0% found this document useful (0 votes)
354 views31 pagesQuestion's
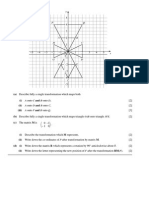
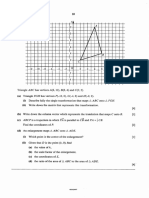
This document contains 4 geometry problems involving transformations of triangles. [1] The first problem asks the reader to describe a single transformation that maps triangle XYZ onto triangle XPQ, and provides the vectors for a translation. [2] The second problem involves finding the coordinates of a point Q after a translation maps a triangle A onto triangle B, describing a transformation that maps triangle A onto triangle C, and drawing and labeling a new triangle D after a given shear. [3] The third problem describes a transformation that maps triangle CAB onto triangle CDE and calculates a vector. [4] The final problem involves finding coordinates related to reflections and rotations of triangles A, B, and C, drawing a new triangle D after a given transformation
Uploaded by
Elie aCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
354 views31 pagesQuestion's
This document contains 4 geometry problems involving transformations of triangles. [1] The first problem asks the reader to describe a single transformation that maps triangle XYZ onto triangle XPQ, and provides the vectors for a translation. [2] The second problem involves finding the coordinates of a point Q after a translation maps a triangle A onto triangle B, describing a transformation that maps triangle A onto triangle C, and drawing and labeling a new triangle D after a given shear. [3] The third problem describes a transformation that maps triangle CAB onto triangle CDE and calculates a vector. [4] The final problem involves finding coordinates related to reflections and rotations of triangles A, B, and C, drawing a new triangle D after a given transformation
Uploaded by
Elie aCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Transformations: An introduction covering fundamental concepts behind transformation questions in the context of O Level mathematics.
- Transformation Problem 1: Problem involving mapping of one set of points and triangles onto another using transformations.
- Transformation Problem 2: Explores transformations through translation, rotation, and other matrix operations on geometric figures.
- Transformation Problem 3: Examines transformation mappings among multiple triangles using linear equations.
- Transformation Problem 4: Problem focuses on transformations and finding specific points after the transformations.
- Transformation Problem 5: Introduces complex transformations that involve matrices and rotational mechanics.
- Transformation Problem 6: Explores scale transformations and the calculations of transformation centers.
- Transformation Problem 7: Problem entails calculating matrices and geometric translations within a plane.
- Transformation Problem 8: Emphasizes rotational and translational transformations on geometric shapes.
- Transformation Problem 9: Details vector transformations and scale alterations on basic geometries.
- Transformation Problem 10: Challenges involve enlargements and rotatable transformations of triangle sets.
- Transformation Problem 11: Involves solving for matrix transformations and angle of alterations in plane geometry.
- Transformation Problem 12: Engages transformations through extensions and rotational pivoting involving triangle enlargements.
- Transformation Problem 13: Linear transformations and inverse finding focus in mathematical contexts.
- Transformation Problem 14: Problem involving matrix representations of transformations and their impacts.
- Transformation Problem 16: Addressing sub-transformations involving translations, rotations and enlargements on triangles.
- Transformation Problem 15: Analyzes transformations from coordinates to angled areas in triangle settings.
- Transformation Problem 17: Geometric transformations challenge focusing on reflection and rotational calculations.
- Transformation Problem 18: Investigates linear transformations and calculations of geometric center points.
- Transformation Problem 19: Emphasizes the use of transformational matrices in a geometric problem context.
- Transformation Problem 20: Complex transformation problem analyzing effects on geometric shapes through various transformations.
- Transformation Problem 21: Involves mappings and rotations of points within quadrant setups of transformations.
- Transformation Problem 22: Details shear transformations and matrix inverse calculations within geometric frames.
- Transformation Problem 23: Continues investigation into matrix-based transformations and modular triangle modifications.
- Transformation Problem 24: Comprehensive set of transformation tasks using matrices for complex geometry problems.
- Transformation Problem 25: Final assessment of transformations through enlargements and matrix articulation.
- Transformation Problem 27: Investigates rotations and stretch factors in enhancing geometric transformations.
- Transformation Problem 26: Integrating various transformation principles into problem-solving exercises.
- Transformation Problem 28: Engages with coordinate-based exercises in transformation problems for linear geometries.