0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views27 pagesSession 2
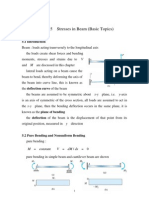
The document provides detailed calculations and formulas related to shock absorber performance, including ride rate, wheel rate, spring rate, static damper load, and natural frequency. It also covers concepts such as roll rate, roll couple, body roll angle, and damping coefficients, along with examples for practical application. Additionally, it discusses spring design parameters and includes a comprehensive example illustrating the calculations for a car's suspension system.
Uploaded by
Hazem TahaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views27 pagesSession 2
The document provides detailed calculations and formulas related to shock absorber performance, including ride rate, wheel rate, spring rate, static damper load, and natural frequency. It also covers concepts such as roll rate, roll couple, body roll angle, and damping coefficients, along with examples for practical application. Additionally, it discusses spring design parameters and includes a comprehensive example illustrating the calculations for a car's suspension system.
Uploaded by
Hazem TahaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd