0% found this document useful (0 votes)
792 views22 pagesOrganizational Structures Guide
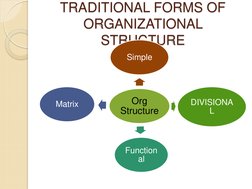
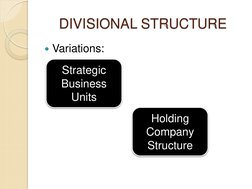
This document discusses and compares different organizational structures including divisional, matrix, strategic business unit, and holding company structures. A divisional structure groups products, projects, or markets internally and gives divisional executives control over objectives and performance. A matrix structure combines functional and divisional reporting where individuals report to multiple managers. It increases responsiveness but can also cause uncertainty and conflicts. The document provides examples of Intel's and Nike's uses of divisional and matrix structures.
Uploaded by
Klyne Ally PeraltaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
792 views22 pagesOrganizational Structures Guide
This document discusses and compares different organizational structures including divisional, matrix, strategic business unit, and holding company structures. A divisional structure groups products, projects, or markets internally and gives divisional executives control over objectives and performance. A matrix structure combines functional and divisional reporting where individuals report to multiple managers. It increases responsiveness but can also cause uncertainty and conflicts. The document provides examples of Intel's and Nike's uses of divisional and matrix structures.
Uploaded by
Klyne Ally PeraltaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Divisional & Matrix Structure Overview: Provides an introduction to divisional and matrix organizational structures, including definitions, advantages, and disadvantages.
- Divisional Structure: Explains the divisional structure, its advantages and disadvantages, and provides an example with Intel's divisions.
- Matrix Structure: Explains the matrix structure, highlighting its advantages and disadvantages, and offers real-world examples like the Nike matrix organization.