Structured Finance
Course description
01. Overview of structured finance and cash flows
Example of securitization
02. Project finance case study
03. Acquisition finance case study
04. Asset & Export finance
05. Organization of structured finance divisions : from
origination to distribution
20/09/2021 2
� Structured Finance
Definition
• There is no universal definition of structure
finance.
• . . . techniques employed whenever the
requirements of the originator or owner of
an asset, be they concerned with funding,
liquidity, risk transfer, or other need, cannot
be met by an existing, off-the-shelf product
or instrument. Hence, to meet this
requirement, existing products and
techniques must be engineered into a tailor-
made product or process. Thus, structured
finance is a flexible financial engineering
tool.
20/09/2021 3
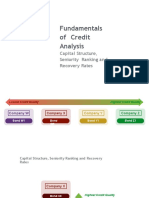
� Structured Finance
characteristics
One or more of following elements generally characterize a structured finance transaction:
• a complex financial transaction that may involve actual or synthetic transfer of assets or risk
exposure, aimed at achieving certain accounting, regulatory, and/or tax objectives;
• a transaction ring-fenced in its own special purpose vehicle;
• a bond issue that is asset-backed and/or external reference indexlinked;
• a combination of interest-rate and credit derivatives;
• a transaction employed by banks, other financial institutions, and corporations as a source of
funding and/or favorable capital, tax, and accounting treatment; and
• disintermediation between banks and other corporate entities
20/09/2021 4
� Structured Finance
Definition
Structured finance instruments can be defined through three key characteristics:
(1) pooling of assets (either cashbased or synthetically created);
(2) tranching of liabilities that are backed by the asset pool (this property
differentiates structured finance from traditional “pass-through” securitizations);
(3) de-linking of the credit risk of the collateral asset pool from the credit risk of the
originator, usually through use of a finite-lived, standalone special purpose
vehicle (SPV).
20/09/2021 5
� Are debt and equity enough ?
Assets Liabilities
20/09/2021 6
� Are debt and equity enough ?
Assets Liabilities
Equity :
• Residual payments
• Upside and downside
• Residual claims
• Voting control rights
Future Cash Flows of the asset
Debt :
• Contractual int. & principal
• No upside
• Senior claims
• Control via restrictions
20/09/2021 7
� Benefits of structured finance
• Enables the financing of a unique asset class that (1) previously may have been financed only by traditional borrowing
methods or (2) could not be financed at all without structured finance.
• Offers issuers flexibility in terms of maturity structure, security design, and asset types, which in turn allows issuers to
provide enhanced return and a customized degree of diversification commensurate with investors’ appetite for risk.
• Contributes to a more complete capital market by offering a trade off along the efficient frontier of optimal diversification
at minimum transaction cost.
• Allows the issuer to obtain better credit ratings and/or more leverage compared to senior unsecured debt issuance.
• May reduce borrowing costs; often captive finance companies and independent companies can obtain capital at rates better
than those obtainable for the originator of the securitized assets.
• May provide funding and liquidity by converting illiquid assets into cash.
• May transfer the risk of assets or liabilities to allow a bank originator to do additional business without ballooning its
balance sheet.
• May enable a financial institution to exploit regulatory capital arbitrage, for example through securitization of assets that
offer a low return on regulatory capital.
• Can be used to shelter corporations from potential operating liabilities.
20/09/2021 8
� Securitization
Securitization is a technique used to convert illiquid
assets / claims into tradable securities.
Securitization acts not only as a means to raise cash on
the capital markets, but also as a credit risk transfer
tool.
For investors it provides attractive and diversified
investment opportunities without the need to set up a
complex and expensive client-facing infrastructure.
Instead they can leverage and benefit from the
lending and servicing expertise of originators.
Removing loans from the balance sheet of banks can
also have macro-economic benefits as banks can
create more new lending.
20/09/2021 9
�Benefits for the original lenders / originators Benefits for investors
• Creation of liquidity • Tailored instruments
• Funding diversification • Portfolio diversification
• Reduction in funding costs • Risk sharing
• Risk reduction and transfer
• Regulatory capital relief
• Raise capital without prospectus-type
disclosure
20/09/2021 10
� Securitization
Parties involved
20/09/2021 11
� The Special Purpose Vehicule
20/09/2021 12
�20/09/2021 13
� Credit enhancement technique
• Over-collateralization
• Guarantee
• Diversification
• Selection of assets
• Tranches
20/09/2021 14
� Overview of ABS collateral type
20/09/2021 15
� Overview of collateral type
• Any resources with predicable cash flows can be securitized as follows :
• Bills that are made at a 5 star hotel
• Tickets that are to be sold at a cinema hall
• Future billings of an airline
• Hire purchases receivables
• Non performing assets of a financial entity
20/09/2021 16
� Note tranches
Risk / return
20/09/2021 17
� Cash flow waterfall
20/09/2021 18
� Actors of the SPV
20/09/2021 19