SECURITY ANALYSIS AND PORTFOLIO
MANAGEMENT
�Indian Financial Systems
IFC- Indian Financial Corporation
Money
Market
Capital Market
Commodity
market
FOREX
�UNIT- I INVESTMENT SETTING
Financial and economic meaning of Investment.
Characteristics & objectives of Investment
Types of Investment
Investment Alternatives
Choice and Evaluation
Risk and Return concepts
�Security: Interchangeable, negotiable instrument
representing financial
value.
Debt Securities , Equity Securities and Derivatives
Issuer: The company issuing the security
Securities Contracts Regulation Act (1956) defined securities include (i)
shares, bonds, stocks or other marketable securities of like nature in or of
any incorporate company or body corporate, (ii) government securities,
(iii) derivatives of securities, (iv) units of collective investment scheme, (v)
interest and rights in securities, and security receipt or any other
instruments so declared by the central government.
�Characteristics of Securities:
Represented by a certificate or by an electronic book entry.
Certificates may be bearer ( the holder to rights under the security)
Include shares of corporate stock or mutual funds, bonds issued by
corporations or governmental agencies, stock options, limited partnership
units and various forms of formal investment instruments
Help the economy for those with money to find those who need investment
capital.
Trading easy and make markets more efficient.
�What is Portfolio?
Combination of various assets such as stocks, bonds and/or cash which
have different risk return characteristics.
A grouping of financial assets such as stocks, bonds and cash equivalents,
as well as their mutual, exchange-traded and closed-fund counterparts.
Portfolios are held directly by investors and/or managed by financial
professionals.
�Security Analysis
Traditional Theory
Modern Theory
An analysis of the fundamental It relies on fundamental analysis
value of a share and its forecast of the security and also risk return
for the future through
intrinsic worth of the share.
the
analysis.
�Objectives of Security Analysis:
1. To present the important facts regarding a stock or bond issue useful to
actual or potential owner.
2. To reach dependable conclusions .
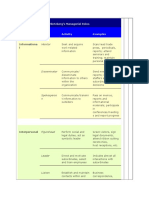
�Portfolio Management
Traditional Portfolio
Theory
Modern Portfolio Theory
Selection of securities
would fit in well with the
asset preferences, needs
and choices of investor.
Maximization of return and
or minimization of risk
will yield optimal returns .
Choice and attitude of
investor is the ultimate aim
while making an
investment decision.
Choices and attitudes of
investors are only a starting
point for investment
decision.
Risk return analysis is not
considered.
Risk return analysis is
necessary for optimization
of returns.
�INVESTMENT
What is Investment?
The money you earn is partly spent and the rest saved for meeting future
expenses. Instead of keeping the savings idle you may like to use savings
in order to get return on it in the future. This is called Investment.
Definitions:
Investment involves employment of funds on assets with the aim of
achieving additional income or growth in values.
�Financial Meaning of Investment
Commitment of a persons fund to derive future income or appreciation in
the value of their capital.
Future income may be
Interest
Dividends
Premium
Pension benefits
Purchasing of shares/debentures
Post office saving certificates
Insurance policies
�Economic meaning of Investment
Net addition to the economys capital stock which consists of goods and
services that are used in the production of other goods and services.
Formation of New and productive capital
New construction
Plant and machinery
Inventories
All these investments generate physical assets
�Characteristics of Investment
Return
Risk
Safety
Liquidity
Marketability
Concealability
Capital growth
Purchasing power
Stability of income
Tax benefits
�Return
Return refers to expected rate of return from an investment
The primary objective of it is deriving a return.
Return = capital appreciation+ Yield
Purchase price
Whereas,
Capital appreciation = sale price purchase price
Yield= Dividend or interest received from the investment
The return from the investment depends upon the nature of the investment,
the maturity period and other factors.
Ex:
Share purchased in 1998 at Rs. 50 disposed at Rs. 60 in 1999 and the
dividend yield is Rs.5 then the return would be?
Return = 30%
�Risk
Risk refers to the loss of principal amount of an Investment. It is one of the major
characteristics of an investment.
The risk depends on the following factors:
A. The investment maturity period is longer, in this case,
investor will take larger risk.
B. Government or Semi Government bodies are issuing
securities which have less risk.
C. In the case of the debt instrument or fixed deposit, the risk
of above investment is less due to their secured and fixed
interest payable on them. For instance Debentures.
��Safety
Safety refers to protection of investor principal amount and expected rate
of return
Safety is also one of the essential and crucial elements of investment.
Investor prefers safety about his capital.
Ex: If investor prefers less risk securities, he chooses Government bonds. In
the case, investor prefers high rate of return investor will choose private
Securities and Safety of these securities is low.
�Liquidity and Marketability
Liquidity refers to an investment ready to convert into cash
position.
Liquidity means that investment is easily realizable, saleable or marketable.
When the liquidity is high, then the return may be low.
Marketability
Marketability refers to buying and selling of Securities in market.
Marketability means transferability or saleability of an asset. Securities are
listed in a stock market which are more easily marketable than which are
not listed. Public Limited Companies shares are more easily transferable
than those of private limited companies.
�concealability
Concealability means investment to be safe from social disorders,
government confiscations or unacceptable levels of taxation, property must
be concealable and leave no record of income received from its use or sale.
�Capital Growth
Capital Growth refers to appreciation of investment.
Investors and their advisers are constantly seeking growth stock in the
right industry and bought at the right time
�Purchasing Power Stability
It refers to the buying capacity of investment in market.
Purchasing power stability has become one of the important traits of
investment.
Investment always involves the commitment of current funds with the
objective of receiving greater amounts of future funds.
�Stability of Income
It refers to constant return from an investment.
Stability of income must look for different path just as security of
principal. Every investor always considers stability of monetary income
and stability of purchasing power of income.
�Objectives of Investment
Maximization of return
Minimization of risk
Hedge against inflation
�Investment Vs Speculation
Short Term Perspective
Stakes of risk and returns are higher
Maximizes the return through buying and selling and delivery of securities
is least important in trade
�Basis of
Distinction
Investor
Speculator
Planning Horizon
Relatively longer
Very Short
Holding Period
Atleast One Year
Few days to few
months
Risk Disposition
Not willing to
assume more than
moderate risk
Willing to assume
high risk
Return Expectation
Seeks a modest rate
of return
Looks for a high rate
of return
Basis for Decisions
Greater Significance
to fundamental
factors and Careful
evaluation
Market Psychology
and Hearsay
Leverage
Use his own fund &
avoids borrowed
funds
Use borrowed funds
Source of Income
Earnings from
enterprise
Change in market
price
�Gambling:
Act of playing for stakes in the hope of winning including the payment of
a price for a chance to win a prize
Ex: Horse races, car races, card games, lottery, etc..
�Basis of
Distinction
Investment
Gambling
Duration
Result of Investment Result of Gambling
is known after long
is known more
time.
quickly.
Purpose
Rational People
invest for income
not for fun.
Rational People
invest for fun not for
income.
Risk Taking Capacity
Risk takers as well
as risk avoiders
Risk takers
Legal Aspect
It is regulated within
four corners of law
It is not regulated by
any law.
�Choice of Investment:
1. Security of Principal and Income
2. Rates of Return
3. Marketability and Liquidity
�1. Security of Principal and
Income
Paramount importance.
Want to be able to get their money back or not
lose money on their investments
Five different types of risks to investment values:
1. Financial Risk
2. Market Risk
3. Interest rate Risk to value of existing
investments
4. Interest rate Risk to income from investments
5. Purchasing power Risk
�Types of Risk
Description
Financial (Credit) Risk
Issuers of Investments run into
financial difficulties
Market Risk
Price fluctuations for a whole
securities market, for an
industrial group or for an
individual security regardless of
the financial ability of particular
issuers to pay promised
investment returns or stay
solvent
Interest rate Risk to value of
existing investments
A rise in general market
interest rates tends to cause a
decline in market prices for
existing securities or vice
versa.
Formula: General Market
Interest Rate is inversely
proportional to Market Prices for
existing Securities.
Interest rate Risk to income
from Investments
Any change in Interest Rate
may cause a decline in dividend
income from bonds that are
�Types of Risk
Description
Purchasing power of the risk
Uncertainty over the future. It
depends on the general price
level in the economy. When
Prices rise, purchasing power
declines and when prices
declin, purchasing power rises.
Other Risk
Associated with international
securities.
Risk that the value of the
foreign currency in which the
investment will fall with respect
to the value of the dollar.
�2. Rates of Return
i) Annual Rates of Return from Income (Yield):
A) Nominal Yield:
Nominal Yield = Annual Interest or
dividends/Investments par or face value
The Nominal Yield is often called the coupon
rate when applied to bonds and the dividend
rate when applied to preferred stocks with a par
value.
For example, a bond with a maturity value of
$1000 that pays interest of $70 per year. What
is the Nominal Yield or the Coupon Rate? 7%
�B) Current Yield:
Current Yield = Annual investment Income /
Investments current price or value
A common stock selling at $50 per share
with an annual dividend rate of $1.00. What
is the Current Yield? = 2%
�C) Yield to Maturity:
For a bond selling at a Discount:
YTM = (annual coupon interest +
( Discount / No. of yrs to maturity))/(Current
market price of bond + par value)/2
For a bond selling at a premium:
YTM = (annual coupon interest ( Premium / No. of yrs to maturity))/(Current
market price of bond + par value)/2
�ii) Capital Gains and total Rates of Return:
It results from the appreciation in the value
of assets.
3) Marketability and Liquidity:
Marketability: to find a ready market to sell
an investment
Liquidity: Not only marketable but also
highly stable in price
�Evaluation of Investment;
1. Mutual Fund Net Asset Value
Net Asset Value = Current market price of
the funds net assets / no. of shares issued.
When he decides to buy, he has to pay the
current NAV per share, plus any sales
charge.
When the NAV appreciates, he decides to
sell the share, the fund will pay him NAV
minus any other sales load.
�2. shares:
Earnings per share (EPS):
It helps in deciding shares investment and
also helps in comparing and evaluating
between companies X and Y.
Step: 1 Earnings after interest and tax
Step: 2 Deduct dividends on preferred stock
from step 1 that is called as amount
Step: 3 Divide the amount by the
outstanding number of shares
�Price Earning Ratio:
It helps to gauge the general trust or
confidence the market has in the companys
ability to grow.
Step: 1 Note down the Market price per share
of the company
Step : 2 Divide Market value per share by EPS
Better Investment Opportunity is the
Companys having P/E ratio of between 7 to
10.
�3. Debenture/Bonds:
The Current Yield refers to Yield of the bond
for a one year period (until maturity).
Step: 1 Note down the coupon rate of the
bond
Step:2 Divide the coupon rate by the bonds
current market price.
�4. Ways to value real property:
Market Approach
Cost Approach - Labor costs and material
prices. Add this value to an estimate of the
market value of the land
Income Approach -
�Investment Alternatives
Precious
Objects
�Marketable Financial Assets
Marketable financial assets those instruments which are transferable or
saleable and traded in any organized financial market.
The marketable financial assets includes
Equity shares
Preference shares
Bonds
Debentures
Money market instruments
�Equity shares
Equity shares represent ownership capital.
The equity shareholder have ownership stake in the company.
This means they have a residual interest in income and wealth .
It is more risky than preference share and bonds.
Types:
Rights share:
These are the shares issued to the existing share holders of a company to protect
the ownership rights of the investors.
Bonus share:
These are the type of shares given by the company to its shareholders as a
dividend.
Sweat equity share:
These shares are issued to exceptional employees or directors of the company
for their exceptional job in terms of providing know-how or IPR to the company.
�Preference share
Preference share are entitled to a fixed rate of dividend.
There is no Voting rights for preference share holder.
No right to participate in management.
Arrears of dividend may accumulate in certain cases.
they carry preferential right with regard to the dividend as well as
repayment of capital in case of winding up of the company.
�Types of preference shares
Cumulative and Non cumulative preference shares
Cumulative preference shares gives the right to the preference shareholders
to receive arrears of dividend which were not paid in previous years due to
company making loss.
While Non cumulative preference shareholders do not have rights like
cumulative preference share and they cannot demand any arrears of
dividend which were not paid during previous years by company.
Participating and Non participating preference shares
Participating preference shareholders have the right to receive any
remaining profit which is left after payment of dividend to equity
shareholders. While Non participating preference shareholders do not have
such rights
Convertible and non convertible preference shares:
Convertible preference shares can be converted into equity shares if
preference shareholders decides to do so, while non convertible preference
shares do not have any such right.
Redeemable and Non- Redeemable preference share:
Redeemable preference shares are those shares , the company will repay the
capital amount to the preference shareholders on the date of maturity and
discontinue the dividend payment thereon. Irredeemable preference share
cannot be redeemed by company excepting on winding up on the company. It
is also called perpetual preference share.
�Bonds
Bond is a long term debt instrument issued by government agencies as
well as large corporations that promises to pay a fixed annual sum as
interest for specified period of time.
Types:
Secured and unsecured bonds:
Secured bond is secured by real assets of the issuer. In case of insecure bonds
there is no such collateral.
Perpetual bonds and redeemable bonds:
Bonds that do not mature are called perpetual bonds. The interest alone
would be paid.
In irredeemable bond ,the bond is redeemed after a specific period of time.
Zero coupon bonds: These are issued at discount of the face value. There is
no interest paid for this bond. The return will be paid on maturity.
�Debentures
A debenture is an unsecured loan offer to a company. The company does
not give any collateral for the debenture, but pays a higher rate of interest
to its creditors. In case of bankruptcy or financial difficulties, the
debenture holders are paid after the bondholders
Types:
Redeemable Debentures
Irredeemable Debentures
Secured Debentures
Unsecured Debentures
�Money market instruments
Debt instrument which have a maturity less than one year at the time of issue
is called money market instruments. Common money market instruments are:
Treasury bills
Commercial paper
Certificate of deposit
Treasury bills are short term money market instrument issued by government. .
Its maturity period is year or less than a year. It gives very low returns.
Commercial paper: It is a short term negotiable instrument with fixed maturity
period. It is an unsecured promissory note issued by corporations either
directly or indirectly through a bank. It s maturity period is maximum 9
months.
Certificates of deposits:
The certificates of deposit are basically time deposit that are issued by the
commercial banks with maturity period ranging from 3 months to 5 year.
The return is higher than treasury bills because it assumes higher level of
risk
�Non Marketable Financial Assets
These are neither transferable nor traded in any organized financial market.
They are,
o
Fixed deposits/ term deposits
Post office schemes
Company provident fund
Public provident fund
Mutual funds