0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views1 page16EARS
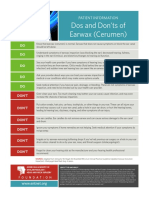
Earwax is beneficial for cleaning the ears and usually self-cleans, but blockage may require removal. Three methods for cleaning include using a cotton swab carefully, irrigating with warm water, and using eardrops, with the most effective method being a combination of softening drops followed by irrigation. Caution is advised to avoid damaging the ear canal or eardrum during cleaning.
Uploaded by
Tanvir Mahmood KamalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views1 page16EARS
Earwax is beneficial for cleaning the ears and usually self-cleans, but blockage may require removal. Three methods for cleaning include using a cotton swab carefully, irrigating with warm water, and using eardrops, with the most effective method being a combination of softening drops followed by irrigation. Caution is advised to avoid damaging the ear canal or eardrum during cleaning.
Uploaded by
Tanvir Mahmood KamalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd