Hybrid Layouts
Hybrid Layouts
Hybrid layouts modify and/or combine
some aspects of product and process
layouts.
Examples:
Group technology & manufacturing cells used in Just-inTime manufacturing
Grocery stores
Three hybrid layouts:
Cellular layouts (presented by Maria Roig)
Flexible manufacturing systems
Barnes)
(presented by Brian
�Hybrid Layouts: Cellular
layouts
Cellular layouts group dissimilar
machines into work centers
(called cells) that process families
of parts with similar shapes or
requirements.
Combines the flexibility of a process layout with
the efficiency of a product layout.
�Designing Hybrid Layouts
One of the most popular hybrid layouts uses
Group Technology (GT) and a cellular layout
GT has the advantage of bringing the efficiencies
of a product layout to a process layout
environment
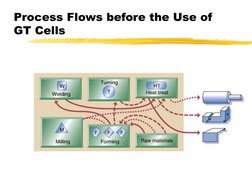
�Process Flows before the Use of
GT Cells
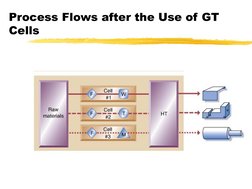
�Process Flows after the Use of GT
Cells
�Hybrid Layouts: Cellular
layouts
Characteristics of the process:
Cells are arranged in relation to each other so that material
movement is minimized.
Large machines that cannot be split among cells are
located near to the cells that use them (point of use)
The layout of machines within each cell resembles a small
assembly line.
Adjustments can be used to arrange the machines within
the cell.
Computer programs can be used to locate cells.
�Hybrid Layouts: Cellular
layouts
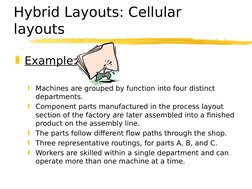
Example:
Machines are grouped by function into four distinct
departments.
Component parts manufactured in the process layout
section of the factory are later assembled into a finished
product on the assembly line.
The parts follow different flow paths through the shop.
Three representative routings, for parts A, B, and C.
Workers are skilled within a single department and can
operate more than one machine at a time.
�Hybrid Layouts: Cellular
layouts
Original
Process
Layouts
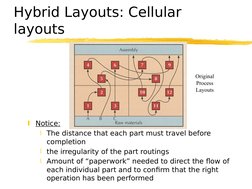
Notice:
The distance that each part must travel before
completion
the irregularity of the part routings
Amount of paperwork needed to direct the flow of
each individual part and to confirm that the right
operation has been performed
�Hybrid Layouts: Cellular
layouts
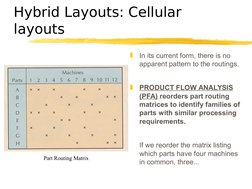
In its current form, there is no
apparent pattern to the routings.
PRODUCT FLOW ANALYSIS
(PFA) reorders part routing
matrices to identify families of
parts with similar processing
requirements.
Part Routing Matrix
If we reorder the matrix listing
which parts have four machines
in common, three...
�Hybrid Layouts: Cellular
layouts
Revised Layout with Three Cells
Part Routing Matrix Reordered to Highlight Cells
�Hybrid Layouts: Cellular
layouts
Advantages:
Reduced material handling
and transit time
Reduced setup time
Reduced work-in-process
inventory
Better use of human
resources
multifunctional workers
Easier to control
Easier to automate
Disadvantages:
Inadequate part families
Poorly balanced cells
Expanded training and
scheduling of workers
Increased capital investment
�Types of Layout - Example
Manufacturing Cell
Animated Picture
�Types of Layout - Example
Manufacturing Cell
An example of a hybrid layout
�Types of Layout - Example
Automated Manufacturing Cell
An example of a hybrid layout
�Types of Layout - Example
Flexible Manufacturing Cell
An example of a hybrid layout
�Types of Layout - Example
Manufacturing Cell
An example of a hybrid layout
�Types of Layout - Example
Automated Manufacturing Cell
An example of a hybrid layout
�Types of Layout - Example
Flexible Manufacturing Cell
An example of a hybrid layout
�Types of Layout
Work Cell, Focused Work Center, and
Focused Factory
Work Cell
Assembly or Production line-oriented arrangement of
machines and personnel in what is ordinarily a processoriented facility. Cells can be formed on a temporary
basis.
Example: job shop with rearranged machinery and
personnel to produce 30 unique control panels
Focused Work
Center
A permanent assembly-line-oriented arrangement of
machines and personnel in what is ordinarily a processoriented facility
Example: manufacturing of pipe brackets at a
shipyard
Focused Factory A permanent facility to produce a product or component
in a product-oriented facility
Example: a plant to produce window mechanisms for
automobiles
�Principles of a Good Layout
Manufacturing
Straight-line Flow Pattern when possible
Backtracking kept to a Minimum
Predictable Production Time
Little In-process materials storage
Open Floor plans so everyone can see what is going
on
Bottlenecks under control
Workstations close together
Minimum of material handling
Easy adjustment to changing conditions
�New Trends in Manufacturing
Layouts
Designed for quality and flexibility
Ability to quickly shift to different product
models or to different production rates
Cellular layout within larger process layouts
Automated material handling
U-shaped production lines use to better
accomplish flow control
More open work areas with fewer walls,
partitions, or other obstacles
Smaller and more compact factory layouts
Less space provided for storage of inventories
throughout the layout
�Wrap-up
Attaining Lean Production
Focus on inventory reduction
Build systems that help employees
Reduce space requirements
Develop close relationships with suppliers
Educate suppliers
Eliminate all but value-added activities
Develop the workforce
Make jobs more challenging
Set sights on perfection!