Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Business
Uploaded by
Erika_ES_Envalt0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views56 pagesThe document discusses the goals and functions of business. It can be summarized as follows:
1. The primary goal of any business is to maximize profits by providing goods and services to fulfill customer needs and wants.
2. Besides profit maximization, businesses must also be responsible to their customers, employees, creditors, stockholders, environment, and community.
3. Businesses operate within an environment that includes factors such as historical, natural, political/legal, social/cultural, economic, international, and technological influences. The business environment affects how businesses function and what they can achieve.
Original Description:
Original Title
Presentation 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the goals and functions of business. It can be summarized as follows:
1. The primary goal of any business is to maximize profits by providing goods and services to fulfill customer needs and wants.
2. Besides profit maximization, businesses must also be responsible to their customers, employees, creditors, stockholders, environment, and community.
3. Businesses operate within an environment that includes factors such as historical, natural, political/legal, social/cultural, economic, international, and technological influences. The business environment affects how businesses function and what they can achieve.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views56 pagesIntroduction To Business
Uploaded by
Erika_ES_EnvaltThe document discusses the goals and functions of business. It can be summarized as follows:
1. The primary goal of any business is to maximize profits by providing goods and services to fulfill customer needs and wants.
2. Besides profit maximization, businesses must also be responsible to their customers, employees, creditors, stockholders, environment, and community.
3. Businesses operate within an environment that includes factors such as historical, natural, political/legal, social/cultural, economic, international, and technological influences. The business environment affects how businesses function and what they can achieve.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 56
What is Business?
People need work for living
Salary: to buy goods for everyday used
Various types of SELLER
(aim to make profit)
Activity of providing goods and services to fulfill
customers needs and wants can be termed as
BUSINESS
3
BUSINESS GOALS
To make profit encourage business to
open and expand their
business
Amount of money that a
business earns
after all expenses have
been deducted from sales
revenue
- To make profit: need administer and manage the
business effectively and efficiently
- Therefore, the starting point in any business
management is setting goals
4
EFFECTIVENESS & EFFICIENCY
5
DEFINITIONS OF GOAL
Goal is an objectives that a business hopes and
plans to achieve
Can also be interpreted as an end-state that the
business is expected to achieve
Simple term:
THE THING THAT ONE EXPECTS TO ACHIEVE
To ensure organization to function systematically
Ensures all resources will be utilized effectively and
efficiently .
6
TYPES OF GOALS
Three (3) types of goals:
1. Purpose
2. Mission
3. Objective
7
TYPES OF GOALS
1. Purposes
Is the reason for the business organizations
existence
As the reason for various organizations
existence
Eg: profit & non-profit organizations
purpose are different from each other
8
TYPES OF GOALS
2. Mission
Is the means by which a business can fulfill
its purpose
Indicates how a business will achieve its
purposes
eg:
AirAsia: Everyone can Fly
UiTM: to be World Class University
9
TYPES OF GOALS
3. Objective
Specific statements detailing what a business
organization intends to accomplish as it goes
about its mission
Eg:
Air Asia: offering affordable air fare
McDonald: serve all customers within 2
minutes of their order
10
LEVELS OF GOALS
Three levels of goals
1. Long-term goals
2. Intermediate goals
3. Short-term goals
11
LEVELS OF GOALS
1. Long-term goals
Formulated by the higher level management
group in a business organization
Set for a long period of time 5yrs and above
Eg:
Touch n Go: To be No. 1 in the electronic
payment system for micro payment towards
realizing a cashless society
12
LEVELS OF GOALS
2. Intermediate goals
Set for period one year to 5yrs
Set by middle managers of a business
Eg:
Marketing manager targeted sales for the
following year
R&D manager targeted new types of
technology
HR manager forecast manpower for the
following year
13
LEVELS OF GOALS
3. Short-term goals
For one year and less
Eg:
Marketing manager monthly performance
HR manager quarterly staff performance
14
GOALS OF BUSINESS
1. PROVIDE GOODS AND SERVICES
a. Making raw materials useful to customers
b. Creating new products
i. Expand to new products diversify the business
ii. Improve the product quality
c. Creating an organized markets
i. Responsible to transfer the service & product to the
customer at the right time & right place
ii. Product availability & convenient to customer, eg.
Shopping mall
Input Process Output
15
GOALS OF BUSINESS
2. PROVIDE EMPLOYEMENT
corporate social responsibility
business: opening more jobs opportunity to society reduce
poverty
3. HELPING THE COUNTRY TO INCREASE THE GROWTH
RATE
international trade promote exchange rate between
two countries (economic)
helps country to maintain high standard of living
16
GOALS OF BUSINESS
4. HELPING TO PROTECT THE ENVIRONMENT
to preserve the environment, reduce contamination and
pollution
together with consumer; promote the environmentally
safe product & services
eg: biodegradable fertilizer, merchandise
117
The primary goal of a business is to
maximize profit.
Besides, a business must also be
responsible to its:
Customers
Employees
Creditors
Stockholders
Environment
Community
1. Management process of planning, organizing,
motivating & controlling the organizational resources in
order to achieve its goals.
2. Marketing process of planning and executing the
conception, pricing, promotion and distribution
3. Finance the means in which firms obtain and use fund
for their operations
4. Accounting summary and analysis of the firms financial
conditions
5. Information System interrelated components that
collects, processes, stores and distributes information to
support the activities of a business
18
FUNCTIONS OF BUSINESS
19
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
Business: must aware of changes and be responsive to
many environmental factors change and
adapt to the changes
1. Historical
2. Natural-physical
3. Political and legal
4. Social and cultural
5. Economic
6. International
7. Technological
20
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS: HISTORICAL
Consists of records of events and activities that have taken
place daily - provides background for all the other
environments
Business need to look at historical records of various
companies performance - useful guide to run business
effectively & efficiently
By examining its historical past, a business is better able to
anticipate new developments and plan for them
Eg: SIME DARBY tries acquire IJN failed, protest by Banks
employees (MAYBANK & CIMB)
21
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS:
NATURAL PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENT
Consists of all natural resources (water, oil, gas) and many
other raw materials
Business is restricted by its natural environment
whenever it relies on the availability of natural resources
to produce goods resources become reduced as we
produce more and more goods & sometimes not
replaceable
Problems of pollution would arise and have a very serious
business impact on the ecology is the study of
relationship between people and environment
22
Other depressing situations related to pollution of the
water, noise and waste cost of cleaning up the
environment has to be borne by business organizations
and societies
Therefore, business needs to be innovative and proactive
in its effort to develop its business production of goods
and services using natural-physical resources may have
to be reduced with substitutes to be invented
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS:
NATURAL PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENT
23
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
POLITICAL & LEGAL
Consists of law, regulations, and activities of the
government and its agencies which restrict business
activities and protect the customers
Government intervention into business affairs have been
increasing because need to protect customers right
from unfair business practices, preservation of the
environment and to reduce discrimination in the work
place
24
Roles of government in business areas are:
1. Government as a business regulator and promoter
By implementing favorable budget policies, government promotes
business activities that stimulate economies
By encouraging certain business activities, government can target
the standard living of nations
Government will also hand out certain guidelines concerning price
fixing, advertising, minimum wage and working conditions which
the business must follow
Legislation directed towards improving and maintaining the nations
physically quality has been set up to regulate business interaction
with the environment
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
POLITICAL & LEGAL
25
Roles of government in business areas are:
2. Government as a customer
Government buys goods and services, ranging from office machines,
computers to war materials for defense purpose from private firms
Government acts as owner and competitor by providing goods and
services in the market place. They also act as suppliers as they own a
great deal of the nations natural resources. Eg: land which is
occasionally sells to a business
Current MSC project launched in early 1997 will open up new
opportunities for many companies such as TELEKOM, HSBC, in
providing related services, and providing other infrastructures
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS:
POLITICAL & LEGAL
26
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS:
SOCIAL & CULTURAL
Includes demographics and consumer preferences represent social
tendencies to which business is exposed
* characteristics of the human population or specific segments of the
population, eg: increase in the elderly population has led to an
increased demand for many prescription drugs.
changes in consumers demand may also affect the demand for products
produced, eg: technology advances: SEGA to PLAYSTATION, X-BOX, VIDEO to
CD, DVD, Download Music Online
Societys values and customs have become guidelines to many
organizations methods of operation.
Social and cultural environment are made of beliefs, attitudes, customs and
norms of every group in society Eg: drive-thru of McDonald & KFC due to
our busy lifestyle
27
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS: ECONOMIC
Have a strong impact on the performance of each business
When company is strong, employment is high and compensation paid
to employees is also high
Since people have good income under this conditions, they
purchase large amount of products
Firms that produce the products benefit from the large demand
Will hire many employees to ensure that they can produce a
sufficient amount of products to satisfy the demand
Can also afford to pay wages to employees
Expand their operations results in increased demand for
supplies, materials, construction services
In the end, many working opportunity can be created
28
Economy is weak firms tend to lay off some of their
employees
Cannot afford to pay high wages people will receive
low income
People will purchase small amount of product affect
the producer
Producer will facing losses retrenched many
employees
Employees lose their jobs
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS: ECONOMIC
29
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS: INTERNATIONAL
May affect business directly or indirectly
1. Attract foreign demand
some companies unable to increase their market
share in US because of intense competition within
their industry - try to find foreign market where
potential demand may exist
Eg: Wal-Mart (China), KFC, P&G
30
2. Capitalize in technology
many US companies established new businesses in the so-called
developing countries which have relatively low levels of
technology (Latin America)
DELL (Penang) to capitalize its technology
3. Use inexpensive resources
Labor and land costs can vary significantly among countries
firms often attempt to set up production at a location where land
and labor are inexpensive
Cost of labor is much higher in developed countries (US, UK) than
other countries (Mexico, India)
Therefore, numerous US company has established subsidiaries in
those low cost labor countries
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS:
INTERNATIONAL
31
Some firms rely on foreign countries for raw materials supply or
sell their products in various countries
firms establish subsidiaries in foreign countries where they can
produce and sell the products
Even if firm is not planning to sell its products in foreign
countries, it must be aware of the global environment because it
may face foreign competition when it sells its products locally
Furthermore, global economic conditions can affect local
economic conditions if economic weaken in foreign countries,
the foreign demand and sales for Malaysian products will
decrease
General income level for affected firm will decline & consumer
will have less money to spent
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS:
INTERNATIONAL
32
ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS: TECHNOLOGY
Includes scientific and technological breakthrough and
advancement in industries as well as society
Nowadays, many organizations used high level of
technology to assist them in the process of producing
goods
Companies are competing with one another to
produce quality products more efficient and effective
with the help of technology
Eg: telecommunication industry, construction industry
33
FORMS OF BUSINESS OWNERSHIP
Major forms of business ownerships are:
Sole Proprietorship
Partnership
Corporation
Cooperative
34
Sole proprietorship
- Considered to be the simplest form of business organization
whereby it is owned by one person
- e.g: restaurant, laundry shop, bakery shop.
Advantages Disadvantages
Total independence in
making decisions
Entirely responsible for
debts and risks
Sole ownership of
profits
Unlimited personal
liability
Pay only income tax not
business tax
Limited access of
capital
Low set-up cost Limited skills &
capabilities
Feeling isolation
35
Characteristics of a Successful Sole
Proprietors
Willing to accept full responsibility for the firms
performance.
Willing to work flexible hours.
Feel responsible for the success of the business and
continually monitor business operations.
Exhibit strong leadership skills, well-organized and
communicate well with employees.
36
Partnership
Definition: An association of two or more persons to act as co-
owners of a business for a profit.
Types of Partnership
i. General Partnership
ii. Limited Partnership
iii.Other types of Partnership
a) Silent partners
b)Secret partners
c) Dormant partners
d)Senior partners
e) Junior partners
37
General Partnership
An association of two or more persons with each general
partners as co-owner having unlimited legal liability.
Responsible for the business operation and receive a
salary.
Assume unlimited liability for its debt
Each partner can enter into contracts on behalf of all the
others.
Share the profit and losses of the business.
If one partner withdraw from partnership, he has to give
notice to creditors, customers and suppliers in order to
avoid future liability.
38
Limited Partnership
An association in which one or more (but not all)
partners have limited legal liability for the debt of the
firm.
Partners are not legally liable for debts beyond the
amount they invested.
May or may not participate in managing the business
Share the profit and loss of the firm
At least one partner must be a general partner
39
Other types
a) Silent partners those who are known as owners in the
business, but take no active role in managing the operation
b) Secret partners owners who take an active role but do not
want to reveal their identity to the public
c) Dorman partners partners who take no active role in running
the business and at the same time remain unknown to the
public.
d) Senior partners general partners who have been with the
partnership for the long time and who own a large share of the
general partnership
e) Junior partners made of those who have been owners for a
short time and are not assuming substantial responsibilities.
40
Advantages/Disadvantages of
Partnership
Advantages Disadvantages
1. Additional fund -
Increase source of
capital and credit
2. Losses are shared
3. More Specialization -
Improve decision
making
4. Possibilities for
expansion
5. Personal interest in
business
1. Control is shared -
Managerial problems,
lack of continuity,
difficulty in resolving
conflict
2. Unlimited liability of
partners (general
partners)
3. Profits are shared
41
Corporations
An association of individuals united for some
common purpose and permitted by law to use
a common name.
Types of corporations
1. Private of business corporation
2. Public and government corporation
3. Open or close corporation
4. Domestic and Alien corporation
42
Types of Corporation
1. Private corporation a business privately operated for profit for
the benefit of stockholders. Oriental Motor Co, Eastern Kodak
2. Public or Government Corporation A corporation chartered by
the federal government, a state or a city, for a public purpose. Eg.
FAMA, MARA, FELDA
3. Open or close corporation
a) Open corporation a profit making corporation whose
stock is sold in the open market, eg. Digi, UEM, TNB
b) Close corporation a corporation whose stock is closely
held by members of a family or by a relatively few
stockholders.
4. Domestic and Alien Corporation
a) Domestics Corporation a business
chartered under the corporate laws of
one state
b) Alien Corporation a company doing
business in the country by chartered by
a foreign government. Eg: Citibank
44
Advantages/Disadvantages of
Corporation
Advantages Disadvantages
1. Limited liability of
stockholders
2. Access of funds - Large
financial capability of
growth potential
3. Transfer of ownership -
Ease of ownership
transfer
4. Continuity of life
5. Specialized management
1. High Organization
Expense
2. Financial Disclosure.
3. Agency Problems -
Lack of Personal
interest
4. High Taxes and double
taxation of earnings
5. Legal restrictions on
activities
6. Charter Restrictions
45
Corporation Merger
.Merger combining of two companies to form
a new company in order to increase
profitability.
Reasons for a business merger:
1. Take over a going company and to expand market
2. To achieve tax advantage
3. To gain new source of goods
4. To acquire cash resources it still leaves each
company to manage the company themselves.
46
Corporate structure
Stockholders Directors
President Top Officer
Subordinates
&
Manager
Workers
Choose Elect
Appoints Choose
Employ
47
Stockholders
Also known as shareholders
Are individuals who have purchased shares of stock in the
corporation.
Have a right to vote for the Board of Directors.
Voting power depends on number of shares owned.
Proxy a written authorization that allows someone to cast
votes at the stockholders meeting. Vote on behalf of the
shareholder.
Have the right to sell their stock whenever they wish.
Buy additional stock from a new issue before it is offered to
the public.
Inspect the firms records.
48
Board of Directors
Responsible for seeing that the business is
managed properly formulate long-term
strategy.
Approves top management plans and set major
policies.
Not liable for any corporate acts except for
frauds, negligence etc.
49
Cooperatives
Cooperative is a modification of the corporation.
It is a business owned and operated for the
benefit of its members.
It aims is to give service to its members rather
than to earn a profit.
Profits are commonly returned to members in
the form of patronage dividends
50
Characteristics of
Cooperatives
1) Owners are called members, who are the users of the
co-ops services.
2) There is a limit to the amount of capital one member
may subscribe.
3) Only one vote per member regardless of number of
shares owned.
4) Patronage dividends paid are in proportion to the
amount of goods a member has brought or sold.
5) Directors receive no salary, only managers and
employees are paid.
6) Interest on their investments is paid to members.
51
Comparing Form of
Business Ownership
Form Liability Continuity Management Capital
Sole
Proprietorship
Personal/
unlimited
Ends with death
or decision of
owner
Personal,
unrestricted
Personal
Partnership Personal Ends with death
or decision of
any partner
Unrestricted,
Or depends on
partnership
agreement
Personal
by
partners
Corporation Capital
Invested
As stated in
charter,
perpetual or for
specified period
of years
Under control of
BOD which is
selected by
stockholders
Purchase
of stock
52
Business Support System (BSS)
Business Support Systems (BSS) are the
systems that a telephone operator or Telco uses
to run its business operations.
The term BSS is no longer limited to telephone
operators offering mobile to fixed and cable services
but also can apply to service providers in all sectors
such as utility providers.
53
Typical types of activities that count as part of BSS are
taking a customers order, managing customer data,
billing, rating, and offering B2B and B2C services.
In summary, Business Support Systems (BSS) cover 4 main
areas:
1. Product management
2. Customer management
3. Revenue management
4. Fulfillment management
Business Support System (BSS)
54
1. Product Management:
Product management supports the sales and
management of products, offers and bundles to
businesses and mass-market customers. Product
Management regularly includes offering cross-
product discounts, appropriate pricing and
customer loyalty programs.
2. Customer Management:
Service Providers require a single view of the
customer and regularly need to support complex
hierarchies across customer-facing applications.
Customer Management also covers requirements
for partner management and 24x7 Web-based
customer self-service.
55
3. Revenue Management:
Revenue Management is a BSS focus on billing, charging
and settlement, that can handle any combination of
OSS services, products and offers. BSS Revenue
Management supports OSS order provisioning and
often partner settlement.
4. Fulfillment Management:
Fulfillment Management as part of assurance is
normally associated with Operational Support Systems
though Business Support Systems are often the
business driver for Fulfillment Management and order
provisioning.
56
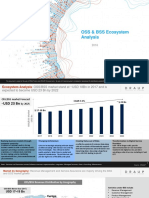
BSS plays a critical role to support
operations of a service provide
and its increasing business
services
Business Support System (BSS)
You might also like
- Entrep Reviewer FinalsDocument7 pagesEntrep Reviewer FinalsKrysha FloresNo ratings yet
- 2006 Business Studies NotesDocument53 pages2006 Business Studies NotesroseNo ratings yet
- MARKETINGDocument16 pagesMARKETINGFarrukhsgNo ratings yet
- Business Environment 1Document23 pagesBusiness Environment 1NihalNo ratings yet
- Business Environment: 1 Semester BBM 2011 - 2012Document64 pagesBusiness Environment: 1 Semester BBM 2011 - 2012Sai KiranNo ratings yet
- Business Environment ProjectDocument9 pagesBusiness Environment ProjectAbdulNo ratings yet
- Global Business Environment: NSS College.Document19 pagesGlobal Business Environment: NSS College.Rajesh Mg100% (1)
- Business & Its EnvironmentDocument65 pagesBusiness & Its Environmentnikithasreekantha7450% (2)
- BussinessDocument18 pagesBussinessNguyễn Đinh Tường VyNo ratings yet
- Business and Its Environment: Unit IDocument69 pagesBusiness and Its Environment: Unit IPrima DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Business Enivironment and LawDocument321 pagesBusiness Enivironment and Lawajit4allNo ratings yet
- Business Activities, Objectives, Strategies and The Business EnvironmentDocument53 pagesBusiness Activities, Objectives, Strategies and The Business EnvironmentMohamed LisaamNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT UNIT IDocument8 pagesBUSINESS ENVIRONMENT UNIT Ivedha0118No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial OpportunityDocument15 pagesEntrepreneurial OpportunityAnvi RaiNo ratings yet
- Business Types AND Business Activities: Prepared By: Sarah Joy B. Del RosarioDocument43 pagesBusiness Types AND Business Activities: Prepared By: Sarah Joy B. Del RosarioMa. Patricia Lainne TorresNo ratings yet
- 2010 Business Studies NotesDocument20 pages2010 Business Studies NotesFyaNo ratings yet
- MARKETINGDocument14 pagesMARKETINGFarrukhsgNo ratings yet
- ED UNIT 2Document49 pagesED UNIT 2pecmba23No ratings yet
- Be TextDocument207 pagesBe TextssjdxqmqtgNo ratings yet
- Start UpDocument103 pagesStart UpRamalingam ChandrasekharanNo ratings yet
- Business Environment and StrategyDocument168 pagesBusiness Environment and StrategySumit DasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business EnvironmentDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Business Environmentjahazi2No ratings yet
- Mgt101a RM1Document15 pagesMgt101a RM1Yassimynn RagontonNo ratings yet
- entre lec 2Document36 pagesentre lec 2Anthony AntonieNo ratings yet
- Satisfaction of Human Wants". Acc. To F.C. Hooper" Business Means The Whole of Complex Commerce & Industry The Transportation and So On"Document41 pagesSatisfaction of Human Wants". Acc. To F.C. Hooper" Business Means The Whole of Complex Commerce & Industry The Transportation and So On"Riya AndaniNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument16 pagesBusiness EnvironmenteclipseknotsNo ratings yet
- Ops Management Final by MZSDocument57 pagesOps Management Final by MZSzubairsalmanpkNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument6 pagesBusiness EnvironmentLavina D SouzaNo ratings yet
- Bussiness EnvironmentDocument24 pagesBussiness EnvironmentRajeswari DeviNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Concept of Business EnvironmentDocument12 pagesMeaning and Concept of Business EnvironmentPreeti singhNo ratings yet
- BCP 2.2.2 / BCH 2.2.2 Business EnvironmentDocument15 pagesBCP 2.2.2 / BCH 2.2.2 Business EnvironmentRashmi Ranjan PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Business Environment FactorsDocument7 pagesBusiness Environment FactorsRENUKA THOTENo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Chapter 1: Operations and ProductivityDocument55 pagesOperations Management: Chapter 1: Operations and ProductivityzubairsalmanpkNo ratings yet
- VO MBA S3 Business Environment and Strategy U1Document15 pagesVO MBA S3 Business Environment and Strategy U1kiranroy6777No ratings yet
- CM Unit 1Document13 pagesCM Unit 1bhoi.hardik2510No ratings yet
- Business: 1. All The External ForcesDocument34 pagesBusiness: 1. All The External ForcesjitendraNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To Business EnvironmentDocument52 pages1-Introduction To Business EnvironmentRavitej Philkhana100% (1)
- Business EnvironmentDocument27 pagesBusiness Environmenthazel joy Banayo100% (1)
- Policy Ch3 The EnvironmentDocument41 pagesPolicy Ch3 The EnvironmentJohn David RaquipoNo ratings yet
- 1 Planning The EnterpriseDocument29 pages1 Planning The EnterpriseCharvenn Buncag80% (5)
- Case Studies 2 1 6-2 10Document12 pagesCase Studies 2 1 6-2 10api-253927188No ratings yet
- SM Fast TrackDocument93 pagesSM Fast TrackVaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Global Entrepreneurship EnvironmentDocument21 pagesGlobal Entrepreneurship EnvironmentShruti BarlaNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument44 pagesBusiness Environmentsshiva8812100% (14)
- Business Organization and EnvironmentDocument6 pagesBusiness Organization and EnvironmentJiny LeeNo ratings yet
- Business and Its Environment NotesDocument48 pagesBusiness and Its Environment NotesPrashant M Shah100% (4)
- The Business EnvironmentDocument6 pagesThe Business EnvironmentUnicorn ProjectNo ratings yet
- Assess Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesDocument22 pagesAssess Personal Entrepreneurial CompetenciesDhaisie GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Business Management Unit 1 Exam Revision SheetDocument7 pagesYear 11 Business Management Unit 1 Exam Revision SheetnorbetNo ratings yet
- OrgzmanDocument6 pagesOrgzmanSharon Almoza Felix LardizabalNo ratings yet
- Business Environment: Module-1Document33 pagesBusiness Environment: Module-1Aadarsh S SNo ratings yet
- Business EnvironmentDocument41 pagesBusiness EnvironmentShavi KhanNo ratings yet
- ITB Chapter 01-JknDocument24 pagesITB Chapter 01-JknArafat SifatNo ratings yet
- Understanding Marketing EnvironmentsDocument33 pagesUnderstanding Marketing EnvironmentsnirakhanNo ratings yet
- Z Notes AS Business Studies (2182)Document47 pagesZ Notes AS Business Studies (2182)brandonoverwatch9No ratings yet
- Module 3Document28 pagesModule 3Josh LaxaNo ratings yet
- Business and The Social EnvironmentDocument20 pagesBusiness and The Social EnvironmentPiran UmrigarNo ratings yet
- TLE ENTREPRENEURSHIP FinalDocument33 pagesTLE ENTREPRENEURSHIP FinalTwilightNo ratings yet
- Green Business - People - Planet - Profit - 2023/24: A Comprehensive Guide to Building & Managing A Sustainable Business.: Volume 1, #1From EverandGreen Business - People - Planet - Profit - 2023/24: A Comprehensive Guide to Building & Managing A Sustainable Business.: Volume 1, #1No ratings yet
- Oss Bss.Document12 pagesOss Bss.Atul JawalkarNo ratings yet
- Telecom Billing PDFDocument33 pagesTelecom Billing PDFOzioma IhekwoabaNo ratings yet
- The Definition of OSS and BSS - OSS LineDocument4 pagesThe Definition of OSS and BSS - OSS Linechrism29900No ratings yet
- Alepo Company PDFDocument27 pagesAlepo Company PDFHasan RteilNo ratings yet
- Document From Shubham ParsewarDocument15 pagesDocument From Shubham ParsewarakshayNo ratings yet
- EAIDocument13 pagesEAIYoon NooyNo ratings yet
- Comptel IL Architecture & Design Training v0.1Document34 pagesComptel IL Architecture & Design Training v0.1Arif Pratama Zulkarnain50% (2)
- Telecom OSS/BSS OverviewDocument20 pagesTelecom OSS/BSS Overviewpriya_z3z100% (1)
- Oss BSSDocument20 pagesOss BSSAnonymous pDZaZjNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Telecom Management Ecosystem - DraupDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The Telecom Management Ecosystem - DraupDraup for TalentNo ratings yet
- Salesforce Industries Communications - : Catalog-Centered DesignDocument27 pagesSalesforce Industries Communications - : Catalog-Centered DesignJosh DavidNo ratings yet
- OSS - BSS. IntroductionDocument8 pagesOSS - BSS. IntroductionalexfarcasNo ratings yet
- IT and Network Integration in Telecom Companies: Creating Efficiency and Customer SatisfactionDocument28 pagesIT and Network Integration in Telecom Companies: Creating Efficiency and Customer SatisfactionkunalNo ratings yet
- OSS BSS Systems and Platforms IndiaDocument5 pagesOSS BSS Systems and Platforms IndiavaseemNo ratings yet
- Telecom Digital Transformation: TechnologyDocument31 pagesTelecom Digital Transformation: TechnologyAnkit SumanNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication in It & Ites: by M.Kamal TejDocument24 pagesTelecommunication in It & Ites: by M.Kamal TejMahesh BabuNo ratings yet
- X (Bss-Oss) BSS - Oss Portfolio Success Why ComarchDocument76 pagesX (Bss-Oss) BSS - Oss Portfolio Success Why Comarchzulhelmy photo100% (2)
- Tender Doc Final T631 CDR 11062018 PDFDocument845 pagesTender Doc Final T631 CDR 11062018 PDFharindramehtaNo ratings yet
- Operations Support SystemDocument7 pagesOperations Support Systemnick19291No ratings yet