0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views5 pagesDesign Process VLSI Lecture
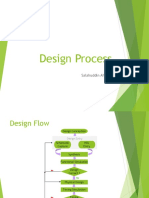
The document describes the design process flow, which includes design conception, entry through schematic or HDL capture, synthesis, functional simulation to check for design correctness, physical design including timing simulation to ensure timing is met, and chip configuration. Key steps are architectural decisions on number of sub-blocks and interconnects, schematic or HDL entry describing the design, synthesis to implement the design, and multiple simulations to verify functionality and timing.
Uploaded by
Mohammod Ahad ArianCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views5 pagesDesign Process VLSI Lecture
The document describes the design process flow, which includes design conception, entry through schematic or HDL capture, synthesis, functional simulation to check for design correctness, physical design including timing simulation to ensure timing is met, and chip configuration. Key steps are architectural decisions on number of sub-blocks and interconnects, schematic or HDL entry describing the design, synthesis to implement the design, and multiple simulations to verify functionality and timing.
Uploaded by
Mohammod Ahad ArianCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5