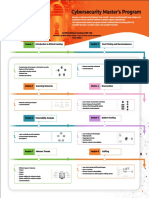
Security threats and mitigation
Unit objectives
Describe and explain common security
threats
Explain ways to mitigate security
threats
Topic A
Topic A: Security threats
Topic B: Threat mitigation
Security threats
Technology weaknesses
Configuration weaknesses
Policy weaknesses
Human error or malice
Technology weaknesses
TCP/IP
Operating systems
Network equipment
Configuration weaknesses
Unsecured accounts
System accounts with weak
passwords
Internet services
Default settings
Network equipment
Trojan horses
Viruses
Human error and malice
Human error
Accident, ignorance, stress
Malice
Dishonesty
Impersonation
Disgruntled employees
Snoops
DoS attacks
Identify theft
Viruses, worms, Trojan horses
Worms
Trojans
Zombies and botnets
Rootkits
Activity A-1
Identifying common security threats
Social engineering
Hacking people, not computers
Goals include fraud, network intrusion,
espionage, identify theft, disruption
Shoulder surfing
Dumpster diving
Phone directories
Organizational charts
Policy manuals
Calendars
Outdated hardware
System manuals, network diagrams
Online attacks
Instant messenger and e-mail
Unwitting employees run code or
applications
Countermeasures
Discard items properly
User education and awareness
Phishing
Fraudulent e-mail appears to be from
a trusted sender
Clues
Countermeasures
Activity A-2
Discussing social engineering
Denial of service attacks
Consume or disable resources by
flooding systems with TCP/IP packets
Attacks hit client computers and
servers
TCP 3-way handshake
SYN flood defense
Smurf attacks
Floods a host with ICMP packets
Uses third-party network
Configure routers to drop specific
ICMP packets
Ping of death
Outdated attack
IP packets manipulated to cause
buffer overflows
Activity A-3
Discussing DoS attacks
Distributed DoS attacks
Attacker uses multiple hosts
Handlers
Zombies
DDoS countermeasures
Packet filtering
Turn off directed broadcasts
Block ports
Activity A-4
Assessing your vulnerability to DDoS
attacks
Man-in-the-middle
Web spoofing
Information theft
TCP hijacking
ARP poisoning
ICMP redirect
DNS poisoning
Spoofing
IP address spoofing
ARP poisoning
Web spoofing
DNS spoofing
IP address spoofing
1. Attacker identifies a target to be the
attack victim and a machine trusted
by the victim
2. Attacker determines sequence
numbers
3. Victim accepts and responds to
spoofed packets
4. Attacker responds
Activity A-5
Port scanning
Topic B
Topic A: Security threats
Topic B: Threat mitigation
Security policies
Acceptable use
Due care
Privacy
Separation of duties
Need-to-know information
Password management
Account expiration
Service level agreements
How to destroy or dispose of equipment,
media, and printed documents
Acceptable use
Defines how computer and network
resources can be used
Protects information and limits
liabilities and legal actions
Addresses productivity issues
Employees should read and sign
document
Due care
Diligence or care to exercise in a given
circumstance
Identifies risks to organization
Assesses risks and measures to be
taken to ensure information security
Privacy
Privacy of customer and supplier
information
Contracts
Sales documents
Financial data
Personally identifiable information
Compromised information causes
entities to lose trust
Separation of duties
Avoids one person having all
knowledge of a process
Potential for abuse
Knowledge leaves with person
Distribute tasks
Document all procedures
Security divided into multiple elements
Each element assigned to different
people
Need to know
Sensitive information accessed only
by those who must access
Give IT team just enough permissions
to perform duties
Give explicit access to those who
need it
Password management
Minimum password length
Required characters
Reset interval
Reuse
How users handle
Check for weak passwords
Account expiration
Unneeded counts disabled or deleted
Disable accounts for extended leaves
Service-level agreement
Contract between service provider and
end user
Defines levels of support
Documents penalties
Covers disaster recovery plans
Contingency plans
Disposal and destruction
Degauss magnetic media
Zeroize drives
Physically destroy media
Lock recycle bins
Shred or burn documents
Activity B-1
Creating a security policy
Human resources policy
Document manual procedures for
automated duties
Access policies
ID badges
Keys
Restricted access areas
Personnel management
Hiring process
Employee review and maintenance
Employee termination
Activity B-2
Creating a human resources policy
Incident response policy
1. Preparation
2. Detection
3. Containment
4. Eradication
5. Recovery
6. Follow-up
Preparation
Have steps in place
Balance easy access with effective
controls
Identify steps to be taken
Acceptable risks
Due diligence
Detection
Ask questions and document
responses
Containment
Shut down or take equipment offline
Increase monitoring
Eradication
Clean or delete files
Restore data
Recovery
Equipment
Storage devices
Passwords
Follow up
Document process
Update existing documents
Activity B-3
Creating an incident response
and reporting policy
Change management
Set of procedures
Request for change
Approval process
RFC scheduled and completed
Changes implemented
Configuration management documentation
Wiring schematics
Physical network diagram
Logical network diagram
Baseline
Policies, procedures, and
configurations
Regulations
Activity B-4
Implementing change management
Education
Educate staff about security
Network administrators
End users
Enables all employees to be part of security
team
Enables regular user to see potential
security issues or security violation
Customize to provide level of knowledge
needed by student
Big picture for end users
Detailed knowledge for administrative users
Exhaustive knowledge for security
administrators
Communication
Identify what information can be
shared and with whom
Identify what information can never be
shared
Prove identity
Social engineering threats
User awareness
Reason for training
Security contacts
Who to contact about security incidents
Actions to take
Policies about system account use
Policies about system media use
Techniques for sanitizing media and hard
copies
Maintaining security of accounts
Application and data policies
Internet, Web, and e-mail policies
Activity B-5
Identifying the need for user education and
training
Types of training
On-the-job
Classroom
Online
Activity B-6
Identifying education opportunities and
methods
Unit summary
Described and explained common
security threats
Explained ways to mitigate security
threats