0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles PDF
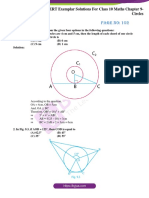
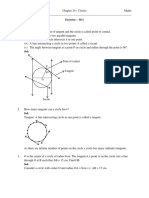
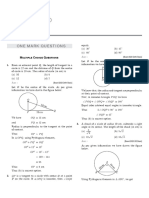
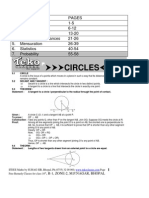
The document provides a series of questions and solutions related to the topic of circles from Class X Maths, specifically focusing on tangents, secants, and properties of circles. It includes exercises from NCERT books with detailed solutions using geometric principles and theorems. Key concepts covered include the number of tangents, properties of tangents and secants, and proofs related to tangents drawn from external points.
Uploaded by
priyankasharma946224Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Circles PDF
The document provides a series of questions and solutions related to the topic of circles from Class X Maths, specifically focusing on tangents, secants, and properties of circles. It includes exercises from NCERT books with detailed solutions using geometric principles and theorems. Key concepts covered include the number of tangents, properties of tangents and secants, and proofs related to tangents drawn from external points.
Uploaded by
priyankasharma946224Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd