0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesInflammatory Markers
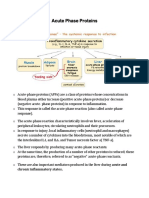
The document outlines various proteins and their changes in inflammation, highlighting their functions and clinical relevance. Key markers such as C-Reactive Protein and Serum Amyloid A increase during inflammation, while Albumin and Transferrin decrease. It also categorizes markers into acute and chronic types, detailing their significance in diagnosing infections and chronic diseases.
Uploaded by
imarairshad11Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesInflammatory Markers
The document outlines various proteins and their changes in inflammation, highlighting their functions and clinical relevance. Key markers such as C-Reactive Protein and Serum Amyloid A increase during inflammation, while Albumin and Transferrin decrease. It also categorizes markers into acute and chronic types, detailing their significance in diagnosing infections and chronic diseases.
Uploaded by
imarairshad11Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd