Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poster Pablo Aguilar 3
Poster Pablo Aguilar 3
Uploaded by
Juan Pablo AguilarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Poster Pablo Aguilar 3
Poster Pablo Aguilar 3
Uploaded by
Juan Pablo AguilarCopyright:
Available Formats
Adherence improvement using Shared Decision in tobacco
dependence treatment. Open randomized controlled clinical trial.
Aguilar JP1; Tarcisio MA2
1Universidade Federal da Bahia , Programa de Ps-Graduao em Medicina e Sade, Av. Reitor Miguel Calmon, S/N,
Canela, Salvador, Ba - Brasil, E-mail: pkjpablo@gmail.com, (71)984318399, Sociedad Civil Empodrate, La Paz,
Bolivia.2Docente na Universidade Federal da Bahia- Programa de Ps-Graduao em Medicina e Sade, E-mail
Universidade Federal tarcisio@ufba.br Faculdade de
da Bahia Medicina da Bahia
Table 1. Primary outcomes and measure of absolute reduction risk among two
Introduo tobacco dependent groups of patients, one of them using ShD in Salvador,
Brazil 2015-2016
Tobacco use is a global epidemic that causes around 6 million of deaths
per year 1. Treatment of tobacco dependence in Brazil is free and is ShD group Control group p
covered by Brazilian Public Health System (SUS). But researches that Characteristics ARR
value
evaluate this program, show low participation rate and cessation. (n=34) (n=30)
Shared Decision (ShD) is the pinnacle of patient-centered care and it Morisky-Green scale1
can improve the adherence to tobacco dependence treatment 2-4. Do you ever forget to take your medicine?
9 25.7 18 52.9 0.021 28.6%
number (%)
.
Are you careless at times about taking
12 34.3 21 61.8 0.022 27.5%
Objective your medications? number (%)
When you feel better, do you sometimes
6 17.1 10 29.4 0.227 17.2%
stop taking your medications? number (%)
To compare the adherence to tobacco dependence treatment between
Sometimes, if you feel worse when you
two groups of patients: control group - the type of treatment is chosen take your medicine, do you stop taking it? 5 14.3 6 17.6 0.539 6.3%
by the physician, and intervention group - the type of treatment is number (%)
chosen using ShD. Patients adherents, according the MG scale
15 42.9 3 8.8 0.001 44.1%
number, number (%)1
Day of participation in the first four weeks of
Method 3.8 0.4 3.2 1.0 0.040*
the CBT, mean (SD)
Day of participation in CBT at the end of 12-
8.8 2.8 7.3 3.1 0.018*
Clinical trial with 12-week follow-up, 104 smokers were recruiting and weeks, mean (SD)
therapeutic resources recommended by INCA (Brazilian National Patients adherents in the first four weeks of
39 97.5 33 75.0 0.003 45.8%
CBT, mean (SD)
Cancer Institute) were used: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), with
Patients adherents in CBT at the end of 12-
or without drug therapy (nicotine patch or bupropion). weeks, mean (SD)
25 62.5 21 47.7 0.174 14.9%
Abandonment of tobacco dependence
6 15.0 17 38.6 0.015 29.7%
treatment
Results
1. Only employed in patients who used some type of medication; (ShD group
Participants were 104 smokers enrolled and randomized in ShD group or n= 35 and Control group n= 34)
usual treatment, their sociodemographic and clinical characteristics * Students t test: and the rest chi-square test
doesnt significant distribution between groups at base line, 84 patients ShD = shared decision; CBT = cognitive behavioral therapy; MG escale =
completed the study. Patients with ShD (n=40) according to Morisky Morisky-Green scale; SD= Standard deviation; IC 95% = 95% confidence
Green Scale had better adherence compared to control (42.9% vs 8.8% interval
p= 0.001); Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR) to not be adherent to the
treatment of 44.1% (95%CI= 22.3 to 65.9) and a Number Needed to
Treat of 3 (95%CI 2 to 5) to have an adherent patient. Participation in Table 2. Secondary outcomes and measure of absolute reduction risk among
CBT in the first month was higher in the ShD group (97.5% vs 75.5%, p= two tobacco dependent groups of patients, one of them using ShD in Salvador,
0.04); at the last month it was similar. At the end, abandonment was Brazil 2015-2016
higher in the control group (15.0% vs 38.6%, p= 0.015); ARR of 29.7%
(CI= 7.8% - 51.5%).
ShD group Control group P
Characteristics RAR
value
(n=34) (n=30)
Number of cigarettes/day after the first four
15.4 (10.1) 10.4 (8.9) 0.026*
weeks treatment, mean (SD)
Number of cigarettes/day at the end of 12-
19.2 (12.4) 15.5 (11.7) 0.281*
weeks, mean (SD)
Abstinence patients in the first 4 weeks
15 (37.5) 10 (22.7) 0.139 17.6%
number (%)
Abstinence patients at the end of 12-weeks,
25 (62.5) 20 (45.5) 0.118 17.1%
number (%)
Kappa Index 1
Between the groups and INCAs protocol,
0.5 (0.001) 0.7 (<0.001)
kappa index (p-value)
1. Kappa Index between the type of treatment chosen in both groups vs the
INCAs protocol; Values equal to 0 = no agreement, 0 to 0.19 = poor
agreement, 0.20 to 0.39 = weak agreement, 0.40 to 0.59 moderate
agreement, 0.60 to 0.79 substantial agreement, 80 to 1 = perfect
agreement.
ShD = shared decision; SD Standard deviation; IC 95% = 95% confidence
interval.
*Mann-Whitney U test: and the rest chi-square test
Conclusion
Patients who had the opportunity to choose the type of treatment, had better
Graphic 2 flow chart
adherence compared with those patients who had a usual treatment. The
ShD = shared decision; CBT = cognitive behavioral therapy
use of ShD to treat tobacco dependence does not deviate from the INCA
criteria.
Bibliographic
1. Eriksen M, Mackay J, Schluger N, Gomeshtapeh FI, Drope J. The tobacco atlas. 5th ed. Atlanta, Georgia USA: American Cancer Society, World Lung
Foundation;2015.
2. Warner DO, LeBlanc A, Kadimpati S, Vickers KS, Shi Y, Montori VM. Decision Aid for Cigarette Smokers Scheduled for Elective Surgery. Anesthesiology.
2015;123(1):18-28.
3. Stacey D, Legare F, Col NF, Bennett CL, Barry MJ, Eden KB, et al. Decision aids for people facing health treatment or screening decisions. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. 2014(1):CD001431.
4. Joosten EA, De Jong CA, de Weert-van Oene GH, Sensky T, van der Staak CP. Shared decision-making: increases autonomy in substance-dependent
patients. Subst Use Misuse. 2011;46(8):1037-8.
You might also like
- ATI Acute ProctoredDocument6 pagesATI Acute Proctoredyoderjess425No ratings yet
- Ce Mark - Application FormDocument3 pagesCe Mark - Application Formrajivsinghal90No ratings yet
- Whatevidencefor RCTJournalof Diabetes 2009173Document3 pagesWhatevidencefor RCTJournalof Diabetes 2009173api-26007957No ratings yet
- 2020 Article 843Document16 pages2020 Article 843zjcincoNo ratings yet
- Effect of VareniclineDocument8 pagesEffect of VareniclineDANIELA GUARDO CARMONA ESTUDIANTENo ratings yet
- An Internet-Based Intervention For Adjustment Disorder (TAO) : Study Protocol For A Randomized Controlled TrialDocument10 pagesAn Internet-Based Intervention For Adjustment Disorder (TAO) : Study Protocol For A Randomized Controlled TrialHelenaNo ratings yet
- Tailoring Evidence-Based Interventions To Reduce Methamphetamine Use Among Hiv-Positive Patients On Methadone in Ho Chi Minh, VietnamDocument8 pagesTailoring Evidence-Based Interventions To Reduce Methamphetamine Use Among Hiv-Positive Patients On Methadone in Ho Chi Minh, VietnamIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Predicting Avoidable Emergency Department Visits Using The NHAMCS DatasetDocument10 pagesPredicting Avoidable Emergency Department Visits Using The NHAMCS DatasetlsnzgiNo ratings yet
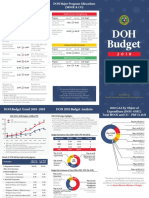
- DOH Budget (2018)Document2 pagesDOH Budget (2018)Hannah Rachel UlepNo ratings yet
- HCPC Europe White Paper Patient Friendly Pharmaceutical Pack DesignDocument42 pagesHCPC Europe White Paper Patient Friendly Pharmaceutical Pack DesignSadman ShakibNo ratings yet
- NCD's Survey Report-Group 3Document13 pagesNCD's Survey Report-Group 3Ibrahim PashaNo ratings yet
- Irene Gómez Gómez A Multiple Health Behaviour ChangeDocument9 pagesIrene Gómez Gómez A Multiple Health Behaviour Change19910808No ratings yet
- Dr. Lisa Marsch's NPF PresentationDocument32 pagesDr. Lisa Marsch's NPF PresentationNational Press Foundation100% (1)
- Medication Errors, P.reddy, Mallesh.Document9 pagesMedication Errors, P.reddy, Mallesh.gnaneshwerNo ratings yet
- ATI Psych ProctoredDocument6 pagesATI Psych Proctoredyoderjess425No ratings yet
- 221208-Whitepaper Codan Report 2022 DigitalDocument13 pages221208-Whitepaper Codan Report 2022 Digitalأياام زمانNo ratings yet
- Two-Year Outcomes of An Adjunctive Telephone Coaching andDocument6 pagesTwo-Year Outcomes of An Adjunctive Telephone Coaching andRaquel BoffNo ratings yet
- 2000, Shapiro - Managed Care Effects On The Physician-Patien RelationshipDocument11 pages2000, Shapiro - Managed Care Effects On The Physician-Patien RelationshipKevin CeroNo ratings yet
- Oncotarget V7i33 10742Document10 pagesOncotarget V7i33 10742Mai BasionyNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis On The Effects ofDocument15 pagesA Systematic Review and Meta Analysis On The Effects ofAlan EhrichNo ratings yet
- Non-Pharmacological Treatment of Cognitive Impairment - An OverviewDocument6 pagesNon-Pharmacological Treatment of Cognitive Impairment - An OverviewIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Nurhayati, Sudiyati, Erlin Puspita, Siti Rahmadani: Research ArticleDocument4 pagesNurhayati, Sudiyati, Erlin Puspita, Siti Rahmadani: Research ArticleMery Merdiana IsmailNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Tingkat Perawatan Diri Dengan Outcome Terapi Pada Pasien Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Tipe 2 Rawat Jalan Di Rsud Ratu Zalecha MartapuraDocument1 pageHubungan Tingkat Perawatan Diri Dengan Outcome Terapi Pada Pasien Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Tipe 2 Rawat Jalan Di Rsud Ratu Zalecha MartapuraWilujeng Dwi PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 1-DikonversiDocument15 pagesJurnal 1-DikonversiMas GoenNo ratings yet
- Study Protocol Open AccessDocument18 pagesStudy Protocol Open AccessAlfredo MorenoNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disord - 2023 P99-109. 2Document11 pagesBipolar Disord - 2023 P99-109. 2tnvkcwwwsjNo ratings yet
- Age and Food Preferences in Breast Cancer Patients Before Undergoing Chemotherapy Treatment in NigeriaDocument4 pagesAge and Food Preferences in Breast Cancer Patients Before Undergoing Chemotherapy Treatment in NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- RT1 OA Swetha-EditDocument4 pagesRT1 OA Swetha-EditFrankly VRHNo ratings yet
- The Nutrition Care Process NCPImpacttothe DietaryDocument6 pagesThe Nutrition Care Process NCPImpacttothe DietaryMuhammad Ahyatul FajriNo ratings yet
- Ttos Depresion MayorDocument11 pagesTtos Depresion MayorSusana Pérez ReyesNo ratings yet
- Balachander 2020Document11 pagesBalachander 2020Laura HdaNo ratings yet
- FMCH 2021 001154Document7 pagesFMCH 2021 001154Vinayak NagriNo ratings yet
- Van - Mhute - Research - Methods-ND PHARMACY 2020Document12 pagesVan - Mhute - Research - Methods-ND PHARMACY 2020valentine mhuteNo ratings yet
- Patient Knowledge of Correct Dosage Regimen The Need For Good Dispensing PracticeDocument7 pagesPatient Knowledge of Correct Dosage Regimen The Need For Good Dispensing Practicelail ariftianiNo ratings yet
- Implementing TobaccoDocument17 pagesImplementing TobaccothiagoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0005789419300966 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0005789419300966 Main1klinikpsixologiyaNo ratings yet
- HCQ Is Effective For COVID-19 When Used Early Meta Analysis of 162 StudiesDocument1 pageHCQ Is Effective For COVID-19 When Used Early Meta Analysis of 162 StudiesSeifeddine EL KOUTNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Treatments For People Living With Severe Dementia - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Clinical TrialsDocument14 pagesEffectiveness of Treatments For People Living With Severe Dementia - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Clinical TrialsCCM CCMNo ratings yet
- Studyprotocol Open AccessDocument11 pagesStudyprotocol Open AccessDIMITRANo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0165032716303871 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0165032716303871 MainLara ReisNo ratings yet
- Developing and Pre-Testing A Digital De... and Cessation Among HIV Care ProvidersDocument10 pagesDeveloping and Pre-Testing A Digital De... and Cessation Among HIV Care ProvidersValeriNo ratings yet
- 3188-Article Text-4910-1-10-20211113Document3 pages3188-Article Text-4910-1-10-20211113Minerva Medical Treatment Pvt LtdNo ratings yet
- Drug Resistance in MalariaDocument32 pagesDrug Resistance in MalariaMya MyintzuNo ratings yet
- Self-Medication Prevalence and Related Factors Among Baccalaureate Nursing StudentsDocument8 pagesSelf-Medication Prevalence and Related Factors Among Baccalaureate Nursing StudentsTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1130862119305042 MainDocument4 pages1 s2.0 S1130862119305042 MainsahrirNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1130862120304009 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S1130862120304009 MainsahrirNo ratings yet
- IJMPR0101001Document7 pagesIJMPR0101001IJMPR JournalNo ratings yet
- Chronic Disease: The Challenge of ImplementationDocument32 pagesChronic Disease: The Challenge of ImplementationLis EnsalanderNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Self-Medication With Analgesics in PharmacyDocument7 pagesPrevalence of Self-Medication With Analgesics in PharmacyIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Pengetahuan Dan Sikap Dengan Perilaku Perawat Dalam Pengelolaan Sampah Medis Di Rumah Sakit Daerah Mangusada Kabupaten BadungDocument7 pagesHubungan Pengetahuan Dan Sikap Dengan Perilaku Perawat Dalam Pengelolaan Sampah Medis Di Rumah Sakit Daerah Mangusada Kabupaten Badungindah rahmayaniNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Mental Therapy For Poor Medication Adherence in Depression: A ReviewDocument8 pagesEffectiveness of Mental Therapy For Poor Medication Adherence in Depression: A ReviewArif IrpanNo ratings yet
- 10.1016@S2215 03662030036 5Document2 pages10.1016@S2215 03662030036 5Angela AbreuNo ratings yet
- Table 1 Summary of The Studies Included in ReviewDocument9 pagesTable 1 Summary of The Studies Included in ReviewimranNo ratings yet
- Finish Poster DM TMFDocument1 pageFinish Poster DM TMFpratika wardaniNo ratings yet
- Journal of Consulting and Clinical PsychologyDocument44 pagesJournal of Consulting and Clinical PsychologyHiền AnhNo ratings yet
- Zhou 2020Document8 pagesZhou 2020Rosalía PattyNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life, Respiratory Symptoms, and Health Care Utilization 1 Year Following Outpatient Management of COVID 19: A Prospective Cohort StudyDocument4 pagesQuality of Life, Respiratory Symptoms, and Health Care Utilization 1 Year Following Outpatient Management of COVID 19: A Prospective Cohort StudyFranklin GuamanNo ratings yet
- Social Support On The Adherence To Treatment of Tuberculosis in Cilacap, IndonesiaDocument8 pagesSocial Support On The Adherence To Treatment of Tuberculosis in Cilacap, Indonesiaeis kusmitaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Implementasi NCP Pada DMDocument5 pagesJurnal Implementasi NCP Pada DMwidhy okayantiNo ratings yet
- (OBAT CINA) CAT TherapyDocument6 pages(OBAT CINA) CAT TherapyArga PRNo ratings yet
- Decision Analytics and Optimization in Disease Prevention and TreatmentFrom EverandDecision Analytics and Optimization in Disease Prevention and TreatmentNan KongNo ratings yet
- SHJ 43-91Document11 pagesSHJ 43-91Iveel PurevdorjNo ratings yet
- Prmit To WorkDocument3 pagesPrmit To Worksyed WajihNo ratings yet
- Pop-Up Flush-Mounting Box To Be Equipped - 8 (2X4) Modules - Glossy WhiteDocument1 pagePop-Up Flush-Mounting Box To Be Equipped - 8 (2X4) Modules - Glossy WhiteLhc JuliachsNo ratings yet
- IruChem Co., Ltd-Introduction of CompanyDocument62 pagesIruChem Co., Ltd-Introduction of CompanyKhongBietNo ratings yet
- The Private/Industrial Security & Investigation Industry in Nigeria: Opportunities, Challenges and The Way ForwardDocument13 pagesThe Private/Industrial Security & Investigation Industry in Nigeria: Opportunities, Challenges and The Way ForwardDon OkerekeNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice: Sri Murugan Home Appliances #613 (22-23) 04/01/2023Document1 pageTax Invoice: Sri Murugan Home Appliances #613 (22-23) 04/01/2023RajeshNo ratings yet
- R Haigh-LT RET 2 15 24Document2 pagesR Haigh-LT RET 2 15 24Luis FieldmanNo ratings yet
- SCAR 10 ProcedureDocument21 pagesSCAR 10 ProcedureRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ramirez V GmurDocument3 pagesRamirez V GmurSamantha BugayNo ratings yet
- Green Well Biotech (Bio Products)Document14 pagesGreen Well Biotech (Bio Products)vihatvipulNo ratings yet
- Client Messages and API Return CodesDocument368 pagesClient Messages and API Return CodesELITEKRISHNo ratings yet
- Fluke 925Document1 pageFluke 925sakornthiemNo ratings yet
- Choke ManifoldDocument1 pageChoke ManifoldiswantmachooNo ratings yet
- FTIR IntroductionDocument8 pagesFTIR Introductiontimtailieu2010No ratings yet
- Bill of MaterialsDocument7 pagesBill of MaterialsTerancen RajuNo ratings yet
- A Tire Model For Air Vehicle Landing Gear DynamicsDocument12 pagesA Tire Model For Air Vehicle Landing Gear DynamicsThale1905No ratings yet
- 670 Dragon Series Dredge Web Form OptimizedDocument2 pages670 Dragon Series Dredge Web Form OptimizedIkechukwu UzoNo ratings yet
- Gas Sensor MQ5 - Epro Labs WiKiDocument2 pagesGas Sensor MQ5 - Epro Labs WiKiManish KumarNo ratings yet
- BU272 - Professional PresentationDocument368 pagesBU272 - Professional PresentationDR100% (1)
- BS BuzzDocument8 pagesBS BuzzBS Central, Inc. "The Buzz"No ratings yet
- Matthew Gordon Hiring Manager Boosted Ltd. 120 Vype Street San Fransisco B18 GNFDocument2 pagesMatthew Gordon Hiring Manager Boosted Ltd. 120 Vype Street San Fransisco B18 GNFtitan gilarNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study of Talent Management Process Adopted by Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)Document16 pagesA Comprehensive Study of Talent Management Process Adopted by Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)Ramuk HsitasNo ratings yet
- SH 2016 FinalJuly252016byCJose&BOmbrogDocument117 pagesSH 2016 FinalJuly252016byCJose&BOmbrogMiyageEmplamadoAquinoNo ratings yet
- Exim Bank: Research Brief: Indian Electronics Industry: Perspectives and StrategiesDocument4 pagesExim Bank: Research Brief: Indian Electronics Industry: Perspectives and StrategiesdeepakdecNo ratings yet
- PNP MC 2019-046 PCAD Master Plan Tagataguyod PDF 4Document3 pagesPNP MC 2019-046 PCAD Master Plan Tagataguyod PDF 4Marj Jorie PillejeraNo ratings yet
- Lcci 3012Document21 pagesLcci 3012alee200No ratings yet
- Rian Romadhon Complete 2020Document14 pagesRian Romadhon Complete 2020Mirta0% (1)
- Lehman BrothersDocument38 pagesLehman Brothersapi-370084550% (6)
- Arab Open University Tutor Marked Assignment (TMA)Document4 pagesArab Open University Tutor Marked Assignment (TMA)Elena AbdoNo ratings yet