0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views10 pagesCSS Exp 1
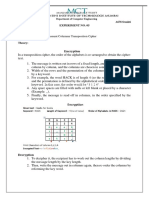
The document outlines the design and implementation of a product cipher using substitution and transposition techniques in encryption. It explains the concepts of substitution ciphers, including a monoalphabetic substitution algorithm, and transposition ciphers, detailing their encryption and decryption processes. Additionally, it provides sample code for both cipher types, demonstrating how to encrypt and decrypt messages using specified keys.
Uploaded by
Madhura KanseCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views10 pagesCSS Exp 1
The document outlines the design and implementation of a product cipher using substitution and transposition techniques in encryption. It explains the concepts of substitution ciphers, including a monoalphabetic substitution algorithm, and transposition ciphers, detailing their encryption and decryption processes. Additionally, it provides sample code for both cipher types, demonstrating how to encrypt and decrypt messages using specified keys.
Uploaded by
Madhura KanseCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd