Liquidity Management
Why a
Bank
faces
liquidity
crisis?
One of the most important
tasks
faced
by
the
management of any bank is
ensuring adequate liquidity.
A bank is considered to be
liquid if it has ready access to
immediately spendable funds
at reasonable cost at precisely
the time those funds are
needed. This suggests that a
liquid bank either has the
right amount of immediately
spendable funds on hand
when they are required or can
quickly raise liquid funds by
borrowing or by selling assets.
� Lack of adequate liquidity is often one of the first
signs that a bank is in serious financial trouble. The
troubled bank usually begins to lose deposits,
which erodes its supply of cash and forces the
bank to dispose of its more liquid Assets. Other
banks become reluctant to lend the troubled bank
any funds without additional security or a higher
rate of interest, which further reduces the earnings
of the problem bank and threatens it with failure.
On the other hand, excess liquid Assets/Liquidity of
a bank is to create some serious financial problems
that effect the profitability of the bank. The idle or
excess liquid assets are incurred some costs call as
cost of fund or opportunity cost. Liquidity has a
critical time dimension. Ensuring adequate liquidity
is a never-ending problem for bank management.
�The
Deman
d and
Supply
of Bank
Liquidit
y
A banks need for
liquidity immediately
spendable funds can be
viewed within a demandsupply framework. What
activities give rise to the
demand for liquidity
inside a bank? And what
sources can the bank
rely upon to supply
liquidity when spendable
funds are needed?
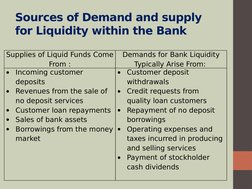
�Sources of Demand and supply
for Liquidity within the Bank
Supplies of Liquid Funds Come
From :
Incoming customer
deposits
Revenues from the sale of
no deposit services
Customer loan repayments
Sales of bank assets
Borrowings from the money
market
Demands for Bank Liquidity
Typically Arise From:
Customer deposit
withdrawals
Credit requests from
quality loan customers
Repayment of no deposit
borrowings
Operating expenses and
taxes incurred in producing
and selling services
Payment of stockholder
cash dividends
�
Liquidity
Liquidity means A banks ability to
ensure the availability of funds to
meet all on and off balance sheet
commitments at a reasonable
price at all times.
�Broadly Bank's Assets are categorized
into 5(Five) groups. These are :
Liquid Assets - Cash, Balance with
other Banks, Money at call & short
notice etc.
Investments - Govt. securities, Bonds,
Treasury Bills, Prize Bonds,
Share/Debenture etc.
Loans & Advances
Fixed Assets - Premises, Land, Building,
Furniture, Computer etc.
Other Assets - Stationary, Stamps,
Suspense, sundry Assets etc.
�What is Liquid Assets?
Cash or cash equivalent or a readily
marketable asset with a relatively stable price that
is reversible or can fully recover the funds originally
invested in the asset. It must have three
characteristics:
A liquid asset must have a ready market so that it
can be converted into cash without delay.
It must have a reasonably stable price so that, no
matter how quickly the asset must be sold or how
large sale is, the market is deep enough to absorb
the sale without a significant decline in price.
It must be reversible so that the seller can recover
the original investment (principal) with little risk or
loss.
�Among the most popular
liquid assets for banks are
shown into two tires :
Tire-1 : Cash & Cash
equivalent
Cash in hand
Foreign currency in hand
Balance with Bangladesh Bank
Balance with Sonali Bank
Balance with Other Bank
Balance with Foreign Bank
Call loans to Banks
STD with Other Bank
�Contd
Tire-2 : Other Liquid Assets which is
considered as SLR
Govt. approved Securities, Bonds &
Treasury Bills
REPO/Reverse REPO with other Banks.
Most of the liquid assets are
performing lower rate of interest. Some
of them earns no interest as cash in
hand, balance with Bangladesh Bank
which is maintained as CRR.
�
REPO (Repurchase
agreement)
Agreement between a seller and a
buyer, usually of government securities,
whereby the seller (bank) agrees to
repurchases the securities at an agreed
upon price and usually at a stated date.
Example : A bank with a temporary
FUNDING SHORTAGE, borrows from an
investor, typically a corporation or bank
with excess cash, using its securities as
collateral.
�REVERSE REPO (Reverse Repurchase
agreement) :
Agreement whereby a bank that has an EXCESS
CASH position, enters into a short-term agreement
to purchase securities from an investor, and the
investor agrees to repurchase them at a later date.
Both agreements are treated as collateralized
lending and borrowing transactions and are carried
on the balance sheet at the amounts at which the
securities were initially acquired or sold. Interest
earned on reverse repurchase agreements and
interest incurred on repurchase agreements are
reported as interest income and interest expenses,
respectively.
�Liquid assets at branch level
deals with :
Cash in hand, Foreign currency in hand,
Balance with Sonali Bank etc.
Liquid assets at H.O level deals
with :
Call loans to banks & other financial
institutions, Govt. approved Securities,
Bonds & Treasury Bills, REPO/Reverse
REPO with other Banks etc.
�
Estimating Liquidity
Needs
Approach for estimating future
deposits and loans :
3 key components :
a trend component
a seasonal component
a cyclical component
�Liquidity Risk Management
Framework
Business as usual
(Going concern, ultimate source of
liquidity is customer's confidence)
Contingency Funding Plan
Liquidity Crisis action Plan
�Liquidity Concerns
Liquidity is inversely related
to risk and expected profitability
Too much liquidity has a negative impact on
profitability
(Excess Cash in hand or maintain excess liquid
assets)
Too little liquidity increases the cost of
funding
(borrow money at a higher rate of interest to meet up
liquidity crisis)
�The Maturity Mismatch
approach(Cash Flow Gap
Analysis)
The
inflows
(Assets)
and
outflows(Liabilities)
into
time
bands, in accordance with their
contractual maturity and the
difference is called as Mismatch
gap.
Taking Short term deposit and
lend it in a Long term investment
creates Mismatch.