Temporal bone, Inner
ear, IAM, CN VII & VIII
CLASS: JC3 2014
COURSE: Neuroscience
CODE : NS 47
LECTURER : Dr. Latifa Nishat
DATE : 10/11/2014 1330 -1430
�TEMPORAL BONE, INNER
EAR,
IAM, VII & VIII
CL A S S : J C3 2 0 1 3
CO U R S E :
N E U RO S C I E N C E C O DE :
NS 44
L E C T U R E R : DR RO H A NA
O C O N N E L L DAT E : 3 1 / 1 0 / 2 0 1 3
1330 -1430
�Learning outcomes
Parts of temporal bone, its
openings and cavities
Structure of inner ear organs of
balance and hearing
Eighth cranial nerve and its
central connections
Seventh cranial nerve: its nuclei,
components and relation to
temporal bone
�Temporal bone
�Temporal bone
�Temporal bone
Squamous
part
Groove for lesser petrosal
nerve
Groove for greater petrosal nerve
Arcuate eminence
Groove for superior petrosal sinus
Groove for sigmoid sinus
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
,
>
I
I
I
I
I
I
II
II
I
�Temporal
bone
Groove for greater
petrosal nerve
Geniculum of facial
nerve
Cochlear
nerve
Facial nerve
(VII)
Internal
acoustic
opening/meat
Vestibulocochl
us
ear nerve
(VIII)
Vestibular
nerve
�Temporal bone
Anterior semicircular
canal
Cochlea
Vestibulocochlear
nerve (VIII)
Posterior semicircular canal
Lateral semicircular canal
�Facial nerve
�Facial nerve
1.
2.
3.
4.
Motor fibres
Sensory fibres
Parasympathetic fibres
Taste fibres
�Facial nerve
Geniculate
ganglion
Facial nerve
(VII)
Internal acoustic
meatus
Greater petrosal
nerve (GPN)
Nerve to
stapedius
muscle
Chorda
tympani
Middle
ear
Stylomastoid
foramen
�Facial nerve
Internal capsule
Internal
capsule
Trigeminal-Spinal
Nucleus and Tract
Nucleus
abducens
VII
VII
Medial
Nucleus
VII
�Facial nerve
(Functional components)
SVE (Special Visceral Efferent)
Motor to striated muscles derived from the
2nd branchial arch
GVA (General Visceral Afferent) Sensory
from visceral touch, temperature, and pain
SVA (Special Visceral Afferent) Taste
GVE (General Visceral Efferent)
Autonomic innervation to mucosal, lacrimal, and
salivary glands
GSA (General Somatic Afferent) Sensory
from somatic touch, temperature, and pain.
�Facial nerve nuclei
Motor nucleus
Pons
Special Visceral Efferent
Branchiomotor: supply all of the
muscles derived from second
branchial arch
In the middle ear : stapedius
Extratemporal: muscles of facial
expression, buccinator, platysma,
posterior belly of digastric
�Facial nerve nuclei
Superior salivatory nucleus (nervus
intermedius)
Pons
General visceral efferent/Parasympathetic
Pterygopalatine ganglion
Submandibular ganglion
GSPN (greater superficial petrosal nerve):
Secretomotor to lacrimal, nasal, palatine
glands
Also receives taste sensation from palate
Chorda tympani:
Taste from anterior 2/3rd of the tongue
�Facial nerve nuclei
Nucleus of tractus solitarius
Medulla oblangata
Special visceral afferent
Taste from tongue (chorda
tympani) and palate (greater
petrosal)
Sensory sense trigeminal (spinal
nucleus)
- eardrum and canal
Guess the functional
Greater component?
Superficial Petrosal Nerve
(GSPN)
1.
2.
3.
Stapedial Nerve
1.
Chorda Tympani Nerve
1.
2.
Posterior Auricular Nerve
1.
2.
Facial Nerve (terminal
branch)
�Facial nerve (Functional
components)
GVA: Light touch, temperature, and pain sensation from
the
soft palate via the GSPN
SVA: Taste from the hard and soft palate via the
greater superficial petrosal nerve (GSPN)
Taste from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue via the
chorda
tympani nerve.
GVE: GSPN transmits preganglionic fibers to the
pterygopalatine ganglion. From the pterygopalatine
ganglion postganglionic fibers cause ipsilateral
lacrimation and mucus secretions of the nasal and oral
cavities.
The GVE component of the facial nerve transmits
preganglionic fibers to the submandibular ganglion via
the chorda tympani nerve. From the submandibular
ganglion postganglionic fibers innervate the
�Facial nerve (Functional
components)
GSA: Touch, temperature, and pain sensation from
part of the external acoustic meatus via the posterior
auricular nerve.
SVE:
1. Stapedius muscle -- dampens movement of the
ossicles
(inserts on stapes of middle ear)
2. Posterior auricular muscle -- posterior movement
of pinna
3. Stylohyoid muscle -- elevates hyoid bone
4. Posterior belly of digastric -- elevates hyoid
bone, depresses mandible
5. Muscles of facial expression -- blinking,
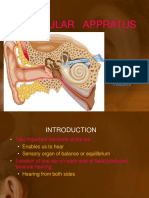
�Inner ear
and
Vestibulocochlear
nerve
�Three anatomical regions of the ear:
the external ear,the middle ear,and the inner ear
External ear
The visible portion
of the ear; collects
and directs sound
waves toward the
middle ear
Auricl
e
Middle ear
Inner ear
An air-filled
chamber;
is connected to
the nasopharynx
by the auditory
Semicircul
tube
ar
canals
Site of sensory organs
for hearing and
equilibrium; receives
amplified sound waves
from the middle ear
Petrous part
of temporal
Facial
nerve (VII)
bone
...., Vestibulocochlear
_
nerve (VIII)
Bony labyrinth
Tympanic cavity
External acoustic
meatus
Tympanic
membrane
(Tympanum or
2011 Pearson Education, Inc.eardrum)
To nasopharynx
Auditory tube
(pharyngotympanic
tube
/Eustachian tube
�Inner ear
The receptors for balance and hearing are
located within fluid-filled chambers and tubes
that form the membranous labyrinth
The fluid of the membranous labyrinth
is called endolymph
The membranous labyrinth is
surrounded and protected by a shell of
bone called the bony labyrinth
The contours of the bony labyrinth closely
resemble the membranous labyrinth
The space between the membranous and bony
labyrinth is filled with a fluid called perilymph
that closely resembles CSF
�Bony labyrinth
Three regions:
Vestibule
Semicircular
canal
Cochlea
�The regions & functions of
cn
membranous
labyrinth
bo dlVKNd
into)
The membranous labyrinth is filled with endolymph and
surrounded by perilymph in the bony labyrinth
Vestibular complex (equilibrium)
he vestibular complex is the part of inner ear
hat provides equilibrium sensations by detecting
Cochlear duct (hearing)
tation, gravity, and linear acceleration
Movement of the stapes at the
Semicircular duct
Utricle & saccule
oval window generates
The three
These chambers
pressure wave that stimulates
semicircular ducts
contain
hair cells at the specific
monitor
receptors sensitive to
locations along the length of
rotational
head position relative
the cochlear duct
movements
to
in three different
planes
gravity; they also
responds
to linear acceleration
�Semicircular canals (SCC)
The anterior, posterior and lateral
SCC are designed to detect
rotation
Each SCC contains a semicircular
duct (SCD)
SCD have dilated ends known as
ampulla
Sensory area in ampulla is known
as Crista
Cupola : gelatinous mass that acts
on hair cells
cupola
�Semicircular canals (SCC)
Membrano
us
labyrinth
Endolym
ph
Cupula
Hair
cells
Crista
Supporting
cells
Sensor
y
(c) Ampulla, sectional
nerve
view
�Semicircular canals Hair cells
The hair cells are the
receptor cells.
They are associated
with supporting cells.
The apical surface of the
hair cell has long
microvilli called
stereocilia (hence, "hair"
cell) and one cilium called
a kinocilium.
The kinocilium and
stereocilia are embedded in
a cupola which nearly fills
the space within the
�Semicircular canals (SCC)
Rotational movements in different planes
are detected by the mechanical distortion
of the stereocilia as fluid moves within the
semicircular ducts
�Utricle and saccule
The utricle and saccule are interconnected
membranous sacs of the membranous
labyrinth found in the vestibule
The endolymph of the utricle is confluent
with that of the semicircular ducts and the
endolymph of the saccule is confluent with
that of the cochlear duct
The utricle and saccule are interconnected
by a narrow endolymphatic duct that ends
in a blind pouch called the endolymphatic
sac
�Inner ear - parts
Anterior semicircular canal & Ampulla
Dura
duct
e
Posterior semicircular
canal
mater
Endolymphatic
& duct
sac
Endolymphatic
duct in
Common bony & membranous
vestibular aqueduct
limbs canal &
Lateral semicircular
Utricle
duct
Saccule
Otic capsule
Stapes in oval
Helicotrema of
(vestibular)
cochlea
Incu
window
Ductus
Malleu
s
reuniens
s
Tympanic
cavity
External
acoustic
Scala
vestibuli
meatus umbo
- - - -. .:
Cochlear
Tympanic
duct
Scala
membrane
tympani
Round (cochlear)
Cochlear
Vestibu
window closed by
aqueduct
Otic
le
secondary tympanic
capsule
membrane
Pharyngotympanic/auditory
tube
�Utricle and saccule
Both the utricle and saccule contain hair
cells similar to those found in the
semicircular canals
In each sac the hair cells are concentrated
on a oval spot in the wall called a macula
("spot")
The kinocilia and stereocilia of the hair
cells are embedded in a gelatinous
mass that has crystals of calcium
carbonate embedded on its surface
This gelatinous mass with its crystals is
called an otolith and the crystals are called
�Utricle and saccule
Macula and statoconia
�Vestibular complex
Otolith
Gelatinous
matrix
Supporting
cell
( a ) Macula of an utricle or
saccule
Copyright C 2009 Pearson Education,
(b) Crista of an
ampulla
Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings.
Wall of
ampulla
Hair cell
Supporting
cell
�Utricle and saccule
Macula &
statoconia
The difference in density
between the crystals and the
gelatinous matrix causes a mechanical distortion of the
stereocilia of the hair cells when the head is tilted or
the body experiences acceleration. Hence, the hair
cells detect the position of the head in space and linear
acceleration.
�Vestibular connections
�Vestibular nerve
The first-order vestibular afferents have their cell
bodies in the vestibular (Scarpas) ganglion, which
is found at the distal end of the internal auditory
meatus.
Their axons travel in the vestibular portion of the
8th cranial nerve through the internal auditory
meatus and enter the brain stem at the junction
between the pons and the medulla.
Project to one of the 4 vestibular nuclei
�Vestibular nerve
Four 2nd order vestibular nuclei: SLMI (all beneath the
floor of the 4th ventricle)
Second order neurons go to:
1. Vestibulo-spinal tract:
mediate extensor motor neurons, control extensor
muscle tone in anti gravity maintenance of posture
2. Vestibulo-cerebellum/cerebellar reflex:
through the inferior cerebellar peduncle to
the Flocculonodular lobe
3. Vestibulo-ocular reflex:
medial longitudinal fasciculus connects
brainstem nuclei (occulomotor, trochlear
and abducens)
�Vestibular
nerve
Occulomotor
nuclear
complex
Trochlear
nucleus
MLF (ascending
fibers)
Abducens
nucleus
SVN
Semicircular
canals:
Utricle:
ampullae
macula
e
Saccul
e:
macula
To
e
cerebellum
MLF (descending
fibers)
To cervical spinal cord for
adjustment of
Lateral vestibulospinal
tract
- -<..._LI...J....'
To extensor motor
neurons
�Cochlea
The cochlea coils about 2.5 turns around a central
hub called the modiolus. The sensory neurons
that form the cochlear nerve have their cell
bodies in the modiolus in a ganglion called the
spiral ganglion.
�Cochlea
Vestibula
r
membra
ne
Tectorial
membra
ne
Modiolus
Apical
turn
Middle
turn
From
oval
window
Basal
turn
Organ of
Corti
Basilar
membra
ne
To round
window
Spiral
ganglion Cochlear
nerve
Vestibular duct
(scala vestibuli)
contains
perilymph
Cochlear duct
(scala media)
contains
endolymph
Tympanic duct
(scala tympani)
contains
Temporal perilymph
bone
(petrous part)
Vestibulocochlear
nerve
(b) Cochlear section,
diagrammatic
�Organ of Corti
The hair cells that are responsible for
hearing are within the organ of Corti, or
spiral organ.
The organ of Corti rests on a basilar
membrane which
separates the cochlear duct from the
tympanic duct.
The hair cells are arranged in an inner row
and outer rows that follow the turns of the
cochlear duct.
The stereocilia (a kinocilium is lacking) of the
the hair cells are in contact with an
overhanging tectorial ("roof") membrane that
�Cochlea - Organ of
Corti
Modiolus
Spiral
ganglion
Vestibul
ar
membra
Cochlear duct
ne media)
(scala
(a )
TectorialVestibula
r
membran
membran
e
e
Cochlear
duct (scala
media)
Spiral
ganglio
n
Tectorial Inner
membran
hair
Stereocie
cells
liaOuter
hair
cells
cochlear
nerve
(b)
(c)
Copynght C 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Beniamin
Cummings.
�The Auditory
Pathway
Lateral
fissure
Auditory
cortex
Mid
brain
Medial geniculate
nucleus
Inferior
colliculus
Dorsal cochlear
nucleus
Auditory
nerve
�Thank you