0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views10 pagesM S Gowrish Shankar Reddy (Transmission Media)
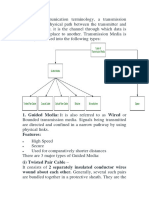
The document discusses transmission media, which are the physical paths for conveying data and signals, categorized into guided (wired) and unguided (wireless) types. It details various types of guided media such as twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and fiber optic cables, along with their characteristics, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. Additionally, it covers unguided media including radio waves, microwaves, infrared, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth, highlighting their features and uses.
Uploaded by
guggillavsaiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views10 pagesM S Gowrish Shankar Reddy (Transmission Media)
The document discusses transmission media, which are the physical paths for conveying data and signals, categorized into guided (wired) and unguided (wireless) types. It details various types of guided media such as twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and fiber optic cables, along with their characteristics, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. Additionally, it covers unguided media including radio waves, microwaves, infrared, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth, highlighting their features and uses.
Uploaded by
guggillavsaiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd