Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 Intro
Uploaded by
nazmulbu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views18 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views18 pagesChapter 1 Intro
Uploaded by
nazmulbuCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
Human Resource
Management
ELEVENTH EDITION
1
GARY DESSLER
Part 1 | Introduction
Chapter 1
Introduction to Human Resource Management
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook
All rights reserved. The University of West Alabama
After studying this chapter, you should be able to:
1. Explain what human resource management is
and how it relates to the management process.
2. Give examples of how all managers can use
human resource management concepts and
techniques.
3. Illustrate the human resources responsibilities
of line and staff (HR) managers.
4. Highlight the challenges facing HRM.
5. Illustrate HR’s role in formulating and
executing company strategy.
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–2
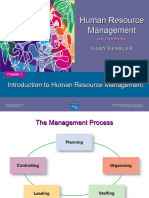
Human Resource Management at Work
• Management process
The five basic functions of planning, organizing,
staffing, leading, and controlling.
• Human Resource Management (HRM)
The policies and practices involved in carrying out
the “people” or human resource aspects of a
management position, including acquiring, training,
rewarding, and appraising employees and attending
to their labor relations, health and safety and fairness
concerns.
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–3
Personnel Aspects Of A Manager’s Job
• Conducting job analyses (determining the nature of
each employee’s job)
• Planning labor needs and recruiting job candidates
• Selecting job candidates
• Orienting and training new employees
• Managing wages and salaries (compensating
employees)
• Providing incentives and benefits
• Appraising performance
• Communicating (interviewing, counseling, disciplining)
• Training and developing managers
• Building employee commitment
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–4
And what a manager should know about:
• Equal opportunity and affirmative action
• Employee health and safety
• Handling grievances and labor relations
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–5
Personnel Mistakes
• Hire the wrong person for the job
• Experience high turnover
• Have your people not doing their best
• Waste time with useless interviews
• Have your company in court because of discriminatory
actions
• Have your company cited by OSHA for unsafe practices
• Have some employees think their salaries are unfair
and inequitable relative to others in the organization
• Allow a lack of training to undermine your department’s
effectiveness
• Commit any unfair labor practices
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–6
Basic HR Concepts
• The bottom line of managing:
Getting results
• HR creates value by engaging
in activities that produce the
employee behaviors that the
company needs to achieve
its strategic goals.
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–7
Line and Staff Aspects of HRM
• Line manager
A manager who is authorized to direct the work of
subordinates and is responsible for accomplishing
the organization’s tasks.
• Staff manager
A manager who assists and advises line managers.
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–8
Line Managers’ HRM Responsibilities
1. Placing the right person on the right job
2. Starting new employees in the organization (orientation)
3. Training employees for jobs that are new to them
4. Improving the job performance of each person
5. Gaining creative cooperation and developing smooth working
relationships
6. Interpreting the firm’s policies and procedures
7. Controlling labor costs
8. Developing the abilities of each person
9. Creating and maintaining department morale
10. Protecting employees’ health and physical condition
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–9
Functions of the HR Manager
• A line function
The HR manager directs the activities of the people
in his or her own department (line authority) and in
related service areas. They also exert implied
authority by virtue of others’ knowledge that HR has
access to top management.
• A coordinative function
HR managers also coordinate personnel activities, a
duty often referred to as functional control.
• Staff (service) functions
Assisting and advising line managers is the heart of
the HR manager’s job.
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–10
Employee Advocacy
• HR must take responsibility for:
Clearly defining how management should be treating
employees.
Making sure employees have the mechanisms
required to contest unfair practices.
Represent the interests of employees within the
framework of its primary obligation to senior
management.
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–11
Examples of HR Specialists
• Recruiters
Search for qualified job applicants.
• Equal employment opportunity (EEO)
coordinators
Investigate and resolve EEO grievances, examine
organizational practices for potential violations, and
compile and submit EEO reports.
• Job analysts
Collect and examine information about jobs to
prepare job descriptions.
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–12
Examples of HR Specialists
• Compensation managers
Develop compensation plans and handle the
employee benefits program.
• Training specialists
Plan, organize, and direct training activities.
• Labor relations specialists
Advise management on all aspects of union–
management relations.
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–13
HR Certification
• HR is becoming more professionalized.
• Society for Human Resource Management
(SHRM)
SHRM’s Human Resource Certification
Institute (HRCI)
SPHR (senior professional in HR)
certificate
PHR (professional in HR)
certificate
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–14
A Changing HR Environment
• Globalization
• Technological Advances
• The Nature of Work
High Tech Jobs
Service Jobs
Knowledge Workers
• Workforce Demographics
Older workers
Women
Minorities
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–15
Strategic Human Resource Management
The linking of HRM with strategic goals and
objectives in order to improve business performance
and develop organizational cultures that foster
innovation and flexibility.
Formulating and executing HR systems—HR policies
and activities—that produce the employee
competencies and behaviors the company needs to
achieve its strategic aims.
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–16
Linking Corporate and HR Strategies
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–17
The Human Resource Manager’s
Proficiencies
• New Proficiencies
HR proficiencies
Business proficiencies
Leadership proficiencies
Learning proficiencies
© 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–18
You might also like
- HRM Garry Dessler 11th EditionDocument86 pagesHRM Garry Dessler 11th EditionAbu Muhammad Affandi20% (5)
- HRMmaimunah Aminuddin - 01Document18 pagesHRMmaimunah Aminuddin - 01Norizati ReesaNo ratings yet
- Dessler-Chapter 1Document13 pagesDessler-Chapter 1Fatih BIYIKLINo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - HRM IntroductionDocument46 pagesChapter 1 - HRM IntroductionAzhar HassanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource ManagementTaz UddinNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Role of Human Resource ManagementDocument21 pagesThe Strategic Role of Human Resource ManagementALEX kinstonNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument42 pagesHuman Resource ManagementAkhil Ranjan TarafderNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 11eDocument31 pagesHuman Resource Management 11egame rangersNo ratings yet
- Dessker 1 2019Document21 pagesDessker 1 2019vinsencia trisnawatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document25 pagesChapter 1Rashedul IslamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource Management: Gary DesslerDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Management: Gary DesslerYasmeen HussAinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource Management: Chapter # 1Document8 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Management: Chapter # 1Sarfaraj OviNo ratings yet
- HRM CH01Document33 pagesHRM CH01Jakowan HNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Role of Human Resource Management: Gary DesslerDocument23 pagesThe Strategic Role of Human Resource Management: Gary DesslerPrexa ShahNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Role of Human Resource Management: Gary DesslerDocument33 pagesThe Strategic Role of Human Resource Management: Gary DesslerArslan AwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction 1Document33 pagesChapter 1 Introduction 1denden007No ratings yet
- Module 1Document34 pagesModule 1Jennifer JosephNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Role of Human Resource ManagementDocument35 pagesThe Strategic Role of Human Resource ManagementAhmed ZidanNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Role of Human Resource Management: Gary DesslerDocument35 pagesThe Strategic Role of Human Resource Management: Gary DesslerTonoy RoyNo ratings yet
- Ch1 HRDocument25 pagesCh1 HRAparna TiwariNo ratings yet
- Ch1 HRDocument25 pagesCh1 HRActor CharumaNo ratings yet
- CH 01 HRM 10e The Strategic Role of HRMDocument30 pagesCH 01 HRM 10e The Strategic Role of HRMOMAR SAMIRNo ratings yet
- Ch1 HRDocument25 pagesCh1 HRAnonymous bwz9Rq6xtjNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument8 pagesHuman Resource ManagementAneesUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- Gary Dessler: Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument19 pagesGary Dessler: Introduction To Human Resource ManagementÁhmèđ ĄţəfNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Role of Human Resource ManagementDocument33 pagesThe Strategic Role of Human Resource Managementsadiqaftab786No ratings yet
- The Strategic Role of Human Resource Management: Gary DesslerDocument30 pagesThe Strategic Role of Human Resource Management: Gary Desslermariya aliNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Role of HRM2Document13 pagesThe Strategic Role of HRM2edraul_rodlac2No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document30 pagesChapter 1NNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Role of Human Resource ManagementDocument29 pagesThe Strategic Role of Human Resource ManagementumalshNo ratings yet
- Dessler01 091005045156 Phpapp01Document13 pagesDessler01 091005045156 Phpapp01gamerzonline6No ratings yet
- Chap 1.introduction To HRMDocument26 pagesChap 1.introduction To HRMTip SceneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Managementpunjabiyaanz funNo ratings yet
- Management CH12 RevisedDocument45 pagesManagement CH12 RevisedKomal TariqNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management CH # 1Document16 pagesHuman Resource Management CH # 1sea waterNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document39 pagesChap 1Chandani PatelNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management EssentialsDocument45 pagesHuman Resource Management Essentialsshanza.alvi02No ratings yet
- Lecture#1 - Introduction To HRMDocument8 pagesLecture#1 - Introduction To HRMAbdul WaheedNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 1 Introduction HRMDocument40 pagesChap 1 1 Introduction HRMRifat HoqueNo ratings yet
- Lec1 - HRM-SP 2023 (2)Document19 pagesLec1 - HRM-SP 2023 (2)May FadlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 HRM Part 1 PDFDocument15 pagesChapter 1 HRM Part 1 PDFHadil MansourNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management at WorkDocument18 pagesHuman Resource Management at WorkTamanna AkterNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument41 pagesHuman Resource ManagementDua KhanNo ratings yet
- Bangor Transfer Abroad ProgrammeDocument23 pagesBangor Transfer Abroad ProgrammeSivaraman P. S.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource ManagementAbir AhmedNo ratings yet
- #1 Introduction To HRMDocument19 pages#1 Introduction To HRMRahulRNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Stephen P. Robbins Mary CoulterDocument45 pagesHuman Resource Management: Stephen P. Robbins Mary Coultersufiey84No ratings yet
- HRM Lecture 1Document39 pagesHRM Lecture 1Britney BowersNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HRMDocument25 pagesIntroduction To HRMsami.medsuccourNo ratings yet
- chapter 1 HRMDocument21 pageschapter 1 HRMAmbreen ZainebNo ratings yet
- 3 Strategic ManagementDocument13 pages3 Strategic ManagementHamza RajpootNo ratings yet
- Dessler-Chapter 3Document13 pagesDessler-Chapter 3Fatih BIYIKLINo ratings yet
- Robbins9 ppt12Document45 pagesRobbins9 ppt12ali goharNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource Management: Global Edition 12eDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Management: Global Edition 12eMohammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Role of Human Resource ManagementDocument25 pagesThe Strategic Role of Human Resource Managementسارة ستوران.No ratings yet
- After Studying This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToDocument20 pagesAfter Studying This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToAzam MashkoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document11 pagesChapter 01Abdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- HRM CH01 2020Document40 pagesHRM CH01 2020Sehrish SherryNo ratings yet
- Integrated Marketing Communications Plan For Carbone Auto GroupDocument32 pagesIntegrated Marketing Communications Plan For Carbone Auto GroupKrys Tal Ra IneNo ratings yet
- Redbull ImcDocument6 pagesRedbull Imcdivyajeevan89No ratings yet
- Redbull ImcDocument6 pagesRedbull Imcdivyajeevan89No ratings yet
- LocationDocument1 pageLocationnazmulbuNo ratings yet
- Registration Form of PaypalBDDocument3 pagesRegistration Form of PaypalBDnazmulbuNo ratings yet
- Sourav BRAC UDocument1 pageSourav BRAC UnazmulbuNo ratings yet
- Ccat Booklet cv1 PDFDocument38 pagesCcat Booklet cv1 PDFakashNo ratings yet
- Chair of Malay Studies ReportDocument35 pagesChair of Malay Studies ReportKhaleed AirilNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 English Worksheet - All Writing Tasks PDFDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 12 English Worksheet - All Writing Tasks PDFSathyathenarasu0% (1)
- PHINMA Education NetworkDocument3 pagesPHINMA Education NetworkMichelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Life SkillsDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Life Skillsmoubazed1119No ratings yet
- Comparing Things with Comparative and Superlative AdjectivesDocument9 pagesComparing Things with Comparative and Superlative AdjectivesDaniel MonogaNo ratings yet
- Uman Esource Anagement: Prof. Dr. Armin TrostDocument336 pagesUman Esource Anagement: Prof. Dr. Armin Trostkhaledhassangamal9516100% (3)
- RGCE HOD explains low exam resultsDocument2 pagesRGCE HOD explains low exam resultsSelvam Ramasamy R75% (4)
- Strategy Overview: Reading TestDocument22 pagesStrategy Overview: Reading TestLong TienNo ratings yet
- Essentially Ellington Program PDFDocument32 pagesEssentially Ellington Program PDFLuis Andres Tovar GomezNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Igcse English Literature CourseworkDocument4 pagesEdexcel Igcse English Literature Courseworkbcr57nbx100% (2)
- 2023 P6 Maths Prelim Pei ChunDocument36 pages2023 P6 Maths Prelim Pei ChunKatharina AjengNo ratings yet
- 04 Quiz 1Document1 page04 Quiz 1cdnarido7535valNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 9Document8 pagesLesson Plan in English 9Michelle Denosta100% (1)
- Building Transformer-Based Natural Language Processing ApplicationsDocument3 pagesBuilding Transformer-Based Natural Language Processing ApplicationsGraceSevillanoNo ratings yet
- Samyak Darshan As Explained by Shri VC SreepalajiDocument1 pageSamyak Darshan As Explained by Shri VC Sreepalajiapi-26862135100% (1)
- Concept Attainment Lesson Plan FormDocument17 pagesConcept Attainment Lesson Plan Formapi-351324903No ratings yet
- Thapar UniversityDocument147 pagesThapar Universitydrupsc0% (1)
- Skin Color and Social Mobility Evidence From Mexico - Raymundo Campos, MedinaDocument45 pagesSkin Color and Social Mobility Evidence From Mexico - Raymundo Campos, MedinaAzael MateoNo ratings yet
- Intermediate: Unit Test 4Document3 pagesIntermediate: Unit Test 4Abia WalkerNo ratings yet
- Programmed InstructionDocument17 pagesProgrammed Instructionakhimoloos88% (17)
- N.B.Boopathy E-Mail Mobile ObjectiveDocument2 pagesN.B.Boopathy E-Mail Mobile ObjectiveBoopathy BalajiNo ratings yet
- Ase2000 V2.28 Um PDFDocument292 pagesAse2000 V2.28 Um PDFamin rusydiNo ratings yet
- McCulloch-Pitts NeuronDocument14 pagesMcCulloch-Pitts NeuronRajib DebnathNo ratings yet
- Architect - PMP, Leed Ga: SarayjiDocument1 pageArchitect - PMP, Leed Ga: SarayjiMoath AlhajiriNo ratings yet
- Final Eng10 Q3W2 Las3 Meredes-FinalDocument2 pagesFinal Eng10 Q3W2 Las3 Meredes-FinalChrisAnnCabradillaNo ratings yet
- Graded Examinations in Spoken English (GESE) Grade 5: Guide and Preparation For CandidatesDocument20 pagesGraded Examinations in Spoken English (GESE) Grade 5: Guide and Preparation For CandidatesclaudiaNo ratings yet
- Academy For Institutional InvestorDocument26 pagesAcademy For Institutional Investormcando2012No ratings yet
- Philosophy Video ReflectionDocument2 pagesPhilosophy Video Reflectionapi-307667487No ratings yet
- Answer SheetDocument1 pageAnswer SheetJohn Paul M. Tagapan100% (1)