0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views1 pageLiquefaction Analysis Steps
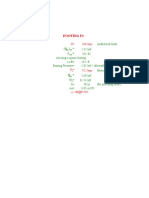
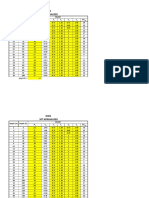
The document outlines the Liquefaction Analysis Procedure using the Seed & Idriss Method, detailing steps from gathering site and soil data to reporting results. Key calculations include total stress, pore water pressure, effective stress, cyclic stress ratio, and factor of safety to assess liquefaction risk. The procedure emphasizes the importance of empirical correlations and corrections for accurate analysis and recommendations based on findings.
Uploaded by
anuragrajtechproCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views1 pageLiquefaction Analysis Steps
The document outlines the Liquefaction Analysis Procedure using the Seed & Idriss Method, detailing steps from gathering site and soil data to reporting results. Key calculations include total stress, pore water pressure, effective stress, cyclic stress ratio, and factor of safety to assess liquefaction risk. The procedure emphasizes the importance of empirical correlations and corrections for accurate analysis and recommendations based on findings.
Uploaded by
anuragrajtechproCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd