0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesStretch and Shear
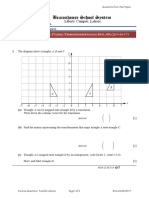
The document outlines various geometric transformations, specifically stretching and shearing, applied to triangles and rectangles. It includes instructions for stretching triangles A, B, J, D, F, H, and L, as well as describing shear transformations for rectangles E, G, I, M, and mapping transformations for other triangles. Each transformation is defined by a scale factor and an invariant line.
Uploaded by
praisemilitsaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesStretch and Shear
The document outlines various geometric transformations, specifically stretching and shearing, applied to triangles and rectangles. It includes instructions for stretching triangles A, B, J, D, F, H, and L, as well as describing shear transformations for rectangles E, G, I, M, and mapping transformations for other triangles. Each transformation is defined by a scale factor and an invariant line.
Uploaded by
praisemilitsaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd