CONSUMER DECISION MAKING PROCESS
Prepared by Eric (nobody) from nowhere
�LEARNING OBJECTIVES
1. Explain why marketing managers should understand consumer behavior.
2. Analyze the components of the consumer decision-making process.
3. Explain the consumers post-purchase evaluation process.
2
�LEARNING OBJECTIVES (CONTINUED)
4. Identify the types of consumer buying decisions and discuss the significance of consumer involvement.
5. Identify and understand the cultural factors that affect consumer buying decisions.
�LEARNING OBJECTIVES (CONTINUED)
6. Identify and understand the social factors that affect consumer buying decisions. 7. Identify and understand the individual factors that affect consumer buying decisions. 8. Identify and understand the psychological factors that affect consumer buying decisions.
�1ST LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Explain why marketing managers should understand consumer behavior.
�CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
Processes a consumer uses to make purchase decisions, as well as to use and dispose of purchased goods or services; also includes factors that influence purchase decisions and the product use.
6
�2ND LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Analyze the components of the consumer decision-making process.
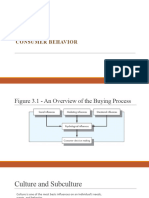
�CONSUMER DECISION-MAKING PROCESS
A five-step process used by consumers when buying goods or services.
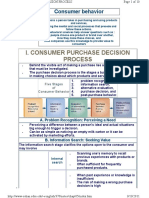
�STEPS IN THE CONSUMER DECISION-MAKING PROCESS
Need Recognition Information Search Evaluation of Alternatives Purchase Postpurchase Behavior
Cultural, Social, Individual and Psychological Factors affect all steps
�A. NEED RECOGNITION
Result of an imbalance between actual and desired states.
10
�NEED RECOGNITION
Marketing helps consumers recognize an imbalance between present status and preferred state
Internal Stimuli and External Stimuli
Preferred State
Present Status
11
�STIMULUS
Any unit of input affecting one or more of the five senses: Sight Smell Taste Touch
Hearing
12
�WHAT DO WE MEAN BY WANT
Recognition of an unfulfilled need and
a product
(or attribute or feature) that will satisfy it.
13
�RECOGNITION OF UNFULFILLED WANTS
When When When
a current product isnt performing properly. the consumer is running out of an product.
another product seems superior to the one currently used.
14
�B. INFORMATION SEARCHES
Process of recalling past information stored
in the memory. Process of seeking information in the outside environment.
15
Internal
External
�INFORMATION SEARCH
Internal Information Search
Recall information in memory
External Information search
Seek information in outside environment
Non-marketing controlled
Marketing controlled
16
�EXTERNAL INFORMATION SEARCHES
Need Less Information
Less Risk More knowledge More product experience Low level of interest
Need More Information
More Risk Less knowledge Less product experience High level of interest
17
�EVOKED SET
Group of brands, resulting from an information search, from which a buyer can choose.
18
�C. EVALUATION OF ALTERNATIVES
Evoked Set
Evaluation of Products:
Analyze product attributes Use cutoff criteria Rank attributes by importance
Chapter 4 Version 3e
Purchase!
19
�D. PURCHASE
To buy or not to buy...
Determines which attributes are most important in influencing a consumers choice
20
�3RD LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Explain the consumers Post-purchase evaluation process.
21
�COGNITIVE DISSONANCE
Inner tension that a consumer experiences after recognizing an inconsistency between behavior and values or opinions.
22
�E. POST-PURCHASE BEHAVIOR
Cognitive Dissonance
Did I make a good decision?
Did I buy the right product?
Did I get a good value?
Can minimize through: Effective Communication Follow-up Guarantees Warranties
23
�4TH LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Identify the types of consumer buying decisions and discuss the significance of consumer involvement.
24
�TYPES OF CONSUMER BUYING DECISIONS
Routine Response Behavior
Limited Decision Making
Extensive Decision Making
Less Involvement
More Involvement
25
�FIVE FACTORS INFLUENCING DECISIONS
1) Level of consumer involvement 2) Length of time to make decision 3) Cost of good or service
4) Degree of information search
5) Number of alternatives considered
26
�ROUTINE RESPONSE BEHAVIOR
Little involvement in selection process
Frequently purchased low cost goods
May stick with one brand
Buy first/evaluate later
Quick decision
27
�LIMITED DECISION MAKING
Low
Low
levels of involvement
to moderate cost goods of a few alternative brands
Evaluation Short
to moderate time to decide
28
�EXTENSIVE DECISION MAKING
High levels of involvement
High cost goods
Evaluation of many brands
Long time to decide
May experience cognitive dissonance
29
�LEVEL OF INVOLVEMENT
Previous Experience
Interest
Factors Determining Level of Involvement
Social Visibility
Perceived Risk of Negative Consequences
Situation
30
�FACTORS INFLUENCING BUYING DECISIONS
Cultural Factors
Social Factors Psychological Factors
Individual Factors
CONSUMER DECISIONMAKING PROCESS
BUY / DONT BUY
31
�5TH LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Identify and understand the cultural factors that affect consumer buying decisions.
32
�CULTURE
Set of values norms, attitudes, and other meaningful symbols that shape human behavior and the artifacts, or products, of that behavior as they are transmitted from one generation to the next.
33
�CULTURAL INFLUENCES ON BUYING DECISIONS
Values Language Myths Customs
Components of American Culture
Rituals Laws Material Artifacts 34
�CULTURE IS...
Pervasive
Functional Learned
Dynamic
35
�VALUES
Enduring belief that a specific mode of conduct is personally or socially preferable to another mode of conduct.
36
�EG. OF CORE AMERICAN VALUES
Success Materialism Freedom Progress
Core American Values
Youth
Capitalism
37
�GLOBAL LANGUAGE BLUNDERS
Chevrolets Nova translated to No Go
Coors Turn it Loose became Suffer from Diarrhea Toyotas MR2 sounded like a swearword in French
Coca-Cola in Chinese means bite the wax tadpole
38
�SUBCULTURE
A homogeneous group of people who share elements of the overall culture as well as unique elements of their own group.
39
�SOCIAL CLASS
A group of people in a society who are considered nearly equal in status or community esteem, who regularly socialize among themselves both formally and informally, and who share behavioral norms.
40
�6TH LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Identify and understand the social factors that affect consumer buying decisions.
41
�SOCIAL INFLUENCES
Social Influences on Buying Decisions
Reference Groups Opinion Leaders
Family Members
42
�REFERENCE GROUP
A group in society that influences an individuals purchasing behavior.
43
�REFERENCE GROUPS
Primary Direct Secondary Types of Reference Groups
Aspirational
Indirect
Non-aspirational
44
�IMPLICATIONS OF REFERENCE GROUPS
They serve as information sources and influence perceptions
They affect an individuals aspiration levels Their norms either constrain or stimulate consumer behavior
45
�OPINION LEADERS
An individual who influences the opinion of others.
46
�FAMILY
Instigators Influencers Decision-Makers Purchasers Consumers
Purchase Roles in the Family
Children Influence Purchase Decisions
47
�7TH LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Identify and understand the individual factors that affect consumer buying decisions.
48
�INDIVIDUAL INFLUENCES
Individual Influences
Gender Age Family Life Cycle
Personality Self-Concept Lifestyle
49
�PSYCHOGRAPHICS
The analytical technique used to examine consumer lifestyles and to categorize consumers. This technique is used to understand the role of above individual influences.
50
�8TH LEARNING OBJECTIVE
Identify and understand the psychological factors that affect consumer buying decisions.
51
�PSYCHOLOGICAL INFLUENCES
Perception
Motivation
Learning
Psychological Influences on Buying Decisions
Beliefs & Attitudes
52
�PERCEPTION
Process by which people select, organize, and interpret stimuli into a meaningful and coherent picture.
53
�PERCEPTION
Selective Exposure
Selective Distortion
Selective Retention
54
�PERCEPTION
Selective Exposure Consumer notices certain stimuli and ignores others.
Selective Distortion
Consumer changes or distorts information that conflicts with feelings or beliefs.
Selective Retention
Consumer remembers only that information that supports personal beliefs.
55
�A CONSUMERS SELECTIVE EXPOSURE
Exposure to over 250 advertisement messages per day
Notices only 11 to 20 ads
56
�MARKETING IMPLICATIONS OF PERCEPTION
Important Higher Brand
attributes
price
names and reliability level of perception
Quality
Threshold Product
changes
57
�THANK YOU
58