0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views8 pagesLight - Grade 7
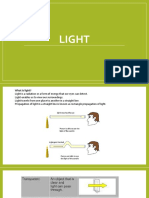
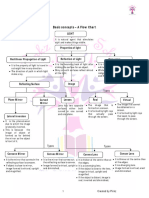
Light is a form of energy that travels in straight lines and can be classified based on its interaction with objects as transparent, translucent, or opaque. Reflection occurs when light bounces off surfaces, and images can be real or virtual depending on the type of mirror or lens used. The document also discusses the properties of spherical mirrors, lenses, and the dispersion of white light through a prism.
Uploaded by
dakshpersonal2024Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views8 pagesLight - Grade 7
Light is a form of energy that travels in straight lines and can be classified based on its interaction with objects as transparent, translucent, or opaque. Reflection occurs when light bounces off surfaces, and images can be real or virtual depending on the type of mirror or lens used. The document also discusses the properties of spherical mirrors, lenses, and the dispersion of white light through a prism.
Uploaded by
dakshpersonal2024Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd