0% found this document useful (0 votes)
487 views2 pagesGD&T Interview Questions Answers
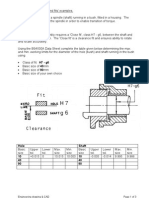
GD&T, or Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing, is a symbolic language used in engineering to define allowable variations in part geometry, ensuring functional requirements and improving design clarity. Key components include geometric characteristic symbols, tolerance values, and datum references, with various types of geometric tolerances such as form and orientation. Important concepts include Maximum Material Condition (MMC), Least Material Condition (LMC), bonus tolerance, and distinctions between position, concentricity, runout, and total runout.
Uploaded by
ankamraojCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
487 views2 pagesGD&T Interview Questions Answers
GD&T, or Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing, is a symbolic language used in engineering to define allowable variations in part geometry, ensuring functional requirements and improving design clarity. Key components include geometric characteristic symbols, tolerance values, and datum references, with various types of geometric tolerances such as form and orientation. Important concepts include Maximum Material Condition (MMC), Least Material Condition (LMC), bonus tolerance, and distinctions between position, concentricity, runout, and total runout.
Uploaded by
ankamraojCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd