0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views3 pagesNatural Vegetation
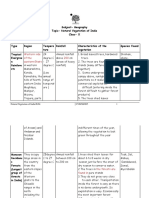
Natural vegetation consists of plants and trees that grow without human intervention and is crucial for ecological balance. Forests provide various products, protect soil, regulate water and carbon cycles, and offer habitats for wildlife. The document discusses different types of vegetation, their characteristics, the reasons for forest exploitation, conservation methods, and the concepts of social and agroforestry.
Uploaded by
Nandini tiwariCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views3 pagesNatural Vegetation
Natural vegetation consists of plants and trees that grow without human intervention and is crucial for ecological balance. Forests provide various products, protect soil, regulate water and carbon cycles, and offer habitats for wildlife. The document discusses different types of vegetation, their characteristics, the reasons for forest exploitation, conservation methods, and the concepts of social and agroforestry.
Uploaded by
Nandini tiwariCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd