Securitization
SECURITIZATION
Financial Engineering UBS Chandigarh
By : RISHI MALHOTRA
By : Rishi Malhotra By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Securitization Defined Securitization of debt, or asset securitization as is more often referred to, is a process by which identified pools of receivables, which are usually illiquid on their own, are transformed into marketable securities through suitable repackaging of cash flows that they generate. Securitization is a structured finance process that distributes risk by aggregating assets in a pool (often by selling assets to a special purpose entity), then issuing new securities backed by the assets and their cash flows. The securities are sold to investors who share the risk and reward from those assets. The process through which an issuer creates a financial instrument by combining other financial assets and then marketing different tiers of the repackaged instruments to investors. The process can encompass any type of financial asset and promotes liquidity in the marketplace.
By: Rishi Malhotra
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
What can be Securitized?
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
In concept, all assets generating stable and predictable cash flows can be taken up for securitization.
Auto loans Credit card receivables Computer leases Unsecured consumer loans Residential and commercial mortgages Franchise/Royalty payments Other receivables relating to telecom, trade, toll road and future export.
Typically, asset portfolios that are relatively homogeneous with regard to credit, maturity and interest rate risk could be pooled together to create a securitization structure.
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Parties in a Securitization Transaction
The Originator also interchangeably referred to as
the Seller is the entity whose receivable portfolio forms the basis for ABS issuance. Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), which as the issuer of the ABS ensures adequate distancing of the instrument from the originator.
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
The Servicer, who bears all administrative responsibilities relating to the securitization transaction.
The Trustee or the Investor Representative, who act in a fiduciary capacity safeguarding the interests of investors in the ABS. The Credit Rating Agency, which provides an objective estimate of the credit risk in the securitization transaction by assigning a well-defined credit rating. pool auditors, et al.
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Parties in a Securitization Transaction
The Regulators, whose principal concerns relate to
capital adequacy, liquidity, and credit quality of the ABS, and balance sheet treatment of the transaction. Service providers such as Credit Enhancers and Liquidity Providers.
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
Specialist functionaries such as legal and tax counsels, accounting firms, pool auditors, et al.
Investors are the ultimate judges of any
securitization Effort more important than all the aforementioned are the investors in the securitised paper.
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
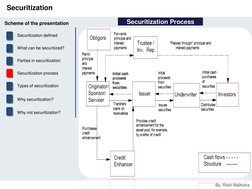
Securitization Process
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Securitization Process
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization?
1. Creation of asset pool and its sale The originator/seller (of assets) creates a pool of assets and executes a legal true sale of the same to a special purpose vehicle (SPV). An SPV in such cases is either a trust or a company. 2. Issuance of the securitised paper
Why not securitization?
This activity is usually performed by the SPV. Design of the instrument however would be based on the nature of interest that investors would have on the asset pool. In the case of pass-through issuances, the investors will have a direct ownership interest in the underlying assets, while pay-throughs are debt issued by the SPV secured by the assets and their cash flows.
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Securitization Process
3. Credit Risk
It must be made abundantly clear at the very outset that the accretions on the asset-backed security, i.e., interest, amortisation and redemption payments, are entirely dependent on the performance of the pooled assets, and will have nothing to do with the credit of the originator.
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
4. Pool Selection
The process of selecting assets to build a securitization pool would take into careful consideration, loan characteristics that are important from a cash flow, legal, and credit points of view, such as type of asset, minimum and maximum loan size, rate, maturity and concentration limits (geographic, single-borrower, etc.).
5. Administration
Formal delineation of duties and responsibilities relating to administration of securitised assets, including payment servicing and managing relationship with the final obligors must be spelt out clearly through a contractual agreement with the entity who would perform those functions.
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Securitization Process In addition, the following features are often included as part of a securitization transaction: Credit enhancement to support timely payments of interest and principal and to handle delinquencies. Independent credit rating of the securitised paper from a well known credit rating agency. Providing liquidity support to investors, such as appointment of market makers.
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Types of Securitization
Asset backed securities (ABS)
Financial security backed by a loan, lease or receivables against assets other than real estate and mortgagebacked securities. An ABS is essentially the same thing as a mortgagebacked security, except that the securities backing it are assets such as Auto loans Credit card receivables Student loans company's receivables royalties
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Types of Securitization
Mortgage backed securities (MBS)
A type of asset-backed security that is secured by a mortgage or collection of mortgages. Furthermore, the mortgage must have originated from a regulated and authorized financial institution. When you invest in a mortgage-backed security you are essentially lending money to a home buyer or business. Mortgage-backed security sub-types include: Residential mortgage-backed security (RMBS) - a passthrough MBS backed by mortgages on residential property. Commercial mortgage-backed security (CMBS) - a pass-through MBS backed by mortgages on commercial property. Collateralized mortgage obligation (CMO) - a more complex MBS in which the mortgages are ordered into tranches by some quality (such as repayment time), with each tranche sold as a separate security.
By: Rishi Malhotra
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Types of Securitization
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
Stripped mortgage-backed securities (SMBS): Each mortgage payment is partly used to pay down the loan's principal and partly used to pay the interest on it. These two components can be separated to create SMBS's, of which there are two subtypes: 1.Interest-only stripped mortgage-backed securities (IO) - a bond with cash flows backed by the interest component of property owner's mortgage payments. 2.Principal-only stripped mortgage-backed securities (PO) - a bond with cash flows backed by the principal repayment component of property owner's mortgage payments.
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Types of Securitization
Collateralized debt obligations(CDO)
They are a type of structured asset-backed security (ABS) whose value and payments are derived from a portfolio of fixed-income underlying assets. CDOs securities are split into different risk classes, or tranches, whereby "senior" tranches are considered the safest securities. Types based on the underlying asset: Collateralized loan obligations (CLOs) -- CDOs backed primarily by leveraged bank loans. Collateralized bond obligations (CBOs) -- CDOs backed primarily by leveraged fixed income securities. Collateralized synthetic obligations (CSOs) -- CDOs backed primarily by credit derivatives. Structured finance CDOs (SFCDOs) -- CDOs backed primarily by structured products (such as asset-backed securities and mortgage-backed securities)
By: Rishi Malhotra
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Why Securitization ?
Advantages to issuer:
Efficient funding Lower Cost Alternative investor base Issuers credit rating becomes irrelevant Reduces asset liability mismatch Lower capital requirements Locking in profits Transfer risks (credit, liquidity, prepayment, reinvestment, asset concentration) Balance sheet management Improves capital utilization Releases capital
By: Rishi Malhotra
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Why Securitization ?
Benefits to consumers-borrowers
Lower cost of funds.
Increased array of credit contracts. Competitive rates of terms nationally and locally. Funds available consistently
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Why Securitization ?
Benefits to investors
Low event risk Higher yields for lower/similar risk Structured issuances: Create instruments to match investment objectives Secondary Market Liquidity Enhanced diversification
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined
Why Not Securitization ?
Disadvantages to issuer:
What can be securitized?
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization?
1. Costs 2. Size limitation 3. Risks
Risks to investors:
1. Liquidity risk : Credit default
2. Event risk Prepayment/reinvestment/early amortization Currency interest rate fluctuations 3. Contractual agreements Moral hazard
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Securitization Indian context First deal in India between Citibank and GIC Mutual Fund, in 1990 for Rs. 160 million. Securitisation of cash flow of high value customers of Rajasthan State Industrial and Development Corporation in 1994-95, structured by SBI cap. Securitisation of overdue payments of UP government to HUDCO by issue of tax-free bonds worth Rs. 500 million Securitisation of Sales Tax deferrals by Government Of Maharashtra in August 2001 for Rs. 1500 million with a green shoe option of Rs. 75 million. First deal in power sector by Karnataka Electricity Board for receivables worth Rs. 1940 million and placed them with HUDCO. Mega securitisation deal of Jet Airways for Rs. 16000 million through offshore SPVs.
By: Rishi Malhotra
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization? Securitization- Indian context
�Securitization
Scheme of the presentation
Securitization defined What can be securitized?
Securitization win-win for all Originators Churn higher returns on lower capital base Investors Can invest in low-risk rated home loans paper without hassles of origination/ servicing. Financial system as a whole Expertise of Specialists helps maintain quality of underlying assets and reduces ALM mismatches. Home Loan Customers Access to cheaper fund
Parties in securitization
Securitization process Types of securitization Why securitization? Why not securitization? Securitization- Indian context
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
References [1] What SEBs Owe - Out standing dues to central utilities, http://www.indiapoweronline.com/Scripts/GNT006C1.ASP?ArtID=450&CatID =1&SecID=14 [2] P.P. Vora (2001), NHB - Promoting A Sound, Healthy, Viable And Efficient Housing Finance System, http://www.shilpabichitra.com/v039.htm [3] Modak, Anand, (2001), Securitization - A boon for Investors and Borrowers, Investime, September 2001, http://www.valuemoney.com/new/sec.pdf
[4] Ghosh, T P, Innovations in asset-backed securities, http://www.financialexpress.com/fe/daily/19990331/fex31002.html
[5] Standard and Poor, Global CBO/CLO Criteria, http://www.standardandpoors.com/ResourceCenter/RatingsCriteria/Structure dFinance/articles/pdf/globalcboclo99.pdf [6] Notes from http://www.vinodkothari.com
By: Rishi Malhotra
�Securitization
Thank you
By : Rishi Malhotra By: Rishi Malhotra