0% found this document useful (0 votes)
242 views27 pagesDental Pulp Anatomy & Function
Dr. Anas Rabata is a dentist who received his Bachelor's degree from Damascus University in 2007 and his Master's degree in Histology and Oral Pathology from Damascus University in 2011. He also received a dental implantation diploma from the Dental College in Beirut, Lebanon in 2010.
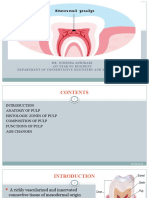
The dental pulp is mesenchymal connective tissue located in the central cavity of a tooth. It has several properties including being inductive in tooth formation, formative in producing dentin, nutritive in maintaining tooth vitality through blood vessels, and defensive in producing reparative dentin.
The pulp contains chambers, canals, and foramina and has distinct cell types, fibers
Uploaded by
talal_11Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
242 views27 pagesDental Pulp Anatomy & Function
Dr. Anas Rabata is a dentist who received his Bachelor's degree from Damascus University in 2007 and his Master's degree in Histology and Oral Pathology from Damascus University in 2011. He also received a dental implantation diploma from the Dental College in Beirut, Lebanon in 2010.
The dental pulp is mesenchymal connective tissue located in the central cavity of a tooth. It has several properties including being inductive in tooth formation, formative in producing dentin, nutritive in maintaining tooth vitality through blood vessels, and defensive in producing reparative dentin.
The pulp contains chambers, canals, and foramina and has distinct cell types, fibers
Uploaded by
talal_11Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd