exceptions of mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Uploaded by
debjani.bhattacharyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
345 views3 pagesIBDP Biology - Questions
The document describes an experiment using dialysis bags to observe the effects of solute concentration changes on cells, specifically noting that the mass of the bag remains unchanged in isotonic conditions but decreases in hypertonic conditions after the addition of albumin. It also discusses the role of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in cells, explaining that while a cell can function temporarily without the ER, it cannot synthesize new ER, as organelles typically derive from pre-existing ones. The document concludes with an explanation of organelle synthesis and the exceptions of mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Uploaded by
debjani.bhattacharyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd