Professional Documents
Culture Documents
POM Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Jen Zabala0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
285 views18 pagesProduction and Operations Management (POM) encompasses forecasting, capacity planning, scheduling, managing inventories, assuring quality, motivating employees, deciding where to locate the facilities and more. The three major functions of business organizations overlap 3 operations -consists of all activities directly related to producing good or providing services. FINANCE - consists of activities related to securing resources at favorable prices and allocating those resources throughout the organization.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProduction and Operations Management (POM) encompasses forecasting, capacity planning, scheduling, managing inventories, assuring quality, motivating employees, deciding where to locate the facilities and more. The three major functions of business organizations overlap 3 operations -consists of all activities directly related to producing good or providing services. FINANCE - consists of activities related to securing resources at favorable prices and allocating those resources throughout the organization.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
285 views18 pagesPOM Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Jen ZabalaProduction and Operations Management (POM) encompasses forecasting, capacity planning, scheduling, managing inventories, assuring quality, motivating employees, deciding where to locate the facilities and more. The three major functions of business organizations overlap 3 operations -consists of all activities directly related to producing good or providing services. FINANCE - consists of activities related to securing resources at favorable prices and allocating those resources throughout the organization.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
1
Production and Operations
Management (POM)
The management of processes or systems
that create goods and/or provide services.
It encompasses forecasting, capacity
planning, scheduling, managing inventories,
assuring quality, motivating employees,
deciding where to locate the facilities and
more.
2
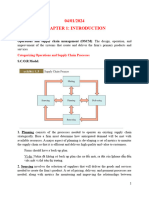
Functions and Business Operation
Organizations are formed to pursue goals that are
achieved more effectively by the concerted efforts of a
group of people than by individuals working alone.
Operations
Marketing
Finance
Figure 1-1. The three major functions of business organizations overlap
3
Three Basic Functions of Business
Organization
1. OPERATIONS
-consists of all activities directly related to producing
good or providing services.
- it can be goods-oriented. (manufacturing and
assembly operations)
- it can be service-oriented. (health care,
transportation, food handling, and retailing)
4
Production and Operation System
Inputs are used to obtained finished goods
using one or more transformation processes
(e.g. storing, transporting, cutting).
To ensure that the desired outputs are
obtained, measurement are taken at a
various point in the transformation process
(feedback) and then compared with the
previously established standard to determine
whether correctively action is needed
(control).
5
2. FINANCE
Comprises of activities related to
securing resources at favorable
prices and allocating those resources
throughout the organization.
6
Finance and operations management personnel
cooperate by exchanging information and
expertise in activities such as:
1.Budget must be periodically prepared to plan
financial requirements.
2. Economic analysis of investment proposals
evaluation of alternative investment in plant
and equipments requires input from both
operations and finance people.
3. Provision of funds necessary funding of
operations and the amount and timing of
funding
7
3. MARKETING
Focus on selling and/or promoting the goods and
services of an organization.
Responsible for assessing customer wants and
needs.
Provide the information needed by the operations
about demand over the short to intermediate
term so that it can plan accordingly (e.g.
purchase materials, schedule work)
Lead time the time between ordering a good or
services and receiving it.
8
Other Functions
1. Accounting supplies information to management on cost of
labor, materials, and overhead and may provide reposts on items
such as scrap, downtime and inventories.
2. Management Information System (MIS) providing management
with the information it needs to effectively manage.
3. Purchasing responsible for procurement of materials, supplies,
and equipment.
4. Personnel or Human Resources _ concerned with recruitment
and training of personnel, labor relations, wages and salaries and
ensuring health and safety of employees.
5. Public Relations responsible for building and maintaining a
positive image of the organization.
6. Distribution involves shipping of goods to warehouse, retail
outlets or final consumer.
7. Maintenance responsible for general upkeep and repair of
equipment, building and grounds, heating and air-conditioning,
removing toxic waste.
9
Differentiating Features of Operations
System
1. Degree of Standardization
2. Type of Operation
3. Production of Goods versus
Service Operation
10
DEGREE OF STANDARDIZATION
Standardized Output
- means that there is a high degree of uniformity in
goods or services.
Customized Output
- means that the product or service is designed for
specific case or individual.
11
TYPES OF OPERATION
The degree of standardized products and the volume of
output of a producer or service influence the way firm
organizes production.
The four Vs of operations:
Volume how many products or services are made by
the operation?
Variety how many different types of products or
services are made by the operation?
Variation how much does the level of demand change
over time?
Visibility how much of the operations internal working
are exposed to its customers?
12
PRODUCTION OF GOODS
VERSUS SERVICE OPERATION
Production of goods - results in a tangible
products.
Service operation - generally implies an act.
13
Differences Between Goods and Services
1. Customer contact
2. Uniformity of input
3. Labor content of job
4. Uniformity of output
5. Measurement of productivity
6. Simultaneous production and delivery
7. Quality assurance
14
The Operations Manager and the
Management Process
The operations manager is the key
figure in the system: he or she has the
ultimate responsibility for the creation
of goods and provision for services.
The operations manager must
coordinate the use of resources through
the management process such as
planning, organizing, staffing, directing
and controlling.
15
OPERATIONS MANAGER AND
DECISION MAKING
General Approaches to Decision Making:
1. Use of models
2. Quantitative methods
3. Analysis of trade-offs
4. The system approach
16
MODEL
- an abstraction of reality; a simplified version of
something
Classification of Models
1. Physical Models look like their real-life counterparts.
2. Schematic Models more abstract than their physical
counterparts (less resemblance to physical reality)
- there are often relatively simple to construct
and change.
3. Mathematical Models the most abstract: they do not look at
all like their real-life counterparts.
- these are usually the easiest to manipulate and
they are important forms of inputs for computers and
calculators.
17
2. QUANTITATIVE APPROACHES
- Quantitative approaches to problem
solving embody an attempt to obtain
mathematically optimum solutions to
managerial problems.
3. ANALYSIS OF TRADE-OFF
- Manager sometimes deal with decision by
listing the advantages and disadvantages
pros and cons of a course of action to
better understand the decision they must
make.
18
4. SYSTEMS APPROACH
System a set of interrelated parts that must work
together.
In a business organization, the organization can be
thought of as a system compose of subsystem.
The system approach emphasizes
interrelationships among subsystems, but its
main theme is that the whole is greater than the
sum of its individual parts.
You might also like
- Bam 199 - P1Document9 pagesBam 199 - P1Mae RapadasNo ratings yet
- Operations Hand OutsDocument7 pagesOperations Hand OutsPavi Antoni VillaceranNo ratings yet
- Ba MGT103Document1 pageBa MGT103Flores, Kristine Hanna U.No ratings yet
- Summary - Chapter 1Document3 pagesSummary - Chapter 1RoseJeanAbingosaPernitoNo ratings yet
- Production of Goods Versus Delivery of ServicesDocument11 pagesProduction of Goods Versus Delivery of ServicesJerianNo ratings yet
- INTRO TO OPS MGMT CHAPTER 1Document20 pagesINTRO TO OPS MGMT CHAPTER 1Riviera MehsNo ratings yet
- Operations and Supply Chain ManagementDocument61 pagesOperations and Supply Chain ManagementSandeep SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Operations ManagementLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- OMGT-1013Document29 pagesOMGT-1013Alexa Nicole GuillermoNo ratings yet
- OM for Managing Operations EffectivelyDocument59 pagesOM for Managing Operations EffectivelyCoolest ChapNo ratings yet
- BM2 Chapter 1Document24 pagesBM2 Chapter 1zhvaiaNo ratings yet
- Raw:/storage/emulated/0/Download/inbound 3081672313263350329Document5 pagesRaw:/storage/emulated/0/Download/inbound 3081672313263350329Marvin Espenocilla EspeñoNo ratings yet
- Overview of Operations ManagementDocument8 pagesOverview of Operations ManagementAmara Bless100% (2)
- Lý thuyếtDocument24 pagesLý thuyếtphutran.31221024063No ratings yet
- Lý thuyếtDocument22 pagesLý thuyếtphutran.31221024063No ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations Management: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument55 pagesIntroduction To Operations Management: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinKayla SheltonNo ratings yet
- Production & Operation ManagementDocument42 pagesProduction & Operation ManagementSandeep GhatuaryNo ratings yet
- 2 - Os As Set DecisionsDocument8 pages2 - Os As Set DecisionsALLYSON BURAGANo ratings yet
- The Management of Operations Notes FinalDocument88 pagesThe Management of Operations Notes FinalSantiago LinderNo ratings yet
- OSCM - Summary Presentations of Sessions 1-8Document151 pagesOSCM - Summary Presentations of Sessions 1-8Frank Edner Javier Rueda KuongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ObjectivesDocument9 pagesChapter 1 ObjectivesMuhammad NadeemNo ratings yet
- OM Overview and CompetitivenessDocument21 pagesOM Overview and CompetitivenessArjay GuillandezNo ratings yet
- Definition of Operations ManagementDocument20 pagesDefinition of Operations ManagementAliyah FazilNo ratings yet
- First Chapter: IntroductionDocument16 pagesFirst Chapter: IntroductionMominul MominNo ratings yet
- HAND OUT PRODUCTIONS & OPERATIONS MGTDocument3 pagesHAND OUT PRODUCTIONS & OPERATIONS MGTSireon TapalesNo ratings yet
- Module 1-4 Operations and Quality Management TermsDocument6 pagesModule 1-4 Operations and Quality Management TermsVicky rederaNo ratings yet
- CBM ReviewerDocument8 pagesCBM Reviewerkrain dropNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - OM NOTESDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - OM NOTESwejdazoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operation ManagementDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Operation Managementpresidonsi100% (1)
- OM: Managing Operations for EfficiencyDocument4 pagesOM: Managing Operations for EfficiencySir Stephen Maverick N CrudaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Operations ManagementAllan CalvoNo ratings yet
- W17Document2 pagesW17Djustize GaboniNo ratings yet
- Operation's Management ReviewerDocument16 pagesOperation's Management ReviewerAnna Jo100% (2)
- Horizontal Loading Vertical Loading Trust TeamsDocument7 pagesHorizontal Loading Vertical Loading Trust TeamsMa. Elizabeth ApolinarNo ratings yet
- Research Intro OpManDocument8 pagesResearch Intro OpManReiner TayabanNo ratings yet
- Bank Operations Manager Manufacturing Operations ManagerDocument6 pagesBank Operations Manager Manufacturing Operations ManagerLauren StuartNo ratings yet
- 1 - Scope of Operations ManagementDocument9 pages1 - Scope of Operations ManagementALLYSON BURAGANo ratings yet
- PRODUCTIONS AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT QnA AnsDocument14 pagesPRODUCTIONS AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT QnA AnsAbhishek MandalNo ratings yet
- The operations function and its goals in organizationsDocument9 pagesThe operations function and its goals in organizationsM RaxidNo ratings yet
- BM2 Chapter 1Document23 pagesBM2 Chapter 1Lowela KasandraNo ratings yet
- Value Chain OperationDocument27 pagesValue Chain OperationHARVY DAVIS CHUANo ratings yet
- Overview of Operations ManagementDocument14 pagesOverview of Operations ManagementCollins AbereNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Lecture NotesDocument68 pagesOperations Management: Lecture Notesasif lashariNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument25 pagesOperations ManagementRhay ZenixNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument6 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Operations ManagementVanesa Calimag ClementeNo ratings yet
- Operations and ProductivityDocument3 pagesOperations and ProductivityaasthaNo ratings yet
- operation managementDocument4 pagesoperation managementxowof70509No ratings yet
- Om 2022Document61 pagesOm 2022Rana SabryNo ratings yet
- FM CBMEC 1 Module 2Document4 pagesFM CBMEC 1 Module 2Angelica MartinNo ratings yet
- Pom NotesDocument126 pagesPom NotesManjunath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Decision Making in Production ManagementDocument5 pagesDecision Making in Production ManagementOshoMosesAdemolaNo ratings yet
- DSC2006 Tutorial 1Document3 pagesDSC2006 Tutorial 1slimsprint100% (1)
- Introduction to Operation Management FunctionsDocument3 pagesIntroduction to Operation Management Functionshehehehehloo100% (1)
- IGNOU MBA MS-05 Free Solved Assignment 2012Document33 pagesIGNOU MBA MS-05 Free Solved Assignment 2012ahesan aliNo ratings yet
- A SummaryDocument125 pagesA SummarySushil PokhrelNo ratings yet
- CH 1-5 OMDocument71 pagesCH 1-5 OMAbu DadiNo ratings yet
- Operations and Supply Chain Management Week 1Document8 pagesOperations and Supply Chain Management Week 1Rhyn RutherfordNo ratings yet
- CH 1-5 OMDocument71 pagesCH 1-5 OMAbu DadiNo ratings yet
- Becoming Lean: Practical Steps to Build CompetitivenessFrom EverandBecoming Lean: Practical Steps to Build CompetitivenessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Record LabelDocument2 pagesRecord LabelBrandonSymondsNo ratings yet
- The Rebirth of Online Shopping: A Quantitative Research of Online Shopping and Its EffectsDocument5 pagesThe Rebirth of Online Shopping: A Quantitative Research of Online Shopping and Its EffectsKen MateyowNo ratings yet
- Nike IncorporationDocument51 pagesNike IncorporationAli Baloch100% (1)
- Capacity of The Tram Stabling and Maintenance AreaDocument20 pagesCapacity of The Tram Stabling and Maintenance AreaRegis ScaliceNo ratings yet
- F&B Revenue Cycle AuditDocument4 pagesF&B Revenue Cycle Auditericlim1010100% (1)
- TT Class XII PDFDocument96 pagesTT Class XII PDFUday Beer100% (2)
- Liushen Shower CreamDocument5 pagesLiushen Shower Creamvarryset2No ratings yet
- AlibabaDocument14 pagesAlibabaSILA100% (1)
- Joint VentureDocument92 pagesJoint VentureShahnawaz100% (2)
- Mens Wearhouse 10 K Annual ReportDocument128 pagesMens Wearhouse 10 K Annual Reportsachin2727No ratings yet
- Ingredient BrandingDocument20 pagesIngredient BrandingVaibhavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Store LayoutDocument2 pagesStore LayoutallahabadNo ratings yet
- Budgeting For Your AlbumDocument12 pagesBudgeting For Your Albumrcpretorius100% (1)
- P&G PresentationDocument23 pagesP&G PresentationSaman Sharif50% (2)
- A Seminar Report On Business Model Comparison of Starbucks and Dunkin' DonutsDocument17 pagesA Seminar Report On Business Model Comparison of Starbucks and Dunkin' DonutsKrishnapalsinh Indrajitsinh VirparaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Bill DetailsDocument8 pagesMobile Bill Detailskashyap_hiraniNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior and MK Strategy in Duty Free MarketDocument53 pagesConsumer Behavior and MK Strategy in Duty Free Market:-*kiss youNo ratings yet
- About Team: - Mani Subramani, Associate ProfessorDocument7 pagesAbout Team: - Mani Subramani, Associate ProfessorNikhil AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Mcdonald Supply ChainDocument5 pagesMcdonald Supply ChainAmitNo ratings yet
- 3rd Term Course OutlinesDocument58 pages3rd Term Course OutlinesmesellioNo ratings yet
- Wells Fargo Way2Save Checking: Important Account InformationDocument5 pagesWells Fargo Way2Save Checking: Important Account InformationBernadette B. Reyes0% (1)
- Walmart Case StudyDocument19 pagesWalmart Case StudygeniusMAHINo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Case Study AnalysisDocument19 pagesEntrepreneurship Case Study AnalysisParth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Joe Schroeder: The New Normal of Network MarketingDocument4 pagesJoe Schroeder: The New Normal of Network MarketingRebecca JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Industry Structure & Competitive Strategy: Keys To ProfitabilityDocument15 pagesIndustry Structure & Competitive Strategy: Keys To ProfitabilityAmi KarNo ratings yet
- Business Plan For Toys On RentDocument22 pagesBusiness Plan For Toys On RentAjit ShindeNo ratings yet
- Competitive AnalysisDocument38 pagesCompetitive AnalysisRui MarquesNo ratings yet
- A Low Cost Retail Giant's Distinctive Business PracticesDocument19 pagesA Low Cost Retail Giant's Distinctive Business PracticesRajesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Debit and Credit Card Usage: Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesDebit and Credit Card Usage: Literature ReviewAdnan Akram0% (1)
- Sales and Distribution Channel of ITC SA PDFDocument12 pagesSales and Distribution Channel of ITC SA PDFRomil SailotNo ratings yet