Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transmission Media Types
Uploaded by
Omkar ThangeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transmission Media Types
Uploaded by
Omkar ThangeCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment No.
1
Title:
Transmission medium and its types.
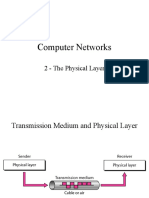
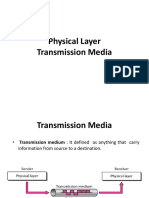
Transmission medium:
Definition:
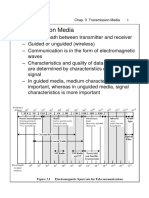
Transmission medium is a physical path between the transmitter and the receiver.
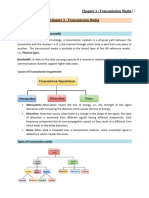
Transmission Medium is broadly classified into the following types:
Transmission
Media
Ungided
Guided media
media
Fibre Twisted Radio- Microwaves
Coaxial optics pair waves Infrarred
Unshielded Shielded
1) Guided Media
• Wired or Bounded transmission media.
• Physical medium through which the signals are transmitted.
• As the path traversed by the signals is guided by the size, shape and length of the
wire, this type of media is called guided media.
There are three major types of Guided Media:
1. Twisted pair cable
• Pair of cables twisted with each other.
• Cheap as compared to other transmission media.
• Installation is easy, and it is a lightweight cable.
• Frequency range: 0 to 3.5 kHz.
Types of Twisted pair:
1) Unshielded Twisted Pair: It is
widely used in telecommunication.
2) Shielded Twisted Pair: It is a cable
that contains the mesh surrounding
the wire that allows the higher
transmission rate.
2. Coaxial Cable
• Commonly used transmission media, E.g.,
TV wire.
• The name of the cable is coaxial, as it
contains two conductors parallel to each
other.
• Higher frequency as compared to twisted pair
cable.
• Types:
1) Baseband transmission: Process of transmitting a single signal at high speed.
2) Broadband transmission: Process of transmitting multiple signals
simultaneously.
3. Fibre Optic cable
• It uses electrical signals for communication.
• It holds the optical fibres coated in plastic that are used to send the data by pulses of
light.
• Provides faster data transmission than copper wires.
2) Unguided Media
• Wireless or Unbounded transmission.
• It transmits the electromagnetic waves without using any physical medium.
• In this, air is the media through which the electromagnetic energy can flow easily.
Unguided transmission is broadly classified into three categories:
1. Radiowaves
• Electromagnetic waves that are transmitted in all the directions of free space.
Example is FM radio.
• Omnidirectional, i.e., the
signals are propagated in all the
directions.
• Frequency Range: 3 KHz to 1
kHz.
• Sending and receiving antenna
are not aligned. i.e., wave sent
by the sending antenna can be
received by any receiving
antenna.
• Further Categorized as: (i)
Terrestrial and (ii) Satellite.
2. Microwaves
• Line of sight transmission i.e. the sending
and receiving antennas need to be properly
aligned with each other.
• Frequency Range: 1GHz – 300GHz.
• Majorly used for mobile phone
communication and television distribution.
3. Infrared
• Wireless technology used for
communication over short ranges.
• Frequency range: 300 GHz to 400 THz.
• Applications: Data transfer between two
cell phones or between computer & cell
phone which resides in the same closed area,
TV remotes and wireless mouse.
You might also like
- Week 06 LecturesDocument49 pagesWeek 06 LecturesHamzah AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Microwave and Wireless Communications TechnologyFrom EverandMicrowave and Wireless Communications TechnologyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Signals and transmission mediaDocument108 pagesSignals and transmission mediaDeepakPradhan100% (1)
- Transmission MediaDocument6 pagesTransmission Mediamahar.nomi1039No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Cellular Coverage of Wireless NetworksDocument23 pagesChapter 2 - Cellular Coverage of Wireless Networksmichellegichuhi94No ratings yet
- Types of Transmission Mediums in Computer NetworksDocument9 pagesTypes of Transmission Mediums in Computer Networkssahan instituteNo ratings yet
- Lec. 2 - Physical Layer - Cont.Document33 pagesLec. 2 - Physical Layer - Cont.MUHAMMAD RAHEEL BSSE-FA20-100No ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer NetworksDocument14 pagesData Communication and Computer NetworksFikir tube100% (1)
- Transmission Modes: Student - Feedback@sti - EduDocument4 pagesTransmission Modes: Student - Feedback@sti - EduKiervin LandarNo ratings yet
- Transmission Medium: Dept. of Electronics and CommunicationDocument37 pagesTransmission Medium: Dept. of Electronics and CommunicationNISHANT395No ratings yet
- Communication 3, EEC 242, Chapter 1, Part BDocument16 pagesCommunication 3, EEC 242, Chapter 1, Part BBahaa MadeehNo ratings yet
- LESSON-5Document22 pagesLESSON-5Laila EbezaNo ratings yet
- Guided vs unguided transmission mediaDocument7 pagesGuided vs unguided transmission mediaMehwish SabirNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument32 pagesTransmission MediaAshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Course Outcomes and Network FundamentalsDocument41 pagesCourse Outcomes and Network FundamentalsmondyNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument10 pagesTransmission Mediasarthak pasrichaNo ratings yet
- DC-Lec-22 (Unguided Media)Document27 pagesDC-Lec-22 (Unguided Media)Farman AfridiNo ratings yet
- ISDN (Integrated Services DigitalDocument47 pagesISDN (Integrated Services DigitalPriyadarshini PatilNo ratings yet
- CN LP U1 T5Document22 pagesCN LP U1 T5etasureshNo ratings yet
- Physical LayerDocument30 pagesPhysical LayerVaishu GoudNo ratings yet
- Wireless Data Communication Networks: Fundamentals of Wireless CommunicationsDocument37 pagesWireless Data Communication Networks: Fundamentals of Wireless Communicationsclaude bangoNo ratings yet
- DCC Unit 2Document39 pagesDCC Unit 2Raj DebadwarNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media Computer NetworkDocument25 pagesTransmission Media Computer Networkالزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument39 pagesTransmission MediaKeyur MahantNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3_networkingDocument9 pagesChapter 3_networkingninjamekwan10No ratings yet
- Network CH 2Document27 pagesNetwork CH 2Aashutosh VyasNo ratings yet
- Data TransmissionDocument7 pagesData Transmissionantonially24No ratings yet
- Transmission Media Types and UsesDocument55 pagesTransmission Media Types and UsesNayan PatilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document12 pagesLesson 4Kean Rafael MarianoNo ratings yet
- Networking Transmission MediaDocument42 pagesNetworking Transmission MediaMaxwell KoomsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Transmission Media and Switching (Total Marks-14)Document38 pagesUnit 2: Transmission Media and Switching (Total Marks-14)shubhamNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Computer Network Topic:-Transmission Media: Subtopic:-Guided Media Unguided MediaDocument11 pagesPresentation On Computer Network Topic:-Transmission Media: Subtopic:-Guided Media Unguided Mediakn_949127469No ratings yet
- CS480 Wireless TransmissionDocument64 pagesCS480 Wireless TransmissionTantrum_5No ratings yet
- M1 AnswersDocument3 pagesM1 AnswersUvuvwevwevwe Onyetenyevwe Ugwemubwem OsasNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: by Anwesha ParidaDocument7 pagesComputer Networks: by Anwesha ParidaAnwesha ParidaNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Transmission MediaDocument76 pages1.8 Transmission Media19epci002 Akhil SNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Transmission MediaDocument20 pagesComputer Network Transmission MediaLeslene LaingNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media 2Document2 pagesTransmission Media 2Manu KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument31 pagesTransmission Mediahadirehman488No ratings yet
- Transmission Media NewDocument38 pagesTransmission Media NewAshutosh PatelNo ratings yet
- Cs 480: Mobile Networks: Lecture PowerpointsDocument54 pagesCs 480: Mobile Networks: Lecture PowerpointsTigerNo ratings yet
- Subject Title: Principles of Communication SystemsDocument29 pagesSubject Title: Principles of Communication SystemsMadrick Ace VillaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks FundamentalsDocument374 pagesWireless Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks FundamentalsMadhavan Sam0% (1)
- ICT Note For Grade 10Document5 pagesICT Note For Grade 10Sosina TilahunNo ratings yet
- MC - Unit 1-2022-23 - 13-2-2023Document19 pagesMC - Unit 1-2022-23 - 13-2-2023ammulove1303No ratings yet
- WCN-Wireless Communications and NetworksDocument18 pagesWCN-Wireless Communications and Networkslaiba noorNo ratings yet
- Telecommunications and NetworksDocument35 pagesTelecommunications and NetworksManish ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 04-transmissionmediaDocument38 pages04-transmissionmedia22520101No ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument35 pagesComputer NetworkSamyuktaAdepuNo ratings yet
- Telecommunications and NetworksDocument35 pagesTelecommunications and NetworksFarel KawilarangNo ratings yet
- DATA TRANSMISSION NotesDocument6 pagesDATA TRANSMISSION NotesTinashe BetaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Media: Transmission MediumDocument13 pagesDifferent Types of Media: Transmission MediumParvesh RishieNo ratings yet
- Chap. 3 Transmission Media 1Document11 pagesChap. 3 Transmission Media 1chaa2014No ratings yet
- Ch 20B - Communicating InformationDocument32 pagesCh 20B - Communicating InformationOKAY JAROD PUGNo ratings yet
- 2SCS3105 Wireless Media - DOC TWODocument11 pages2SCS3105 Wireless Media - DOC TWOmuhwezi jonasNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media CIS748 Class Notes: Alex SDocument5 pagesTransmission Media CIS748 Class Notes: Alex SAxel Ernesto AxelNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media:: A Transmission Medium Can Be Broadly Defined As Anything That Can Carry InformationDocument5 pagesTransmission Media:: A Transmission Medium Can Be Broadly Defined As Anything That Can Carry InformationKanwal TariqNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument39 pagesTransmission Mediachabdulmanan8953No ratings yet
- Dbms Assignment 4Document5 pagesDbms Assignment 4Omkar ThangeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (SPOS) EditedDocument12 pagesAssignment 2 (SPOS) EditedOmkar ThangeNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media TypesDocument3 pagesTransmission Media TypesOmkar ThangeNo ratings yet
- System Programming and Operating System Pass-IIDocument11 pagesSystem Programming and Operating System Pass-IIOmkar ThangeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (SPOS) EditedDocument12 pagesAssignment 2 (SPOS) EditedOmkar Thange100% (1)
- System Programming and Operating System Pass-IIDocument11 pagesSystem Programming and Operating System Pass-IIOmkar ThangeNo ratings yet
- Design of Beam Slide ShareDocument26 pagesDesign of Beam Slide ShareVRKVRK10No ratings yet
- Uk Exs Xl-Series DsDocument4 pagesUk Exs Xl-Series DsAndzar Muhammad FauziNo ratings yet
- FINISH CEILING AND FLOORS Chapter 24Document22 pagesFINISH CEILING AND FLOORS Chapter 24Jonaisa CasanguanNo ratings yet
- ExcavatorDocument2 pagesExcavatorHelar W. Cutipa Machaca50% (2)
- Astm A135Document9 pagesAstm A135banglvhNo ratings yet
- Roof Mounted Smoke Extraction FanDocument7 pagesRoof Mounted Smoke Extraction FanIgor SpirovNo ratings yet
- Concentration of SolutionsDocument42 pagesConcentration of SolutionsAien RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 6ED1052-1FB00-0BA6: Supply VoltageDocument2 pagesData Sheet 6ED1052-1FB00-0BA6: Supply VoltageTrong Hung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ieee Guide For Evaluating The Effect of Solar Radiation On OutdoDocument25 pagesIeee Guide For Evaluating The Effect of Solar Radiation On OutdoIbrahim EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Intensifying ScreenDocument20 pagesIntensifying ScreenLyht TVNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Career ObjectiveDocument5 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Career ObjectiveRavi Shankar ChakravortyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Composite Materials-4 ModuleDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Composite Materials-4 Modulegagan devarajNo ratings yet
- Dual High Broadband AntennaDocument2 pagesDual High Broadband AntennaРоманКочневNo ratings yet
- Meshing Benchmark - Nov 2019Document7 pagesMeshing Benchmark - Nov 2019sitipaniNo ratings yet
- Sa-Ak970 Md0806005ceDocument143 pagesSa-Ak970 Md0806005cearturo ortegaNo ratings yet
- Test Za 6 Odd Za Vtoro Polugodie 2Document3 pagesTest Za 6 Odd Za Vtoro Polugodie 2martin nikolovskiNo ratings yet
- Measure Acceleration of Free FallDocument4 pagesMeasure Acceleration of Free FallVictor CoronelNo ratings yet
- Reynolds Experiment PDFDocument8 pagesReynolds Experiment PDFali najatNo ratings yet
- Series H20: DynaparDocument4 pagesSeries H20: DynaparJULIAN ANDRES ROJASNo ratings yet
- Prepp - In-Preparation Strategy For IAS UPSC CSE Electrical Engineering OptionalDocument6 pagesPrepp - In-Preparation Strategy For IAS UPSC CSE Electrical Engineering Optionalmojo xoxoNo ratings yet
- BEE Assignment Even 2020Document5 pagesBEE Assignment Even 2020Aditya PatelNo ratings yet
- Tower-Sens LB 490 Rod Detector Measures Levels Over 8 MetersDocument2 pagesTower-Sens LB 490 Rod Detector Measures Levels Over 8 MetersBudi PrihartonoNo ratings yet
- Legendre's Linear EquationsDocument3 pagesLegendre's Linear Equationscoder.sanjNo ratings yet
- 9 RayopticsDocument8 pages9 RayopticsViredra Vikash C MNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة 2023-02-02 في 11.30.55 ص PDFDocument50 pagesلقطة شاشة 2023-02-02 في 11.30.55 ص PDFFaisal AlhiallNo ratings yet
- Zn-Mg-Al Corrosion analysis paperDocument12 pagesZn-Mg-Al Corrosion analysis paperrahul.meenaNo ratings yet
- Volume 2 Highways Structures: Design (Substructures and Special Structures), Materials Section 2 Special StructuresDocument86 pagesVolume 2 Highways Structures: Design (Substructures and Special Structures), Materials Section 2 Special Structuresgeorge santiagoNo ratings yet
- MCQs Question of Surveying 1Document9 pagesMCQs Question of Surveying 1jamil ahmedNo ratings yet
- Kabelmetal NYYDocument1 pageKabelmetal NYYDudi MulyadiNo ratings yet
- Tarea 3 TermodinamicaDocument3 pagesTarea 3 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezNo ratings yet