0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views6 pagesCH 11
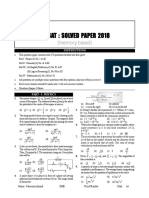
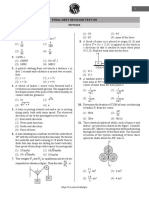
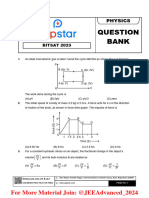
The document is a solved paper for the NEET 2013 exam, detailing the structure and rules of the test, which lasts 3 hours and consists of 180 questions with a total of 720 marks. It includes various physics questions with multiple-choice answers, covering topics such as projectile motion, forces, energy, and thermodynamics. Additionally, it outlines the scoring system, penalties for incorrect answers, and regulations regarding conduct during the examination.
Uploaded by
reeturaj378Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views6 pagesCH 11
The document is a solved paper for the NEET 2013 exam, detailing the structure and rules of the test, which lasts 3 hours and consists of 180 questions with a total of 720 marks. It includes various physics questions with multiple-choice answers, covering topics such as projectile motion, forces, energy, and thermodynamics. Additionally, it outlines the scoring system, penalties for incorrect answers, and regulations regarding conduct during the examination.
Uploaded by
reeturaj378Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd