0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views2 pagesIP Subnetting
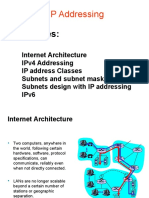
IP Subnetting is the method of dividing a network into smaller subnets to enhance performance and manageability. It involves understanding IP addressing, subnet masks, and CIDR notation, with examples provided for subnetting a given IP address. The benefits include better IP address utilization, improved network performance, and easier management and security.
Uploaded by
AtikCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views2 pagesIP Subnetting
IP Subnetting is the method of dividing a network into smaller subnets to enhance performance and manageability. It involves understanding IP addressing, subnet masks, and CIDR notation, with examples provided for subnetting a given IP address. The benefits include better IP address utilization, improved network performance, and easier management and security.
Uploaded by
AtikCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd