Introduction to Information &
adffsdsdvsds
Communication Technology (CSC-114)
2
Lecture-3:
Processing & Storing Data
dasbhchasdfdbvsdhv
Instructor: Faisal Asad ur Rehman
ascascbasdkcbashkcba
Department of Computer Science
ashcbashcashcashcbasch
Bahria University, Islamabad
� Looking Inside
Computers
Skill Development
�Hardware input devices
Skill Development
�CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Skill Development
�CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The inside of the system unit on a desktop personal computer
includes
Skill Development
� Mother Board
The motherboard is the main circuit
board of the system unit
– A computer chip contains integrated circuits
Skill Development
�Processor
The processor, also called the central processing unit (CPU), interprets
and carries out the basic instructions that operate a computer
Contain a control unit and an arithmetic logic unit(ALU)
Skill Development
��Processor
• The processor contains registers, that temporarily hold data and
instructions
• The system clock controls the timing of all computer operations
• The pace of the system clock is called the clock speed, and is
measured in gigahertz (GHz)
Skill Development
� Processor
• The processor, also called the central processing unit (CPU), interprets
and carries out the basic
• instructions that operate a computer Contain a control unit and an
arithmetic logic unit (ALU)
Multi-core Processor
Dual-core Processor Quad-core processor
A multi-core processor is a computer processor
A dual-core processor is a CPU with A quad-core processor is
integrated circuit with two or more separate
two processors or "execution cores" a chip with four independent
processing units, called cores.
in the same integrated circuit. units called cores
Skill Development
�Multicore
Skill Development
�Skill Development
�Latest Processor
Up to 8 cores
Skill Development
�Memory
• Memory consists of electronic components that store instructions
waiting to be executed by the processor.
• Data needed by those instructions, and the results of processing the
data
Skill Development
�Memory
• The system unit contains two types of memory:
Volatile memory Nonvolatile memory
Does not lose contents
Loses its contents when when power is removed
power is turned off Examples include
Example includes RAM ROM, flash memory, and
CMOS
Skill Development
�Memory
• The amount of RAM necessary in a computer often depends on the
types of software you plan
• to use
Skill Development
�Expansion Slots and Adapter Cards
• With Plug and Play, the computer automatically can configure
adapter cards and other peripherals as you install them
Skill Development
�Expansion Slots and Adapter Cards
• Removable flash memory includes: Memory cards, USB flash drives,
and PC Cards/Express Card modules
Skill Development
�Ports and Connectors
• A port is the point at which a peripheral attaches to or communicates
with a system unit (sometimes referred to as a jack)
• A connector joins a cable to a port
Skill Development
�Ports and Connectors
Skill Development
�Skill Development
�Bays
• A bay is an opening inside the system unit in
which you can install additional equipment
• A drive bay typically holds disk drives
Skill Development
� Input/output
Devices
Skill Development
�Keyboard
• Most Common Input Device
• Usually connected by cable, but can be wireless
• Standardized layouts: First six letters of first row, i.e., QWERTY
• Alternative layouts: Alphabetic and Dvorak keyboard layouts
• Keyboard Keys: Functional, Cursor, Modifiers, Alphanumeric keys.
Skill Development
�Keyboard Keys
• Function Keys: F1, F2, F3
• Input of commands
• Function depend on program in use
• Allows you to input commands without typing long strings of characters or
navigating menus or dialog boxes, i.e., F1 is for help
• Cursor Keys:
• Four keys (up, down, left, right) on keyboard
• Positioning within lists (menus), spread sheets etc
• Basic motion for text-editing tasks
Skill Development
�Keyboard Keys
• Modifier Keys: Shift, Alt, Ctrl (modify input of other keys)Input of commands
• If you hold down the modifier key while pressing another key, the input of second key
changes.
• Example: J and Shift+J
• Alphanumeric keys: Tab, Caps Lock, Back Space, Enter, Letters and numbers
Skill Development
�Keyboard Layout
• Standardized layout:
• Non-alphanumeric keys are placed differently
• Accented symbols of different scripts
• QWERTY arrangement optimal for typing
• Layout to prevent typewriters jamming
Skill Development
�Keyboard Layout
• Alphabetic Layout:
• Keys are arranged in alphabetic order
• Not faster for trained typist
• Not faster for beginners either
Skill Development
�Keyboard Layout
• Dvorak Keyboard.
• Common letters under dominant fingers
• Vowels and the most used symbol characters are on the left, while the most used consonants are on
the right
• Biased towards right hand
• Common combinations of letters alternate between hands
• 10-15% improvement in speed and reduction in fatigue
Skill Development
�Ergonomics
• Ergonomics is the science of designing the job equipment, and workplace to work
properly with human body and reducing the risk of strain and injuries
• Ergonomics involves arranging the environment to fit the person in it
• Ergonomic Design/Products
• Easy to use and comfortable
• Reduce fatigue, strain
• Enhance productivity
Skill Development
�Skill Development
�Repetitive Strain Injuries (RSI)
• Result from continuously using the body in ways it was not designed to work
• Wrist or hand injury caused by using a keyboard for long periods of time
• Tips to avoid RSI
• Use an Ergonomic keyboard
• Use a padded wrist support
• Sit up straight
• Learn to type`
• Take frequent breaks
Skill Development
�Ergonomic Keyboard
Skill Development
�Mouse
• Handheld pointing device
• Very Common
• Easy to use
• Buttons
• Usually from 1 to 3 buttons on top, used for making a selection, indicating an
option, or to initiate drawing etc. Relative movement is detected
• Mapping transformation
• Left/right movement: Direct mapping
• Up/down movement: Away/towards the user
Skill Development
�Mouse
• Two methods for detecting movement
• Mechanical
• Ball on underside of mouse turns as mouse is moved
• Optical
• Light emitting diode on underside of mouse
• Less susceptible to dust and dirt
• Detects fluctuating alterations in reflected light intensity to calculate relative
motion
Skill Development
�Types…
• Foot Mouse:
• Controlling mouse movement with feet
• E.g. Car pedals, sewing machines, Organ and piano pedals
• Touch pads:
• Small touch sensitive tablets
• Finger strokes to move mouse pointer
• Used in Laptops
• Track ball:
• Ball is rotated inside static housing, Like an upside down mouse
• Relative motion moves cursor
• Separate buttons for picking
• hard to draw
• Long movements are difficult
• Joystick:
• Movement of stick defines movement of cursor
Skill Development
�Cont…
• Touch Screens:
• Detect the presence of finger or stylus on the screen
• Direct pointing device
• E.g. ATM, Ticketing machines, Smart Phones
• Stylus & Light Pen:
• Stylus: Small Pen-like pointer to draw directly on screen, used in PDA, tablet and drawing
table
• Pen: uses light from screen to detect location
• Eye Gaze Devices:
• Control interface by eye gaze direction
• E.g. Look at menu item to select it
• Uses Laser Beam reflected off retina
Skill Development
�Skill Development
�Optical Input Devices
• Bar Code Reader
• Supermarkets and departmental stores
• FedEx, DHL etc. to identify packets
• Bar Code: Pattern of printed bars
• Reader emits a laser light, reflection received by a detector that identifies the code
• Scanner
• Takes paper and converts it into a bitmap
• Two sorts of scanner: Flat-bed and Hand-held
• Useful in Document storage and retrieval systems, doing away with paper storage
• Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Converts Bitmap into text
Skill Development
�Output Devices
• Display Device Technology
• Cathode Ray Tube
• Television Screens & Computer Monitors
• Stream of electrons emitted from electron gun, focused and directed by magnetic fields,
hit phosphor-coated screen which glows
• Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
• Form of visual display used in electronic devices, in which a layer of a liquid crystal is
sandwiched between two transparent electrodes.
• PDAs, Notebooks etc
• Increasingly for desktop and home Tv
• Smaller and lighter
• Layer of liquid crystal b/w two glass plates
Skill Development
�Output Devices
• Display Device Technology
• Video Card
• Video Controller or video adapter
• Sends information to the monitor for display
• Built directly into motherboard or as a separate card
• Sound System
• Video Card
• Converts analog sound to digital and vice versa
• Recording and playback
Skill Development
�Processing & Storing Data
Skill Development
�Information Cycle
Skill Development
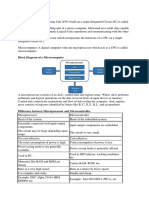
�Processing of Data
• Central Processing Unit
• Control Unit
• Arithmetic Logic Unit
Skill Development
�Roles of CPU
• To perform Arithmetic calculation operation
• To perform Logical Operations
• To control functions of other hardware components
• To fetch the data and program instructions from main memory
• To operate on the data as per program instructions
• To store processed data into RAM
• To continuously execute machine / information cycle.
Skill Development
�Control Unit
• Directs and co-ordinates most of the computer operations, i,e., directs computer
memory, arithmetic and logic unit, input and output devices.
• Decides how to respond to program instruction during execution of program.
• Directs flow of data between CPU and other devices, i.e., main memory and CPU.
• Four Basic Operations
• Fetch: Obtain a program instruction or data item from memory
• Decode: Translates instructions into command.
• Execute: Carry out command, this part is performed by ALU
• Store: Write result into memory
Skill Development
�Machine Cycle & Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
• Four operations of control unit comprise of a machine cycle.
• Also known as instruction cycle
• Instruction time: Time to fetch and decode.
• Execution time: Time to execute and store.
• Execution part of machine cycle is performed by Arithmetic Logic Unit.
Skill Development
�How CPU Executes Instruction?
Skill Development
�CPU registers
• Temporary storage location used by CPU and holds the data which CPU is
currently processing.
• High speed memory in CPU that stores
• Instruction while being decoded
• Location from where instruction was fetched
• Data while the ALU processes it
• Results of a calculation
Skill Development
�Cache Levels
• Holds frequently used data & instructions during program. execution.
• L1 ( 2kB - 64KB ), L2 ( 256KB - 512KB ) and L3 ( 1MB - 8MB ).
Skill Development
�System Clock
• Synchronizes all CPU operations
• Faster clock speed means the CPU can execute more instructions each second
• Units: MHz and GHz
Skill Development
�CPU Time
• The time which processor spends on executing piece of software
• CPU Time can be executed as:
Skill Development
�CPU Time Examples
Skill Development
�Cycles Per Instructions (CPI)
Skill Development
�Comparing Machines
Skill Development
�CPU Architecture
• CISC: Complex instruction set computing
• Complex instruction, hence complex instruction decoding.
• Instruction are larger than one word size.
• Instruction may take more than single clock cycle to get executed.
• RISC: Reduced instruction set computing
• Simpler instruction, hence simple instruction decoding.
• Instruction come under size of one word.
• Instruction take single clock cycle to get executed.
Skill Development
�Parallel Processing
• Multiple processors simultaneously execute a program
• Requires special software to divide up a problem and bring the results back
Skill Development