0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views24 pagesVectors
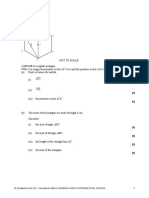
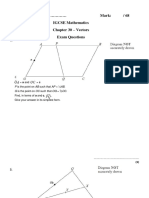
The document contains a series of mathematical problems involving vectors, coordinates, and geometry. It includes tasks such as finding midpoints, equations of lines, position vectors, and ratios within geometric shapes. Each problem is numbered and has designated spaces for answers, indicating a structured assessment format.
Uploaded by
Tety SuryaniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views24 pagesVectors
The document contains a series of mathematical problems involving vectors, coordinates, and geometry. It includes tasks such as finding midpoints, equations of lines, position vectors, and ratios within geometric shapes. Each problem is numbered and has designated spaces for answers, indicating a structured assessment format.
Uploaded by
Tety SuryaniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd