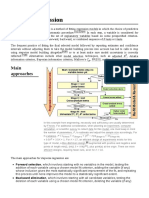
What is stepwise regression?
Stepwise regression is an automated tool used in the exploratory stages of model building to
identify a useful subset of predictors. The process systematically adds the most significant
variable or removes the least significant variable during each step.
Understanding Stepwise Regression
Stepwise regression is achievable in two ways; 1. by trying out various independent variables,
one at a time, by incorporating them in the regression model 2. Incorporating all the potential
independent variable in the regression model and filtering out those that are not significant.
Forward selection, which involves starting with no variables in the model, testing the addition
of each variable using a chosen model fit criterion, adding the variable (if any) whose inclusion
gives the most statistically significant improvement of the fit, and repeating this process until
none improves the model to a statistically significant extent.
Backward elimination, which involves starting with all candidate variables, testing the deletion
of each variable using a chosen model fit criterion, deleting the variable (if any) whose loss
gives the most statistically insignificant deterioration of the model fit, and repeating this process
until no further variables can be deleted without a statistically significant loss of fit.
Stepwise regression. In deciding on the “best” set of explanatory variables for a regression
model, researchers often follow the method of stepwise regression. In this method one proceeds
either by introducing the X variables one at a time (stepwise forward regression) or by including
all the possible X variables in one multiple regression and rejecting them one at a time (stepwise
backward regression). The decision to add or drop a variable is usually made on the basis of the
contribution of that variable to the ESS, as judged by the F test.
Stepwise regression is defined as a step-by-step construction of a regression model that includes
an automatic selection of variables that are independent. The basic concept is to collect
information that is relevant to arrive at an informed decision which is a very common tradition
followed in the world of investment.
The stepwise regression is a detailed step-by-step repeated building of a regression system which
is involving an automatic choice of variables that are independent. The availability of statistical
software modules has made stepwise regression a possibility even when there are several
hundreds of independent variables.
Stepwise regression is a semi-automated process of building a model by successively adding or
removing variables based solely on the t-statistics of their estimated coefficients. Properly used,
the stepwise regression option in Statgraphics (or other stat packages) puts more power and
information at your fingertips than does the ordinary multiple regression option, and it is
especially useful for sifting through large numbers of potential independent variables and/or fine-
tuning a model by poking variables in or out. Improperly used, it may converge on a poor model
while giving you a false sense of security. It's like doing carpentry with a chain saw: you can get
a lot of work done quickly, but it leaves rough edges and you may end up cutting off your own
foot if you don't read the instructions, remain sober, engage your brain, and keep a firm grip on
the controls. It is not a tool for beginners or a substitute for education and experience.
How it works: Suppose you have some set of potential independent variables from which you
wish to try to extract the best subset for use in your forecasting model. (These are the variables
you will select on the initial input screen.) The stepwise option lets you either begin
with no variables in the model and proceed forward (adding one variable at a time), or start
with all potential variables in the model and proceed backward (removing one variable at a
time). At each step, the program performs the following calculations: for each variable
currently in the model, it computes the t-statistic for its estimated coefficient, squares it, and
reports this as its "F-to-remove" statistic; for each variable not in the model, it computes the t-
statistic that its coefficient would have if it were the next variable added, squares it, and reports
this as its "F-to-enter" statistic. At the next step, the program automatically enters the variable
with the highest F-to-enter statistic, or removes the variable with the lowest F-to-remove
statistic, in accordance with certain control parameters you have specified. So the key relation to
remember is: F = t-squared